Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106691-3000
1066913000
HINO
220002030C
220002030c
Rating:
Service parts 106691-3000 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
23600-1232
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106691-3000
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106691-3000
1066913000
HINO
220002030C
220002030c
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-0920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
177
143
211
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.8
1.45
2.15
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
3.45
3.4
3.5
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
8.9
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
102
99
105
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
8.9
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
112
110
114
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
8.9
Pump speed
r/min
1150
1150
1150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
120
117
123
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
4.4+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
11
8
14
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
8.9+0.2
Pump speed
r/min
330
330
330
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
97
94
100
Fixing the lever
*
Remarks
After startup boost setting
After startup boost setting
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
F
Rack position
14.4+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
187
187
207
Fixing the lever
*
Remarks
After startup boost setting
After startup boost setting
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
950+-50
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1150
Advance angle
deg.
2
1.5
2.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
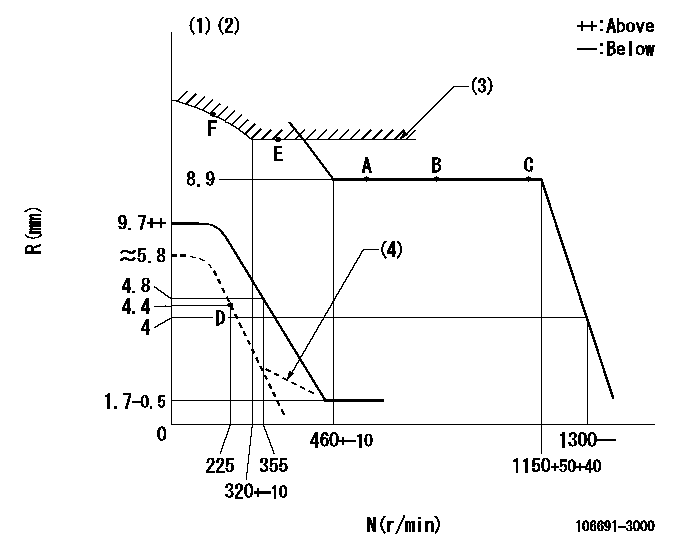
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Beginning of damper spring operation: DL
(2)After adjusting the solid line, set the lever at the dotted line position.
(3)Excess fuel setting for starting: SXL
(4)Damper spring setting
----------
DL=2.4-0.2mm SXL=8.9+0.2mm
----------
----------
DL=2.4-0.2mm SXL=8.9+0.2mm
----------
0000000901
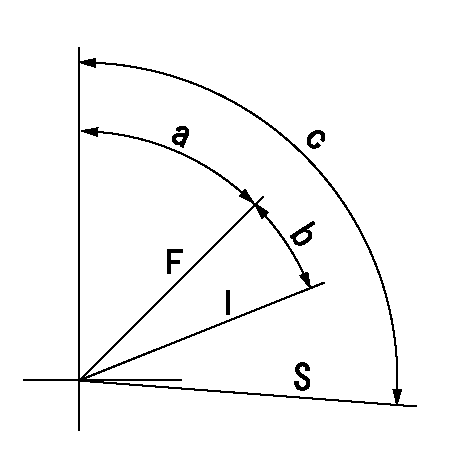
F:Full load
I:Idle
S:Stop
----------
----------
a=66deg+-5deg b=20deg+-3deg c=91deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=66deg+-5deg b=20deg+-3deg c=91deg+-5deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Switch adjustment
Adjust the bolt so that the lower lever position is obtained when the switch is turned ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=300+25r/min Ra=4.4mm
----------
----------
N1=300+25r/min Ra=4.4mm
----------
Information:
Accidental engine starting can cause injury or death to personnel working on the equipment.To avoid accidental engine starting, disconnect the battery cable from the negative (−) battery terminal. Completely tape all metal surfaces of the disconnected battery cable end in order to prevent contact with other metal surfaces which could activate the engine electrical system.Place a Do Not Operate tag at the Start/Stop switch location to inform personnel that the equipment is being worked on.
Water Temperature Fault (WT)
The current flow for the circuit that is described in this section is applicable for all engines. The engine must be running at a speed with a coolant temperature that is hot enough to close the water temperature contactor switch (WTS). The water temperature contactor switch is normally open. The following events occur in the electric circuit in order to shut down the engine. The engine will shut down when the temperature of the coolant system is greater than the maximum temperature that is set for the WTS.
The water temperature contactor switch (WTS) closes across the contacts , which are normally open.
Closing the contacts (WTS-1) and (WTS-2) opens the circuit to slave relay (SR1) (line 33).
When the open circuit de-energizes (SR1) and (SR2), the circuit opens across the relay contacts (SR1-30) and (SR1-87) (line 43).
The open circuit de-energizes the fuel solenoid (FS) which shuts off the fuel flow to the engine. The starter motor circuit can then be engaged. However, there is no fuel flow to the engine and the engine cannot be restarted until the coolant temperature falls below the rating of the water temperature contactor switch. When the water temperature is below the maximum rating for the temperature of the WTS, the circuit opens across contacts (WTS-1) and (WTS-2). The slave relay (SR1) and the fuel solenoid (FS) can then be energized by the engine starting circuit in order to restart the engine.
To avoid possible engine damage or another immediate shutdown, the water temperature fault must be corrected before attempting to restart the engine.
Accidental engine starting can cause injury or death to personnel working on the equipment.To avoid accidental engine starting, disconnect the battery cable from the negative (−) battery terminal. Completely tape all metal surfaces of the disconnected battery cable end in order to prevent contact with other metal surfaces which could activate the engine electrical system.Place a Do Not Operate tag at the Start/Stop switch location to inform personnel that the equipment is being worked on.
2301A Electric Governor Control
The 2301A Electric Governor Control activates all of the components that are in the electric protection system. The components are activated in the same manner when the nonelectric governor is used. One difference exists in the main circuit. The fuel shutoff solenoid (FSOS) (line 43) is not used.When the electric governor control is used, the engine must run in a normal condition in order for the electric circuit to operate in the manner that is described below.
Current flows from the terminals (TS-28) (line 30) and (TS-31) (line 31), which