Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
F 019 Z10 971
f019z10971
ZEXEL
101495-3560
1014953560
KOMATSU
6205711550
6205711550
Rating:
Service parts 101495-3560 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
19.6(200)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
F 019 Z10 971
f019z10971
ZEXEL
101495-3560
1014953560
KOMATSU
6205711550
6205711550
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
F 019 Z10 971
6205711550 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S4D95LE-3 * K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
S4D95LE-3 * K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-4-3
Pre-stroke
mm
3.2
3.15
3.25
Rack position
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-3 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.3
Pump speed
r/min
1075
1075
1075
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
74
73
75
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
46.7
46.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
350
350
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
7.7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
440
440
440
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13.5
12.5
14.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
62
52
72
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Remarks
Rack cap
Rack cap
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
8.7
Boost pressure
kPa
6.7
4
9.4
Boost pressure
mmHg
50
30
70
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
8.9
Boost pressure
kPa
14.7
12
17.4
Boost pressure
mmHg
110
90
130
Boost compensator adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
(9.3)
Boost pressure
kPa
33.3
33.3
33.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
250
250
250
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
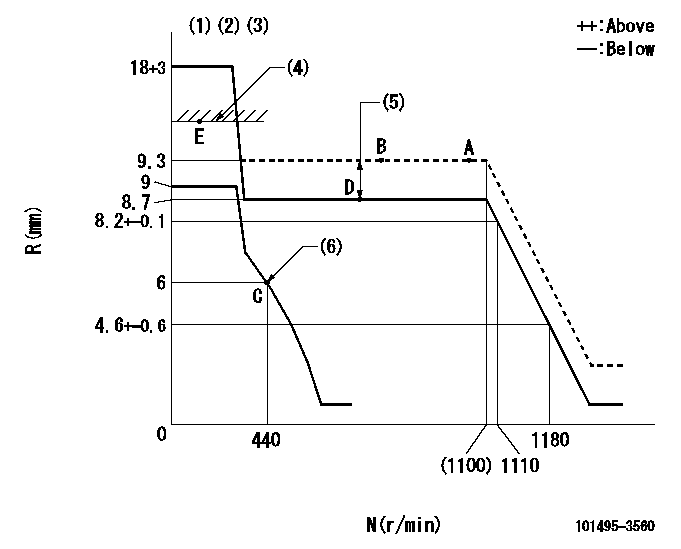
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Deliver without the torque control spring operating.
(4)RACK CAP: R1
(5)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(6)Set idle sub-spring
----------
K=9 R1=(17.5)mm BCL=(0.6)mm
----------
----------
K=9 R1=(17.5)mm BCL=(0.6)mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
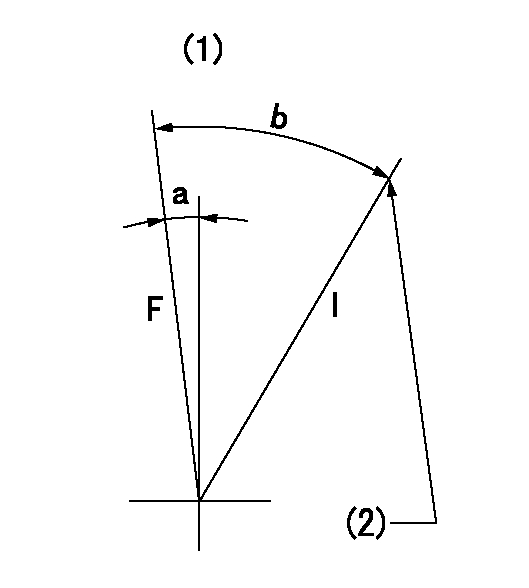
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=60mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=21deg+-5deg
----------
aa=60mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=21deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
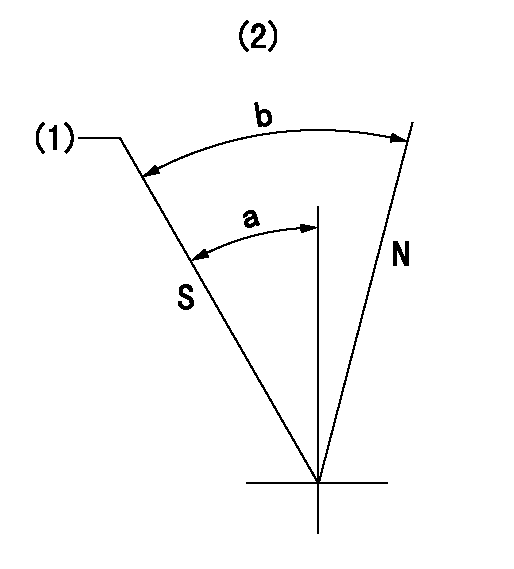
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa, speed = bb (stamp at delivery)
(2)No return spring
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min
----------
a=27.5deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min
----------
a=27.5deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
0000001501 TAMPER PROOF

Tamperproofing-equipped boost compensator cover installation procedure
(A) After adjusting the boost compensator, tighten the bolts to remove the heads.
