Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 612 058
9400612058
ZEXEL
108622-4040
1086224040
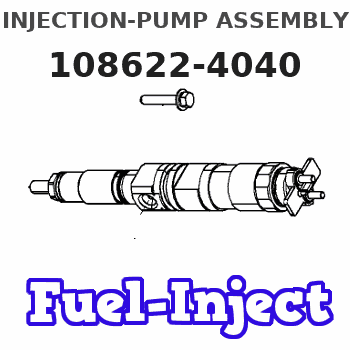
Rating:
Service parts 108622-4040 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
18.1{185}/24.5{250}
14.
NOZZLE
Include in #1:
108622-4040
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 612 058
9400612058
ZEXEL
108622-4040
1086224040
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8250
Bosch type code
1 688 901 101
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
20.7
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
211
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-8020
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407980-2
24*
Digi switch no.
33
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
6.4
6.37
6.43
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
16.1
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
206
204
208
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
2.2+-0.0
1
PS407980-224*
mm
4+-0.05
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
8.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
310
310
310
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
20
18
22
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407980-224*
mm
6.3+-0.0
3
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(16.1)
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
206
204
208
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
82.6
82.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
620
620
PS407980-224*
V
2.2+-0.0
1
PS407980-224*
mm
4+-0.05
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
(R1+0.5)
+0.05-0.
1
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
170
164
176
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
82.6
82.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
620
620
PS407980-224*
V
2.2+-0.0
1
PS407980-224*
mm
4+-0.05
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Rack position
R2-3.7
Boost pressure
kPa
13.3
12
14.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
100
90
110
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Rack position
R2(R1-0.
6)
Boost pressure
kPa
69.3
69.3
69.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
520
520
520
0000001601
Pre-stroke
mm
6.4
6.37
6.43
Remarks
When the timing sleeve is pushed up
When the timing sleeve is pushed up
_02
Connector angle
deg.
11.5
11
12
Remarks
When the eccentric pin is tightened
When the eccentric pin is tightened
_03
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
2.4
2.35
2.45
Output voltage
V
2.95
2.94
2.96
Adjustment
*
_04
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
6.4
6.37
6.43
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_05
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
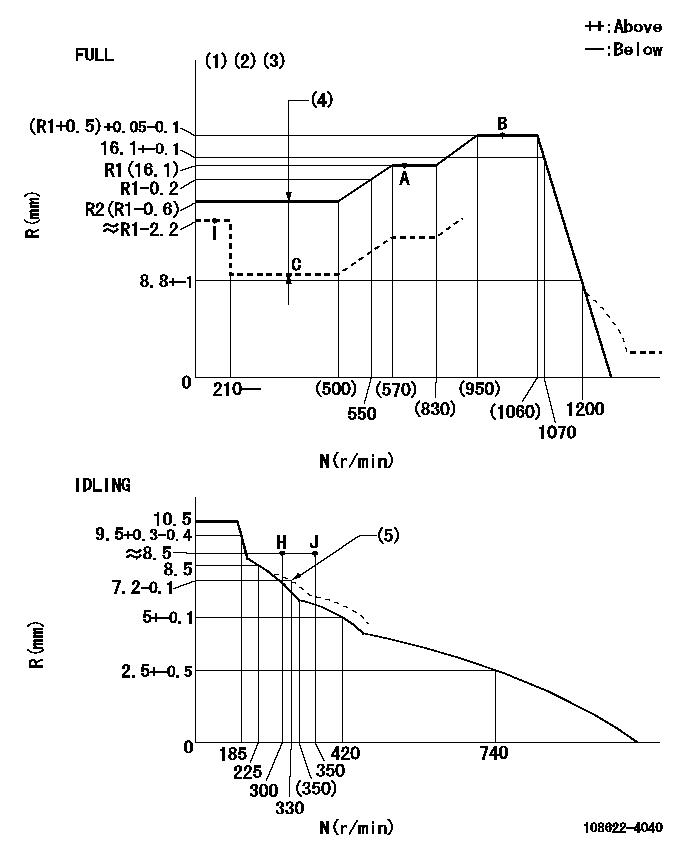
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Microswitch adjustment unnecessary.
