Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 612 187
9400612187
ZEXEL
108622-4051
1086224051
Rating:
Service parts 108622-4051 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
18.1{185}/24.5{250}
14.
NOZZLE
Include in #1:
108622-4051
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 612 187
9400612187
ZEXEL
108622-4051
1086224051
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8250
Bosch type code
1 688 901 101
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
20.7
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
211
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-8020
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407980-2
24*
Digi switch no.
33
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
6.4
6.37
6.43
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
13.9
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
147
145
149
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
2.2+-0.0
1
PS407980-224*
mm
4+-0.05
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
8.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
310
310
310
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
20
18
22
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407980-224*
mm
6.3+-0.0
3
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(13.9)
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
147
145
149
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
69.3
69.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
520
520
PS407980-224*
V
2.2+-0.0
1
PS407980-224*
mm
4+-0.05
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
(R1+0.95
)+0.05-0
.1
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
133
127
139
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
69.3
69.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
520
520
PS407980-224*
V
2.2+-0.0
1
PS407980-224*
mm
4+-0.05
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Rack position
R1-2.05
Boost pressure
kPa
14.7
13.4
16
Boost pressure
mmHg
110
100
120
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Rack position
R1(13.9)
Boost pressure
kPa
56
56
56
Boost pressure
mmHg
420
420
420
0000001601
Pre-stroke
mm
6.4
6.37
6.43
Remarks
When the timing sleeve is pushed up
When the timing sleeve is pushed up
_02
Connector angle
deg.
11.5
11
12
Remarks
When the eccentric pin is tightened
When the eccentric pin is tightened
_03
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
2.4
2.35
2.45
Output voltage
V
2.95
2.94
2.96
Adjustment
*
_04
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
6.4
6.37
6.43
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_05
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
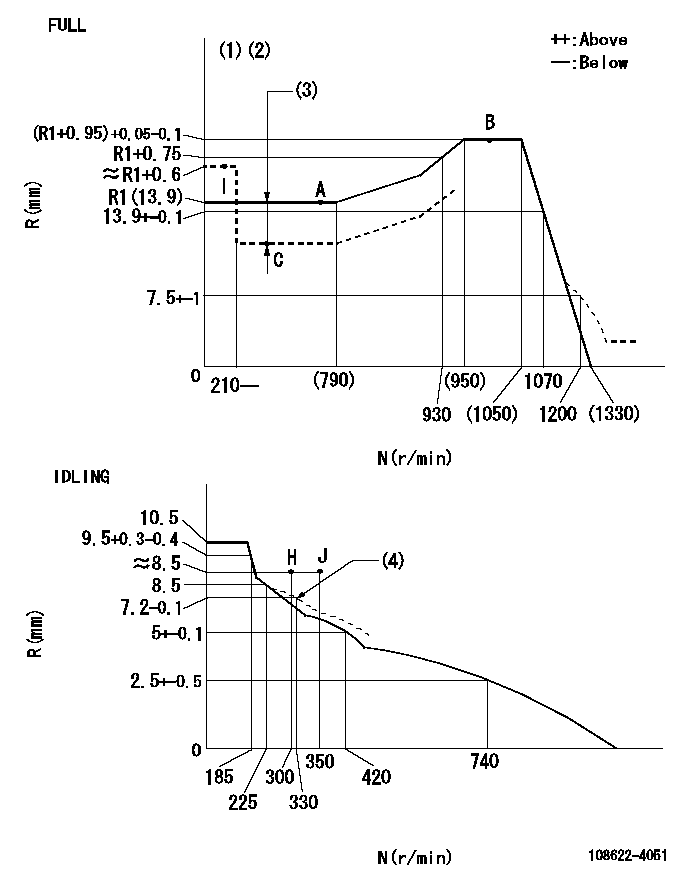
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(4)Damper spring setting
----------
T1=AG97 BCL=2.05+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=AG97 BCL=2.05+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
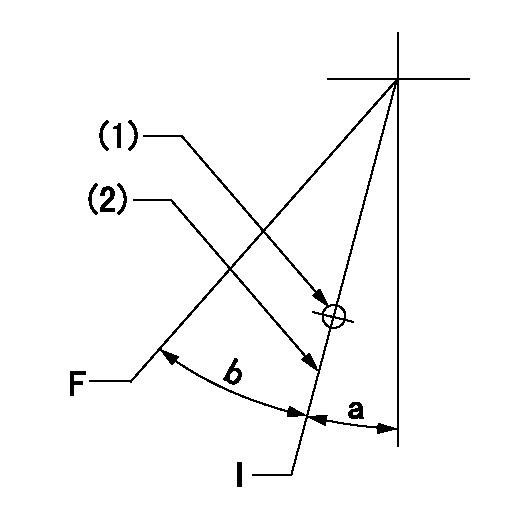
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=37.5mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=34deg+-3deg
----------
aa=37.5mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=34deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
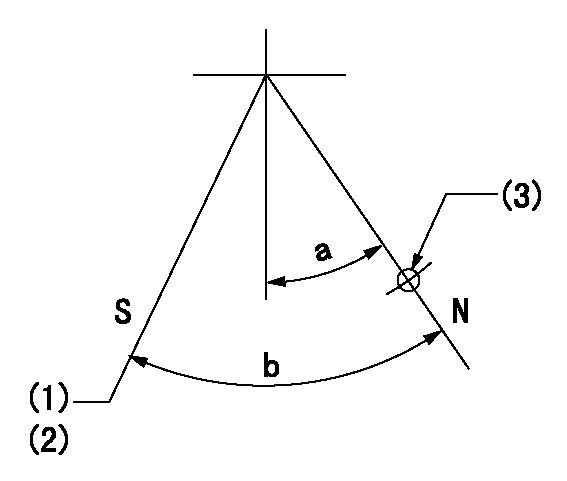
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Pump speed aa, rack position bb
(2)Stopper bolt setting
(3)Use the hole above R = cc
----------
aa=1200r/min bb=3.5+-0.3mm cc=25mm
----------
a=29.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1200r/min bb=3.5+-0.3mm cc=25mm
----------
a=29.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
0000001301
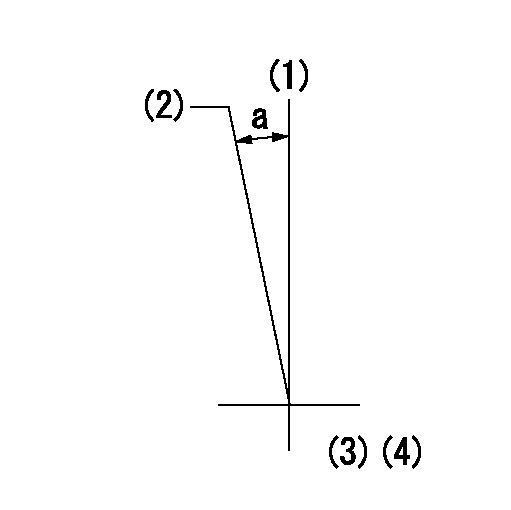
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)Pre-stroke: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=6.4+-0.03mm
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
aa=6.4+-0.03mm
----------
a=(0deg)
0000001901
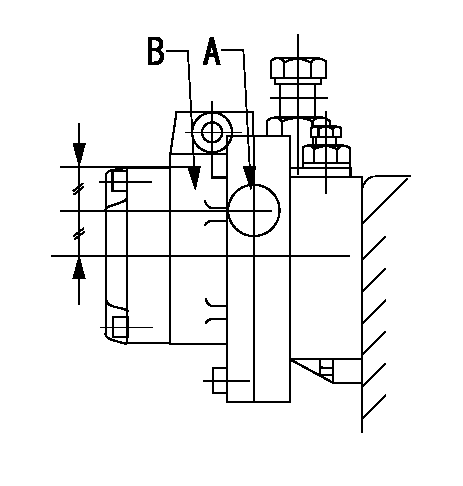
A:Sealing position
B:Pre-stroke actuator
1. When installing the pre-stroke actuator on the pump, first tighten the installation bolts loosely, then move the actuator fully counterclockwise (viewed from the drive side).
