Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 619 148
9400619148
ZEXEL
108622-2253
1086222253
MITSUBISHI
ME152420
me152420
Rating:
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 619 148
9400619148
ZEXEL
108622-2253
1086222253
MITSUBISHI
ME152420
me152420
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
108622-2253
9 400 619 148
ME152420 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D24T2 K
6D24T2 K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8250
Bosch type code
1 688 901 101
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
20.7
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
211
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131425-0220
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
RED3 control unit part number
407910-3
960
RED3 rack sensor specifications
mm
19
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407980-2
24*
Digi switch no.
31
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
8.5
8.47
8.53
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Rack position
(10.3)
Vist
V
2.3
2.3
2.3
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
109
108
110
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
PS407980-224*
V
2.45+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
6.1+-0.0
5
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Rack position
(6.9)
Vist
V
2.8
2.7
2.9
Pump speed
r/min
310
310
310
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
20
18
22
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
PS407980-224*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407980-224*
mm
8.4+-0.0
3
Remarks
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
0000001201
Pre-stroke
mm
8.5
8.47
8.53
Remarks
When the timing sleeve is pushed up
When the timing sleeve is pushed up
_02
Connector angle
deg.
8.5
8
9
Remarks
When the eccentric pin is tightened
When the eccentric pin is tightened
_03
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
6.1
6.05
6.15
Output voltage
V
2.45
2.44
2.46
Adjustment
*
_04
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
8.5
8.47
8.53
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_05
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
5.5
Output voltage
V
3
2.98
3
Confirmation
*
_06
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
Test data Ex:
Speed control lever angle
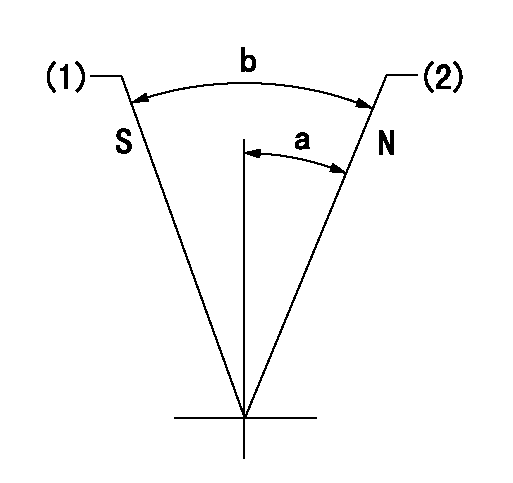
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Rack position bb
----------
aa=1mm bb=20mm
----------
a=19deg+-5deg b=37deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1mm bb=20mm
----------
a=19deg+-5deg b=37deg+-5deg
0000000901
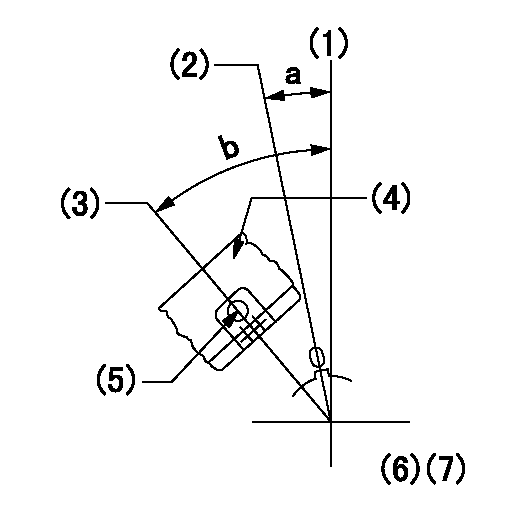
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)At the No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection position, stamp an aligning mark on the damper to align with the pointer's groove.
(4)Damper
(5)Pointer
(6)B.T.D.C.: aa
(7)Pre-stroke: bb
----------
aa=3deg bb=8.5+-0.03mm
----------
a=(0deg) b=(44deg)
----------
aa=3deg bb=8.5+-0.03mm
----------
a=(0deg) b=(44deg)
0000001501
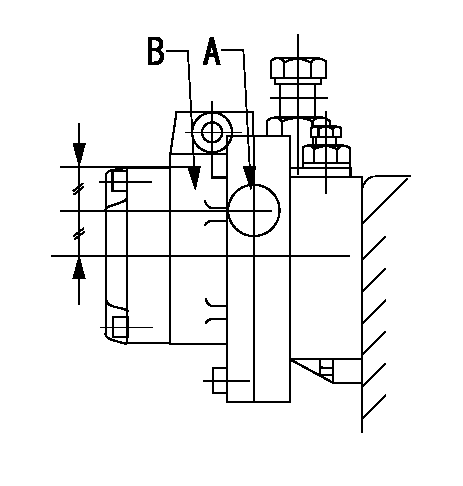
A:Sealing position
B:Pre-stroke actuator
1. When installing the pre-stroke actuator on the pump, first tighten the installation bolts loosely, then move the actuator fully counterclockwise (viewed from the drive side).