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(5)Damper spring setting
----------
T1=AG84 BCL=3.7+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=AG84 BCL=3.7+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
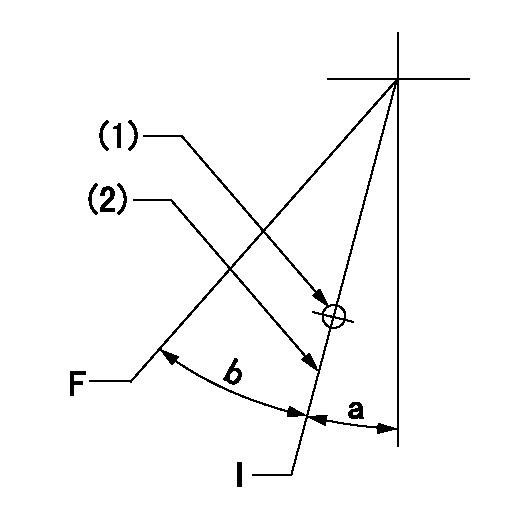
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=37.5mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=36deg+-3deg
----------
aa=37.5mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=36deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
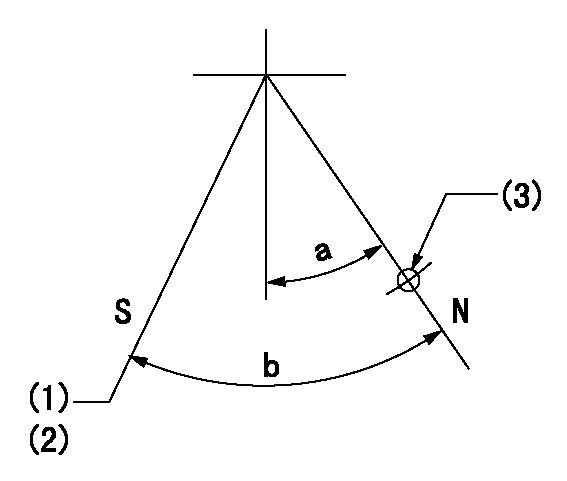
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Speed = aa, rack position = bb
(2)Set the stopper screw.
(3)Use the hole above R = cc
----------
aa=1200r/min bb=3.5+-0.3mm cc=25mm
----------
a=29.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1200r/min bb=3.5+-0.3mm cc=25mm
----------
a=29.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
0000001301
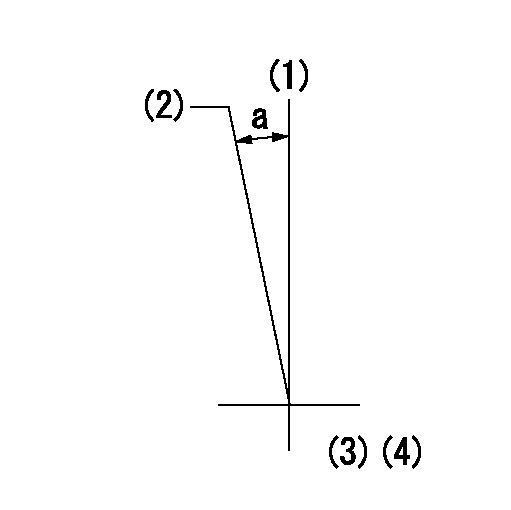
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)Pre-stroke: bb
----------
aa=14deg bb=6.4+-0.03mm
----------
a=(7deg)
----------
aa=14deg bb=6.4+-0.03mm
----------
a=(7deg)
0000001901
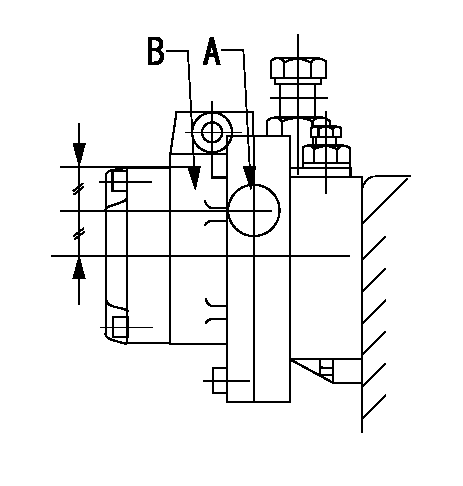
A:Sealing position
B:Pre-stroke actuator
1. When installing the pre-stroke actuator on the pump, first tighten the installation bolts loosely, then move the actuator fully counterclockwise (viewed from the drive side).
Temporary tightening torque: 1 - 1.5 N.m (0.1 - 0.15 kgf.m)
2. Move the actuator in the clockwise direction when viewed from the drive side, and adjust so that it becomes the adjustment point of the adjustment value. Then tighten it.