Temporary tightening torque: 1 - 1.5 N.m (0.1 - 0.15 kgf.m)
2. Move the actuator in the clockwise direction when viewed from the drive side, and adjust so that it becomes the adjustment point of the adjustment value. Then tighten it.
Tightening torque: 7^9 N.m (0.7^0.9 kgf.m)
3. After prestroke actuator installation adjustment, simultaneously stamp both the actuator side and housing side.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000002201 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=300r/min Ra=8.8+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=300r/min Ra=8.8+-0.1mm
----------
0000002301 RACK SENSOR
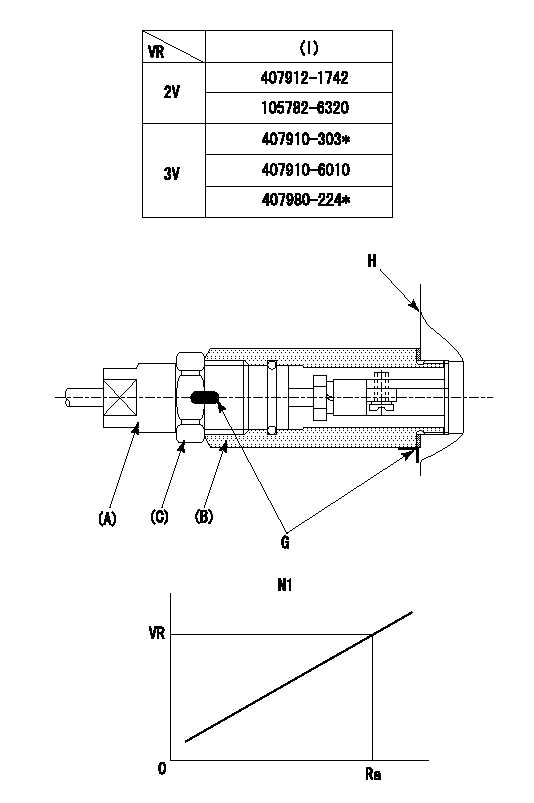
(VR) measurement voltage
(I) Part number of the control unit
(G) Apply red paint.
(H): End surface of the pump
1. Rack sensor adjustment (-0620)
(1)Fix the speed control lever at the full position
(2)Set the speed to N1 r/min.
(If the boost compensator is provided, apply boost pressure.)
(3)Adjust the bobbin (A) so that the rack sensor's output voltage is VR+-0.01.
(4)At that time, rack position must be Ra.
(5)Apply G at two places.
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the nut (F)
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the end surface of the pump (H)
----------
N1=1000r/min Ra=(R1+0.95)+0.05-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=1000r/min Ra=(R1+0.95)+0.05-0.1mm
----------
Information:
Fuel Recommendations
Fill the fuel tank at the end of each day of operation to drive out moist air and prevent condensation. Maintain a fairly consistent level in the day tank (near the top) to avoid drawing moisture into the tank as the level decreases.Do not fill the tank to the top. Fuel expands as it warms, and may overflow.Do not fill fuel filters with fuel before installing them. Contaminated fuel causes accelerated wear to fuel system parts.
