Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 370
9400611370
ZEXEL
108922-2140
1089222140

Rating:
Service parts 108922-2140 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME072662
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7{180}/24.5{250}
14.
NOZZLE
Include in #1:
108922-2140
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 370
9400611370
ZEXEL
108922-2140
1089222140
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8250
Bosch type code
1 688 901 101
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
20.7
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
211
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-8020
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
RED4 control unit part number
407915-0
590
RED4 rack sensor specifications
mm
19
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407980-2
24*
Digi switch no.
52
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-7-8-
5-6-3-4-
9-10
Pre-stroke
mm
8.5
8.47
8.53
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.75 45.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.75 45.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-7 deg. 72 71.75 72.25
Cal 1-7 deg. 72 71.75 72.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-8 deg. 117 116.75 117.25
Cal 1-8 deg. 117 116.75 117.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-5 deg. 144 143.75 144.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 144 143.75 144.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-6 deg. 189 188.75 189.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 189 188.75 189.25
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-3 deg. 216 215.75 216.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 216 215.75 216.25
Difference between angles 7
Cal 1-4 deg. 261 260.75 261.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 261 260.75 261.25
Difference between angles 8
Cal 1-9 deg. 288 287.75 288.25
Cal 1-9 deg. 288 287.75 288.25
Difference between angles 9
Cal 1-10 deg. 333 332.75 333.25
Cal 1-10 deg. 333 332.75 333.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Rack position
(12.1)
PWM
%
56
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
150.5
149.5
151.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
PS407980-224*
V
2.2+-0.0
1
PS407980-224*
mm
6.1+-0.0
5
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Rack position
(6.9)
PWM
%
26.9+-2.
8
Pump speed
r/min
380
380
380
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
19
17
21
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
PS407980-224*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407980-224*
mm
8.4+-0.0
3
Remarks
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
0000001201
Pre-stroke
mm
8.5
8.47
8.53
Remarks
When the timing sleeve is pushed up
When the timing sleeve is pushed up
_02
Connector angle
deg.
11.5
11
12
Remarks
When the eccentric pin is tightened
When the eccentric pin is tightened
_03
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
4.5
4.45
4.55
Output voltage
V
2.95
2.94
2.96
Adjustment
*
_04
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
8.5
8.47
8.53
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_05
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
Test data Ex:
Speed control lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Rack position bb
----------
aa=20mm bb=1mm
----------
a=19deg+-5deg b=37deg+-5deg
----------
aa=20mm bb=1mm
----------
a=19deg+-5deg b=37deg+-5deg
0000000901
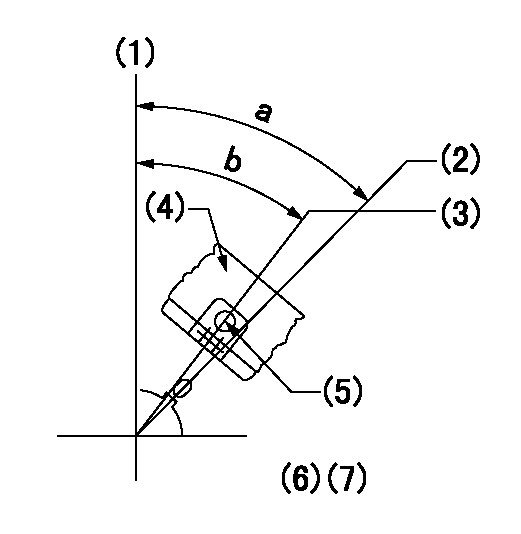
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)At the No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection position, stamp an aligning mark on the damper to align with the pointer's groove.
(4)Damper
(5)Pointer
(6)B.T.D.C.: aa
(7)Pre-stroke: bb
----------
aa=0deg bb=8.5+-0.03mm
----------
a=(45deg) b=(44deg)
----------
aa=0deg bb=8.5+-0.03mm
----------
a=(45deg) b=(44deg)
0000001501
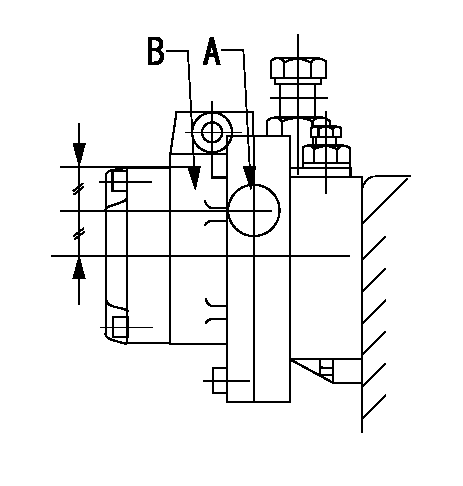
A:Sealing position
B:Pre-stroke actuator
1. When installing the pre-stroke actuator on the pump, first tighten the installation bolts loosely, then move the actuator fully counterclockwise (viewed from the drive side).
Temporary tightening torque: 1 - 1.5 N.m (0.1 - 0.15 kgf.m)
2. Move the actuator in the clockwise direction when viewed from the drive side, and adjust so that it becomes the adjustment point of the adjustment value. Then tighten it.
Tightening torque: 7^9 N.m (0.7^0.9 kgf.m)
3. After prestroke actuator installation adjustment, simultaneously stamp both the actuator side and housing side.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001701

(PWM) Pulse width modulation (%)
(R) Rack position (mm)
Rack sensor output characteristics
1. Rack limit adjustment
(1)Measure the rack position R2 for PWM a2%.
