Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
F 01G 003 004
f01g003004
ZEXEL
101405-3321
1014053321
KOMATSU
4063493
4063493
Rating:
Compare Prices: .
As an associate, we earn commssions on qualifying purchases through the links below
$55.29
17 Dec 2024
0.2752[0.12] pounds
LU: Amazon Global Store
Kilen Suplex Coil Spring Front Axle 20065
Kilen Spring Design: Coil Spring; Coil Spring; Coil Spring; Coil Spring || Quality Product || Brand New
Kilen Spring Design: Coil Spring; Coil Spring; Coil Spring; Coil Spring || Quality Product || Brand New
You can express buy:
Service parts 101405-3321 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
22.0{224}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
F 01G 003 004
f01g003004
ZEXEL
101405-3321
1014053321
KOMATSU
4063493
4063493
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101405-3321
F 01G 003 004
4063493 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SAA4D102 K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
SAA4D102 K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
101405-3321
F 01G 003 004
6737711210 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SAA4D102 K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
SAA4D102 K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-3420
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
2.7
2.65
2.75
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.4
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
117.5
116.5
118.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
66.7
66.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
500
500
Hydraulic cylinder ON
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
6.4+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
525
525
525
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10
9
11
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Hydraulic cylinder ON
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
10.8++
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
90
85
95
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Hydraulic cylinder OFF
*
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Rack position
(8.5)
Boost pressure
kPa
21.3
18.6
24
Boost pressure
mmHg
160
140
180
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Rack position
R1(10.4)
Boost pressure
kPa
53.3
53.3
53.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
400
400
400
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
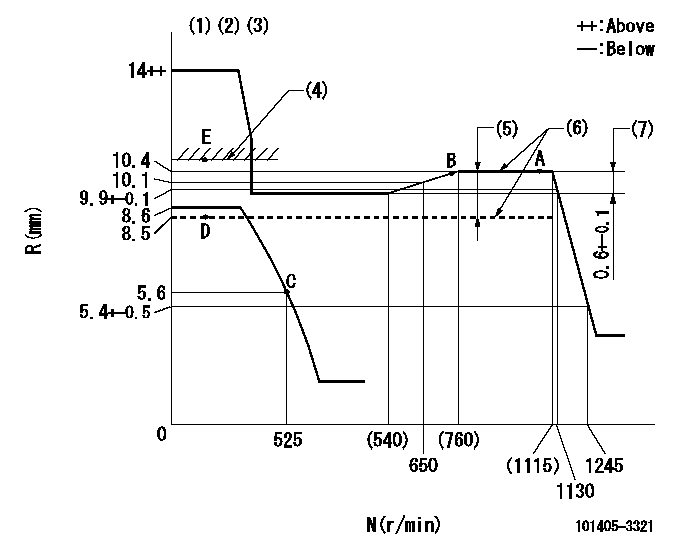
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Adjust the secondary timing before adjusting the governor.