(1)Before adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten the screw to the specified torque.
(Tightening torque T = T1 maximum)
(2)After adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten to the specified torque to break off the bolt heads.
(Tightening torque T = T2)
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
0000001601 I/P WITH LOAD PLUNGER ADJ
Load plunger-equipped pump adjustment
1. Adjust the variation between cylinders and the injection quantity.
2. At Full point A, adjust the pre-stroke to the specified value.
3. After pre-stroke adjustment, reconfirm that the fuel injection quantity and the variation between cylinders is as specified.
----------
----------
----------
----------
Timing setting
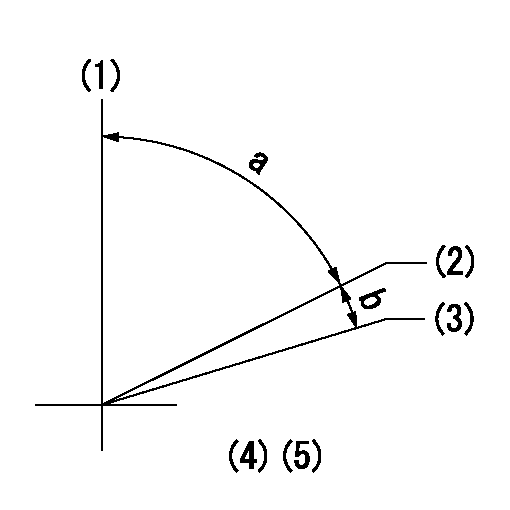
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of key groove at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)Stamp aligning marks on the pump housing flange.
(4)B.T.D.C.: aa
(5)After adjusting the injection quantity, adjust at rack position bb.
----------
aa=6deg bb=9.3mm
----------
a=58deg+-3deg b=2deg+-30min
----------
aa=6deg bb=9.3mm
----------
a=58deg+-3deg b=2deg+-30min
Information:
The purpose of the air induction system is to provide clean air to the engine in an efficient, unrestricted, silent manner while the exhaust system discharges exhaust gases as quickly and as silently as possible with minimum backpressure. Engine horsepower and efficiently will be reduced if either the air inlet or exhaust becomes restricted. Good maintenance practice cannot be over emphasized. AIR CLEANERS: Regular service intervals, along with close visual inspection of the air cleaner, are necessary for proper cleaning of the engine inlet air. The service interval will vary with the weather and working conditions. Where dust conditions are severe, it will be necessary to service the air cleaner frequently. In damp weather and other conditions of little or no dust, the service interval can be extended.To extend the service life of the element, the exhaust and air cleaner inlet pipes should be arranged so that exhaust and/or oil fumes do not enter the engine air cleaner.Visual inspection of the gaskets and seals is important in keeping dust from by-passing the air cleaner. Any dirt allowed to enter, accelerates wear throughout the engine. If the condition of any of the replaceable seals and gaskets is questionable, replace them. If the sealing ends of the filter element or the element pleats are damaged. replace the element.Extra filter elements should be kept on hand for replacement or for use in the air cleaner while the element that was removed is being cleaned.When equipped with a dry-type air cleaner, a service indicator similar to the one shown is available. The air cleaner service indicator is connected to the air inlet pipe between the air cleaner and the manifold. It contains a red marked piston, which gradually rises with restriction to the air flow. When the entire piston is visible it will lock in this position. This indicates a need for air cleaner service. The piston will remain in this position whether or not the engine is running. After servicing the air cleaner, reset the piston by depressing the plunger in the bottom of the indicator.Excessive engine exhaust smoke and/or loss of power may indicate the need for servicing the air cleaner. Never service the air cleaner while the engine is running.(See your truck manufacturer's operator's books for maintenance intervals and instructions.) Air cleaner restriction at high idle should not exceed 25 inches (635 mm) of water.Valve Lash
Make valve lash adjustment with engine stopped.Top dead center (TDC) of the No. 1 piston on the compression stroke is the reference point. The No. 1 piston is at TDC compression stroke when the timing mark on the crankshaft damper or the pulley is aligned with the timing pointer, and No. 1 and No. 2 exhaust and inlet valves are closed. (The rocker arms are free.) To Adjust The Valve Lash
1. Adjust lash for No. 1 and No. 2 exhaust and inlet valves. a. Loosen valve adjusting screw locknut.b. Turn adjusting screw to allow a clearance gauge to pass between the top of
Make valve lash adjustment with engine stopped.Top dead center (TDC) of the No. 1 piston on the compression stroke is the reference point. The No. 1 piston is at TDC compression stroke when the timing mark on the crankshaft damper or the pulley is aligned with the timing pointer, and No. 1 and No. 2 exhaust and inlet valves are closed. (The rocker arms are free.) To Adjust The Valve Lash
1. Adjust lash for No. 1 and No. 2 exhaust and inlet valves. a. Loosen valve adjusting screw locknut.b. Turn adjusting screw to allow a clearance gauge to pass between the top of