Use fuel only as recommended in this section. Fuel grades recommended for use in Caterpillar diesel engines are: No.2-D diesel fuel with low sulfur (0.05 percent maximum), or regular sulfur (0.5 percent maximum). No. 1 grades are acceptable.The following chart lists worldwide fuel standards which meet Caterpillar requirements. Aviation kerosene-type fuels meeting acceptable limits may also be used as an engine fuel. The following chart lists some of the acceptable kerosene-type fuels. Fuel viscosity is a major concern with aviation fuels. A minimum viscosity of 1.4 cSt at 38°C (100°F) is required to properly lubricate Caterpillar fuel system components. These kerosene-type fuels have a lower viscosity for low temperature operation.The kerosene-type fuels have less energy per unit volume than diesel fuels, producing less peak power. More kerosene-type fuel is needed than diesel fuel to do the same amount of work.Caterpillar Diesel Engines are capable of burning a wide range of distillate fuels. Burning clean, stable blends of distillate fuel meeting the following requirements will provide quality engine service life. When economics or fuel availability dictate, other fuel types may be burned in the engine. Consult your Caterpillar dealer for more information and advice on any specific fuel.Cetane Number
Under average starting conditions, direct injection engines require a minimum cetane number of 40. A higher cetane value may be required for high altitude or cold weather operation.Filterability
Clean fuels should have no more than 0.1 percent of sediment and water. Fuel stored for extended periods of time may oxidize and form solids, causing filtering problems.Pour Point
Fuel pour point should be at least 6°C (10°F) below the lowest ambient temperature at which the engines must start and operate. Lower pour points of No.1 or No.1-D fuel may be necessary in extremely cold weather.Cloud Point
The cloud point should be below the lowest ambient temperature at which the engines must start and operate, to prevent the fuel filter elements from plugging with wax crystals. Refer to Fuel Problems in Cold Weather Operation for additional information.Viscosity
Fluid viscosity is a measure of resistance to flow. Fuel viscosity is important because it effects lubrication of fuel system components, and fuel atomization. The provided viscosity limits address both of those effects.Additives
Fuel additives are generally not recommended or needed for the specified fuels listed. Acetone improvers can be used as necessary for direct injection engine requirements. Biocides may be needed to eliminate microorganism growth in storage tanks. In cold conditions, treatment for entrained water may also be necessary.Consult your fuel supplier about the use of additives to prevent incompatibility among additives already in
Fill the fuel tank at the end of each day of operation to drive out moist air and prevent condensation. Maintain a fairly consistent level in the day tank (near the top) to avoid drawing moisture into the tank as the level decreases.Do not fill the tank to the top. Fuel expands as it warms, and may overflow.Do not fill fuel filters with fuel before installing them. Contaminated fuel causes accelerated wear to fuel system parts.
Use fuel only as recommended in this section. Fuel grades recommended for use in Caterpillar diesel engines are: No.2-D diesel fuel with low sulfur (0.05 percent maximum), or regular sulfur (0.5 percent maximum). No. 1 grades are acceptable.The following chart lists worldwide fuel standards which meet Caterpillar requirements. Aviation kerosene-type fuels meeting acceptable limits may also be used as an engine fuel. The following chart lists some of the acceptable kerosene-type fuels. Fuel viscosity is a major concern with aviation fuels. A minimum viscosity of 1.4 cSt at 38°C (100°F) is required to properly lubricate Caterpillar fuel system components. These kerosene-type fuels have a lower viscosity for low temperature operation.The kerosene-type fuels have less energy per unit volume than diesel fuels, producing less peak power. More kerosene-type fuel is needed than diesel fuel to do the same amount of work.Caterpillar Diesel Engines are capable of burning a wide range of distillate fuels. Burning clean, stable blends of distillate fuel meeting the following requirements will provide quality engine service life. When economics or fuel availability dictate, other fuel types may be burned in the engine. Consult your Caterpillar dealer for more information and advice on any specific fuel.Cetane Number
Under average starting conditions, direct injection engines require a minimum cetane number of 40. A higher cetane value may be required for high altitude or cold weather operation.Filterability
Clean fuels should have no more than 0.1 percent of sediment and water. Fuel stored for extended periods of time may oxidize and form solids, causing filtering problems.Pour Point
Fuel pour point should be at least 6°C (10°F) below the lowest ambient temperature at which the engines must start and operate. Lower pour points of No.1 or No.1-D fuel may be necessary in extremely cold weather.Cloud Point
The cloud point should be below the lowest ambient temperature at which the engines must start and operate, to prevent the fuel filter elements from plugging with wax crystals. Refer to Fuel Problems in Cold Weather Operation for additional information.Viscosity
Fluid viscosity is a measure of resistance to flow. Fuel viscosity is important because it effects lubrication of fuel system components, and fuel atomization. The provided viscosity limits address both of those effects.Additives
Fuel additives are generally not recommended or needed for the specified fuels listed. Acetone improvers can be used as necessary for direct injection engine requirements. Biocides may be needed to eliminate microorganism growth in storage tanks. In cold conditions, treatment for entrained water may also be necessary.Consult your fuel supplier about the use of additives to prevent incompatibility among additives already in