Temporary tightening torque: 1 - 1.5 N.m (0.1 - 0.15 kgf.m)
2. Move the actuator in the clockwise direction when viewed from the drive side, and adjust so that it becomes the adjustment point of the adjustment value. Then tighten it.
Tightening torque: 7^9 N.m (0.7^0.9 kgf.m)
3. After prestroke actuator installation adjustment, simultaneously stamp both the actuator side and housing side.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001701
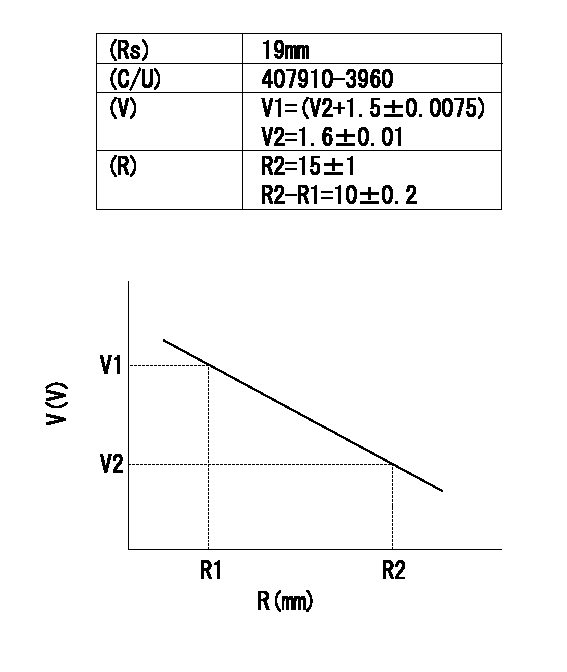
(Rs) rack sensor specifications
(C/U) control unit part number
(V) Rack sensor output voltage
(R) Rack position (mm)
1. Confirming governor output characteristics (rack 19 mm, span 10 mm)
(1)When the output voltages of the rack sensor are V1 and V2, check that the rack positions R1 and R2 in the table above are satisfied.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001901 RACK SENSOR

(VR) measurement voltage
(I) Part number of the control unit
(G) Apply red paint.
(H): End surface of the pump
1. Rack sensor adjustment (154610-0620)
(1)At governor side rack sensor output voltage V1, adjust the bobbin (A) so that the drive side rack sensor output voltage is VR+-0.01.
(2)Apply G at two places.
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the nut (F)
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the end surface of the pump (H)
----------
V1=1.6V
----------
----------
V1=1.6V
----------
Information:
1. Determining Overhaul Timing
The timing of engine overhauls should be determined primarily in accordance with reductions in compression pressure. A reduction in compression pressure may be accompanied by one or more of the following externally observable symptoms:(a) Reduced power(b) Increased fuel consumption(c) Increased engine-oil consumption(d) Increased blowby gas through breather (possibly owing to wear on cylinder liners and piston rings)(e) Gas leakage (possibly owing to poor seating of intake and exhaust valves)(f) Starting problems(g) Increased engine noise(h) Abnormal exhaust-gas color after engine warmupAlthough these symptoms can be caused by a reduction in compression pressure, they can be caused also by other problems that are not related to engine deterioration. Notably, symptoms (b) and (f) may be affected significantly by the injection pump's injection rate, by the injection timing, by plunger wear, by injector defects, and/or by the battery, starter, and other electrical equipment. Symptoms (d) should be given special attention since a decrease in compression pressure owing to wear on the cylinder liners and piston rings is one of the most obvious signs that the engine needs an overhaul. It is essential, however, to measure the compression pressure in each cylinder and to use the results as the primary criteria for making a decision to overhaul the engine.2. Measuring Compression Pressure
2.1 Preparation for InspectionPerform the following checks before starting the inspection.(1) Make sure the engine oil, air cleaner, starter, and battery are normal.(2) Make sure the engine is warm.2.2 Inspection(1) Move the control lever to the stop position.(2) Remove all glow plugs, then connect the Compression Gauge Adapter (ST333060) and compression gauge to the cylinder whose compression pressure is to be checked.(3) Crank the engine using the starter until the needle of the compression gauge stops moving, then read the pressure indication.(4) If the measurement is lower than the specified limit, perform an overhaul.