Tightening torque: 7^9 N.m (0.7^0.9 kgf.m)
3. After prestroke actuator installation adjustment, simultaneously stamp both the actuator side and housing side.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000002201 RACK SENSOR
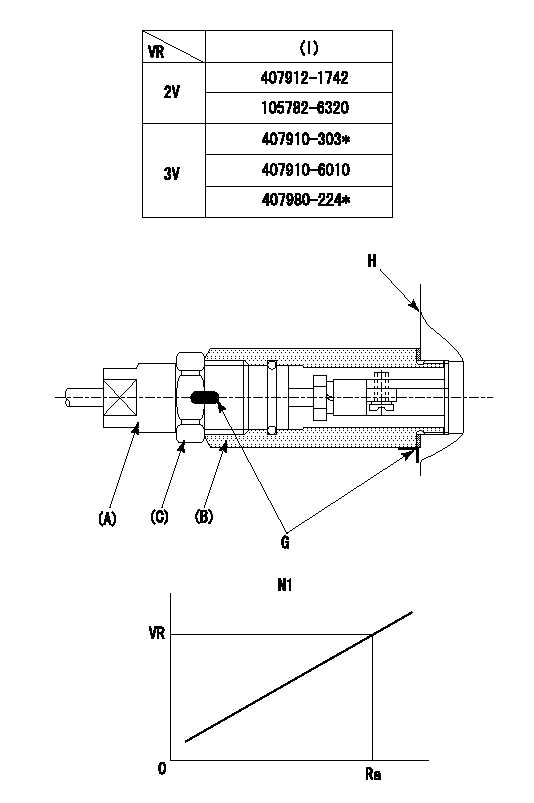
(VR) measurement voltage
(I) Part number of the control unit
(G) Apply red paint.
(H): End surface of the pump
1. Rack sensor adjustment (-0620)
(1)Fix the speed control lever at the full position
(2)Set the speed to N1 r/min.
(If the boost compensator is provided, apply boost pressure.)
(3)Adjust the bobbin (A) so that the rack sensor's output voltage is VR+-0.01.
(4)At that time, rack position must be Ra.
(5)Apply G at two places.
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the nut (F)
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the end surface of the pump (H)
----------
N1=1000r/min Ra=(R1+0.5)+0.05-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=1000r/min Ra=(R1+0.5)+0.05-0.1mm
----------
Information:
Model Views
The sample model view drawings show various typical Caterpillar 3408C and 3412C Engine features. The drawings are generic and do not reflect all available options. Because of individual applications, your engine may appear different from those illustrated.
3408 Model Views:(1) Exhaust(2) Oil Level Gauge (Dipstick)(3) Crankcase Breather(4) Oil Filler Cap(5) Manual Shutoff Shaft(6) Lifting Eye(7) Fuel Priming Pump(8) Fuel Pressure Gauge(9) Fuel Filter(10) Oil Filter(11) Supplemental Coolant Additive Element(12) Oil Drain(13) Air Inlet(14) Turbocharger(15) and Magnetic Pickup Location.
3412 Model Views:(1) Exhaust(2) Oil Level Gauge (Dipstick)(3) Crankcase Breather(4) Oil Filler Cap(5) Manual Shutoff Shaft(6) Lifting Eye(7) Fuel Priming Pump(8) Fuel Pressure Gauge(9) Fuel Filter(10) Oil Filter(11) Supplemental Coolant Additive Element(12) Oil Drain(13) Air Inlet(14) Turbocharger
Typical Generator Set (3408 Shown):(1) Control and Power Panel(2) Exhaust(3) Crankcase Breather(4) Oil Filler Cap(5) Governor Control Lever(6) Manual Shutoff Shaft(7) Radiator Cap(8) Lifting Location(9) Generator(10) Fuel Priming Pump(11) Fuel Filter(12) Oil Level Gauge (Dipstick)(13) Oil Filter(14) and Radiator DrainEngine Information
Engine Descriptions
The Caterpillar 3408C and 3412C Industrial Engines are available as precombustion chamber engines or as direct injection engines.A mechanical governor controls the fuel injection pump output, maintaining the engine rpm selected by the operator. Individual injection pumps (one for each cylinder) meter and pump fuel under high pressure to injection nozzles. Automatic timing advance provides the best fuel injection timing over the full range of engine speed.The fuel ratio control is located on the governor. The fuel ratio control restricts the fuel rack movement. Only the proper amount of fuel is allowed to be injected into the cylinders during acceleration. This minimizes exhaust smoke.Inlet air is filtered by an air cleaner. The air is compressed by a turbocharger before the air enters the engine cylinders. The turbocharger is driven by engine exhaust. The engines can be turbocharged, or turbocharged with jacket water aftercooling.The engines are four cycle engines. Each cylinder head has two inlet valves and two exhaust valves. The rocker arms and the valves are actuated by the camshaft. The action is performed by mechanical lifters and push rods.The cooling system consists of:* two thermostats (one for each bank) to regulate water temperature.* a gear driven centrifugal pump.* an oil cooler, and* a radiator (incorporating a shunt system).The engine lubricating oil, which is both cooled and filtered, is supplied by a gear-type pump. Bypass valves provide unrestricted flow of lubrication oil to the engine parts if oil viscosity is high, or if the oil cooler or the oil filter elements become plugged.Engine efficiency, efficiency of emission controls, and engine performance depend on adherence to proper operation and maintenance recommendations. Engine performance and efficiency also depend on the use of recommended coolant/antifreeze, fuels, and lubrication oils. Follow the recommended Maintenance Schedule found in this publication, paying attention to emission related components, air cleaner, oil, oil filter, fuel and fuel filter maintenance.EPG Information
Caterpillar Electrical Power Generation (EPG) Diesel Engines may be equipped with the Electronic Modular Control Panel II (EMCPII) and the SR4B Generator.The EMCPII provides accurate and reliable engine and generator control and monitoring.