(4)RACK LIMIT (When hydraulic cylinder is OFF)
(5)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(6)When hydraulic cylinder ON: P1
(7)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=13 BCL=(1.9)mm P1=127+-10kPa(1.3+-0.1kgf/cm2) N1=1100r/min N2=400r/min
----------
----------
K=13 BCL=(1.9)mm P1=127+-10kPa(1.3+-0.1kgf/cm2) N1=1100r/min N2=400r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
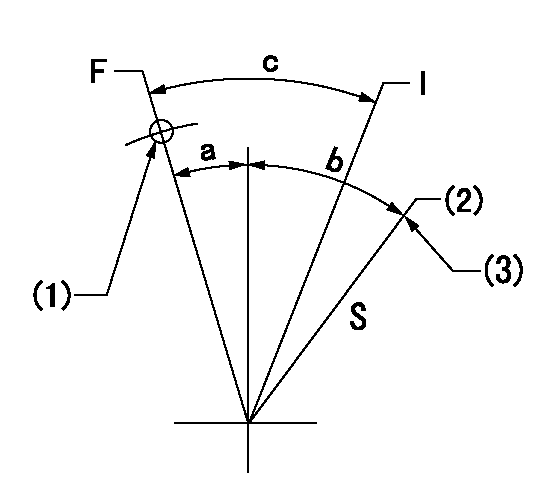
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Rack position = bb, speed = cc
(3)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=80mm bb=2-0.5mm cc=0r/min
----------
a=11deg+-5deg b=31deg+-3deg c=31deg+-5deg
----------
aa=80mm bb=2-0.5mm cc=0r/min
----------
a=11deg+-5deg b=31deg+-3deg c=31deg+-5deg
0000001501 TAMPER PROOF
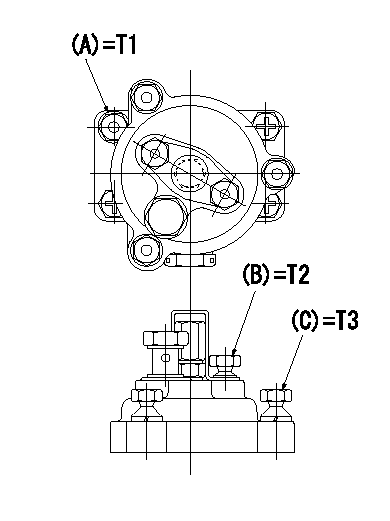
Tamperproofing-equipped boost compensator cover installation procedure
(1)After adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten to the specified torque to break off the bolt heads.
(Tightening torque T = T1 maximum)
(2)After adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten to the specified torque to break off the bolt heads.
(Tightening torque T = T2)
(3)After adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten to the specified torque to break off the bolt heads.
(Tightening torque T = T3)
----------
T1=7.16~9.12N-m(0.73~0.93kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m) T3=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
----------
T1=7.16~9.12N-m(0.73~0.93kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m) T3=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
Timing setting
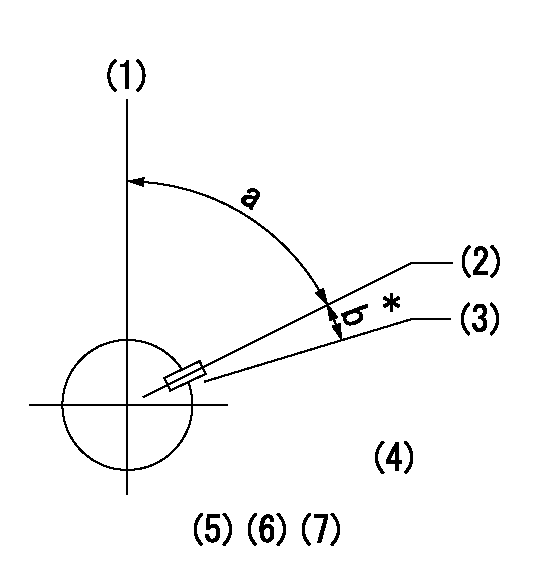
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Key groove position at No. 1 cylinder's beginning of injection position (at BTDC: aa).
(3)Position of the key groove of the No. 1 cylinder at B.T.D.C. bb (fix the governor flyweight at this position for delivery).
(4)B.T.D.C.: aa
(5)At second timing adjustment, set the camshaft at the * position and tighten the flyweight locknut.
(6)Align the flyweight's timing gear position with the lockpin groove and then fully tighten the flyweight to the camshaft.
(7)Remove the lock pin and adjust the governor. Reinstall the lock pin to fix the flyweight for delivery.