(2)Confirm that it is within the range R2 = 15+-1 mm.
(3)Measure the rack position R1 at PWM a %.
(4)Confirm that it is within the range R2 - R1 = 10+-0.1 mm.
2. Check the limp home operation.
(1)Move the switch box's limp home switch to the limp home side.
(2)Confirm rack position L1 (mm ) and L2 (mm) for PWM in the above table.
3. Check the pull down operation.
(1)Confirm that the rack position is 19 mm at PWM B%.
(2)In the conditions described in the above table, move the switch box's pull down switch to the pull down side and confirm that the rack position momentarily becomes 1 mm or less.
----------
a1=16.25 % a2=72.5 % L1=1-- mm L2=19++mm A=5 % B=95 %
----------
----------
a1=16.25 % a2=72.5 % L1=1-- mm L2=19++mm A=5 % B=95 %
----------
Information:
Illustration 21 shows the direction the rack moves when the fuel injector is receiving fuel.
Illustration 22 g01455811
Illustration 1 - Flowchart for the Air in Fuel Test (Test F)
Illustration 23 g01455812
Illustration 2 - Flowchart for the Air in Fuel Test (Test F)Fuel Injector Cranking Test (Test G)
Note: The fuel injector cranking test checks for worn out injectors by measuring the cranking rack.
Illustration 24 g01412134
(3) The rack control (4) The number one fuel injectorNote: Refer to Illustration 24 for the location of the rack control and the location of the number one injector.
Illustration 25 g01412115
Flowchart for the Fuel Injector Cranking Test (Test G)Fuel Shutoff Solenoid Test (Test H)
Note: The fuel shutoff solenoid test determines if the fuel shutoff solenoid and wiring harness are operating properly.
Illustration 26 g01412143
Flowchart for the Fuel Shutoff Solenoid Test (Test H)Fuel Ratio Control (FRC) Setting Test (Test I)
Note: The FRC setting test checks the FRC setting.
Illustration 27 g01412145
Flowchart for the Fuel Ratio Control (FRC) Setting Test (Test I)Governor Servo Retaining Ring Test (Test J)
Note: Do not run the engine during this test.Note: The governor servo retaining ring test checks for faulty internal parts of the governor.
Illustration 28 g01422811
(1) Paddle
Illustration 29 g01422821
(2) Clevis pin
Illustration 30 g01412147
Flowchart for the Governor Servo Retaining Ring Test (Test J)Fuel Transfer Pump Test (Test K)
Note: The fuel transfer pump test is a visual inspection of the fuel transfer pump components.
Illustration 31 g01412150
(1) Screen (2) Inlet check valve (3) Spring (4) Bolt (5) Piston (6) Outlet check valve (7) Freeze plug (8) Piston check valve (9) Passage (10) Tappet Assembly (11) CamNote: Refer to Illustration 31 for the location of the components for the fuel transfer pump.
Illustration 32 g01412149
Flowchart for the Fuel Transfer Pump Test (Test K)Fuel Ratio Control (FRC) Diaphragm Leak Test (Test L)
Note: The FRC diaphragm leak test checks for a leaking FRC diaphragm.
Illustration 33 g01412154
Flowchart for the Fuel Ratio Control (FRC) Diaphragm Leak Test (Test L)
Illustration 22 g01455811
Illustration 1 - Flowchart for the Air in Fuel Test (Test F)
Illustration 23 g01455812
Illustration 2 - Flowchart for the Air in Fuel Test (Test F)Fuel Injector Cranking Test (Test G)
Note: The fuel injector cranking test checks for worn out injectors by measuring the cranking rack.
Illustration 24 g01412134
(3) The rack control (4) The number one fuel injectorNote: Refer to Illustration 24 for the location of the rack control and the location of the number one injector.
Illustration 25 g01412115
Flowchart for the Fuel Injector Cranking Test (Test G)Fuel Shutoff Solenoid Test (Test H)
Note: The fuel shutoff solenoid test determines if the fuel shutoff solenoid and wiring harness are operating properly.
Illustration 26 g01412143
Flowchart for the Fuel Shutoff Solenoid Test (Test H)Fuel Ratio Control (FRC) Setting Test (Test I)
Note: The FRC setting test checks the FRC setting.
Illustration 27 g01412145
Flowchart for the Fuel Ratio Control (FRC) Setting Test (Test I)Governor Servo Retaining Ring Test (Test J)
Note: Do not run the engine during this test.Note: The governor servo retaining ring test checks for faulty internal parts of the governor.
Illustration 28 g01422811
(1) Paddle
Illustration 29 g01422821
(2) Clevis pin
Illustration 30 g01412147
Flowchart for the Governor Servo Retaining Ring Test (Test J)Fuel Transfer Pump Test (Test K)
Note: The fuel transfer pump test is a visual inspection of the fuel transfer pump components.
Illustration 31 g01412150
(1) Screen (2) Inlet check valve (3) Spring (4) Bolt (5) Piston (6) Outlet check valve (7) Freeze plug (8) Piston check valve (9) Passage (10) Tappet Assembly (11) CamNote: Refer to Illustration 31 for the location of the components for the fuel transfer pump.
Illustration 32 g01412149
Flowchart for the Fuel Transfer Pump Test (Test K)Fuel Ratio Control (FRC) Diaphragm Leak Test (Test L)
Note: The FRC diaphragm leak test checks for a leaking FRC diaphragm.
Illustration 33 g01412154
Flowchart for the Fuel Ratio Control (FRC) Diaphragm Leak Test (Test L)