The sample model view drawings show various typical Caterpillar 3408C and 3412C Engine features. The drawings are generic and do not reflect all available options. Because of individual applications, your engine may appear different from those illustrated.
3408 Model Views:(1) Exhaust(2) Oil Level Gauge (Dipstick)(3) Crankcase Breather(4) Oil Filler Cap(5) Manual Shutoff Shaft(6) Lifting Eye(7) Fuel Priming Pump(8) Fuel Pressure Gauge(9) Fuel Filter(10) Oil Filter(11) Supplemental Coolant Additive Element(12) Oil Drain(13) Air Inlet(14) Turbocharger(15) and Magnetic Pickup Location.
3412 Model Views:(1) Exhaust(2) Oil Level Gauge (Dipstick)(3) Crankcase Breather(4) Oil Filler Cap(5) Manual Shutoff Shaft(6) Lifting Eye(7) Fuel Priming Pump(8) Fuel Pressure Gauge(9) Fuel Filter(10) Oil Filter(11) Supplemental Coolant Additive Element(12) Oil Drain(13) Air Inlet(14) Turbocharger
Typical Generator Set (3408 Shown):(1) Control and Power Panel(2) Exhaust(3) Crankcase Breather(4) Oil Filler Cap(5) Governor Control Lever(6) Manual Shutoff Shaft(7) Radiator Cap(8) Lifting Location(9) Generator(10) Fuel Priming Pump(11) Fuel Filter(12) Oil Level Gauge (Dipstick)(13) Oil Filter(14) and Radiator DrainEngine Information
Engine Descriptions
The Caterpillar 3408C and 3412C Industrial Engines are available as precombustion chamber engines or as direct injection engines.A mechanical governor controls the fuel injection pump output, maintaining the engine rpm selected by the operator. Individual injection pumps (one for each cylinder) meter and pump fuel under high pressure to injection nozzles. Automatic timing advance provides the best fuel injection timing over the full range of engine speed.The fuel ratio control is located on the governor. The fuel ratio control restricts the fuel rack movement. Only the proper amount of fuel is allowed to be injected into the cylinders during acceleration. This minimizes exhaust smoke.Inlet air is filtered by an air cleaner. The air is compressed by a turbocharger before the air enters the engine cylinders. The turbocharger is driven by engine exhaust. The engines can be turbocharged, or turbocharged with jacket water aftercooling.The engines are four cycle engines. Each cylinder head has two inlet valves and two exhaust valves. The rocker arms and the valves are actuated by the camshaft. The action is performed by mechanical lifters and push rods.The cooling system consists of:* two thermostats (one for each bank) to regulate water temperature.* a gear driven centrifugal pump.* an oil cooler, and* a radiator (incorporating a shunt system).The engine lubricating oil, which is both cooled and filtered, is supplied by a gear-type pump. Bypass valves provide unrestricted flow of lubrication oil to the engine parts if oil viscosity is high, or if the oil cooler or the oil filter elements become plugged.Engine efficiency, efficiency of emission controls, and engine performance depend on adherence to proper operation and maintenance recommendations. Engine performance and efficiency also depend on the use of recommended coolant/antifreeze, fuels, and lubrication oils. Follow the recommended Maintenance Schedule found in this publication, paying attention to emission related components, air cleaner, oil, oil filter, fuel and fuel filter maintenance.EPG Information
Caterpillar Electrical Power Generation (EPG) Diesel Engines may be equipped with the Electronic Modular Control Panel II (EMCPII) and the SR4B Generator.The EMCPII provides accurate and reliable engine and generator control and monitoring.