----------
aa=11deg bb=0deg
----------
a=55deg48min+-3deg b=5deg30min+-30min
----------
aa=11deg bb=0deg
----------
a=55deg48min+-3deg b=5deg30min+-30min
Information:
Adjustto conform and correspond to specifications.Checkto observe for satisfactory conditions, accuracy, safety or performance.Exchangeto trade a worn or failing component for a remanufactured or rebuilt component.Inspectto examine closely, in critical appraisal, while testing or evaluating components or systems.Inspect/Rebuild or Exchangeto examine closely; then making the decision on repair option (Rebuild or Exchange).Lubricateto apply a lubricant (oil, grease, etc.) as specified for reducing friction, heat and wear between solid surfaces.Protective Devicesindicators such as alarms, lights, emergency shutoffs, etc., that alert an operator that a potential problem may exist. Failure to respond to these indicators in a timely manner could result in serious engine damage.Rebuildto repair a worn or failing component with new parts, components and/or remanufactured components.Replaceto install something new, remanufactured or rebuilt in place of an existing worn or failing component.Service Hours (Electrical)records the time (clock hours) the engine is actually running but does not reflect variations in speed, load, etc. The Maintenance Schedules are developed for calendar time, clock hours or fuel consumption. Hours are expressed in clock hours, not service meter units (unless the service meter is a clock hour device). Hours of operation include only the time that the engine is running. An electric clock device should be connected so it is OFF when the engine is not running. Caterpillar recommends that fuel consumption be used as the preferred method of establishing intervals rather than time or clock hours.Maintenance Intervals
The Maintenance Schedule requires all previous interval maintenance items to be performed first. For instance, if the Every 250 Hour maintenance is being done, then the Daily and Every 250 Hour maintenance items must be completed BEFORE performing the Every 1000 Hour maintenance.Engines may be equipped with various optional components and the Schedule may recommend maintenance for items not installed on your engine. Simply disregard reference to any extraneous items. If unsure of any item, consult your Caterpillar dealer.Overhaul Interval
One interval for some engines is labeled Top End because it involves removal, inspection, and rework of the cylinder head components. This interval is dependent on load-sensitive items/total amount of fuel consumed.The last interval in each chart lists the components inspected, rebuilt, exchanged or replaced at overhaul. Overhaul is defined as the interval at which the major wear items in the engine should be replaced. The intervals represent maintenance of a non-failed engine. In other words, the engine is being rebuilt with certain new parts replacing worn parts such as piston rings, engine rod and main bearings, valves and valve seats., etc.Incidental to the replacement of these relatively few parts is the complete inspection of all other parts that are visible during the overhaul of the engine. The disassembly required to do an overhaul means that disturbed seals and gaskets, etc., will be replaced, and the internal passages of the engine and block be cleaned.* The Overhaul interval assumes that regular maintenance recommendations in the rest of the chart have been carefully followed.* Some users may obtain significantly longer or shorter life than the chart recommends
The Maintenance Schedule requires all previous interval maintenance items to be performed first. For instance, if the Every 250 Hour maintenance is being done, then the Daily and Every 250 Hour maintenance items must be completed BEFORE performing the Every 1000 Hour maintenance.Engines may be equipped with various optional components and the Schedule may recommend maintenance for items not installed on your engine. Simply disregard reference to any extraneous items. If unsure of any item, consult your Caterpillar dealer.Overhaul Interval
One interval for some engines is labeled Top End because it involves removal, inspection, and rework of the cylinder head components. This interval is dependent on load-sensitive items/total amount of fuel consumed.The last interval in each chart lists the components inspected, rebuilt, exchanged or replaced at overhaul. Overhaul is defined as the interval at which the major wear items in the engine should be replaced. The intervals represent maintenance of a non-failed engine. In other words, the engine is being rebuilt with certain new parts replacing worn parts such as piston rings, engine rod and main bearings, valves and valve seats., etc.Incidental to the replacement of these relatively few parts is the complete inspection of all other parts that are visible during the overhaul of the engine. The disassembly required to do an overhaul means that disturbed seals and gaskets, etc., will be replaced, and the internal passages of the engine and block be cleaned.* The Overhaul interval assumes that regular maintenance recommendations in the rest of the chart have been carefully followed.* Some users may obtain significantly longer or shorter life than the chart recommends
Have questions with 101405-3321?
Group cross 101405-3321 ZEXEL
Komatsu
Komatsu
101405-3321
F 01G 003 004
4063493
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SAA4D102
SAA4D102
101405-3321
F 01G 003 004
6737711210
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SAA4D102
SAA4D102