(a) Measure the compression pressure of every cylinder. Measuring the compression pressures of two or three cylinders and simply assuming the compression pressures of the other cylinders is dangerous.(b) The compression pressure varies with the engine speed, so it is important to take all measurements with the same engine speed.
Unit: MPa {kgf/cm2} (psi) Take measurements with an engine speed of 240 min-1.
Compression gauge and adapter
Measuring compression pressure
(a) It is important to measure compression pressures regularly and to keep track of changes in them.(b) During the engine's run-in period and after an overhaul, the compression pressures will increase slightly as the piston rings, valve seats, and other parts fit snugly in position. The pressures will then decrease as parts wear.
3. Troubleshooting
3.1 OverviewDiesel-engine fault symptoms tend to have multiple causes, which influence each other. Consequently, it is often difficult to locate a fault based on the symptoms. Particular care is required when diagnosing faults related to the injection pump, injectors, and compression pressures since such faults may produce the same symptoms.For the above-mentioned reasons, the inspection sequences in the troubleshooting charts on the following pages start with items where the likelihood of a fault is greatest with
The timing of engine overhauls should be determined primarily in accordance with reductions in compression pressure. A reduction in compression pressure may be accompanied by one or more of the following externally observable symptoms:(a) Reduced power(b) Increased fuel consumption(c) Increased engine-oil consumption(d) Increased blowby gas through breather (possibly owing to wear on cylinder liners and piston rings)(e) Gas leakage (possibly owing to poor seating of intake and exhaust valves)(f) Starting problems(g) Increased engine noise(h) Abnormal exhaust-gas color after engine warmupAlthough these symptoms can be caused by a reduction in compression pressure, they can be caused also by other problems that are not related to engine deterioration. Notably, symptoms (b) and (f) may be affected significantly by the injection pump's injection rate, by the injection timing, by plunger wear, by injector defects, and/or by the battery, starter, and other electrical equipment. Symptoms (d) should be given special attention since a decrease in compression pressure owing to wear on the cylinder liners and piston rings is one of the most obvious signs that the engine needs an overhaul. It is essential, however, to measure the compression pressure in each cylinder and to use the results as the primary criteria for making a decision to overhaul the engine.2. Measuring Compression Pressure
2.1 Preparation for InspectionPerform the following checks before starting the inspection.(1) Make sure the engine oil, air cleaner, starter, and battery are normal.(2) Make sure the engine is warm.2.2 Inspection(1) Move the control lever to the stop position.(2) Remove all glow plugs, then connect the Compression Gauge Adapter (ST333060) and compression gauge to the cylinder whose compression pressure is to be checked.(3) Crank the engine using the starter until the needle of the compression gauge stops moving, then read the pressure indication.(4) If the measurement is lower than the specified limit, perform an overhaul.
(a) Measure the compression pressure of every cylinder. Measuring the compression pressures of two or three cylinders and simply assuming the compression pressures of the other cylinders is dangerous.(b) The compression pressure varies with the engine speed, so it is important to take all measurements with the same engine speed.
Unit: MPa {kgf/cm2} (psi) Take measurements with an engine speed of 240 min-1.
Compression gauge and adapter
Measuring compression pressure
(a) It is important to measure compression pressures regularly and to keep track of changes in them.(b) During the engine's run-in period and after an overhaul, the compression pressures will increase slightly as the piston rings, valve seats, and other parts fit snugly in position. The pressures will then decrease as parts wear.
3. Troubleshooting
3.1 OverviewDiesel-engine fault symptoms tend to have multiple causes, which influence each other. Consequently, it is often difficult to locate a fault based on the symptoms. Particular care is required when diagnosing faults related to the injection pump, injectors, and compression pressures since such faults may produce the same symptoms.For the above-mentioned reasons, the inspection sequences in the troubleshooting charts on the following pages start with items where the likelihood of a fault is greatest with
Have questions with 108622-2253?
Group cross 108622-2253 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
108622-2253
9 400 619 148
ME152420
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D24T2
6D24T2