Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 771
9400611771
ZEXEL
107692-5012
1076925012
Rating:
Service parts 107692-5012 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
16600-Z5673
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
19.6{200}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
107692-5012
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 771
9400611771
ZEXEL
107692-5012
1076925012
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8250
Bosch type code
1 688 901 101
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
20.7
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
211
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131425-0520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407910-3
03*
Selector switch no.
01
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407980-2
24*
Digi switch no.
15
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
5.1
5.07
5.13
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
14.7
Pump speed
r/min
1300
1300
1300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
110.5
108.5
112.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
PS407910-303*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407910-303*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
8.4+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
545
545
545
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
22.5
20.7
24.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407980-224*
mm
5+-0.03
PS407910-303*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407910-303*
mm
5+-0.03
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(14.7)
Pump speed
r/min
1300
1300
1300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
110.5
109.5
111.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
28
28
Boost pressure
mmHg
210
210
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
PS407910-303*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407910-303*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1-2.05
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
101.5
97.5
105.5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
28
28
Boost pressure
mmHg
210
210
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
PS407910-303*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407910-303*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
(R2-0.7)
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
47.7
45.7
49.7
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
PS407910-303*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407910-303*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Rack position
(R2-0.7)
Boost pressure
kPa
6.7
5.4
8
Boost pressure
mmHg
50
40
60
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Rack position
R2(R1-3.
95)
Boost pressure
kPa
14.7
14.7
14.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
110
110
110
0000001601
CU407980-224*
*
Actuator retarding type
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
2
1.95
2.05
Output voltage
V
2.83
2.82
2.84
Adjustment
*
_02
CU407980-224*
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
5.1
5.07
5.13
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_03
CU407980-224*
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
_04
CU407910-303*
*
Actuator retarding type
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
2
1.95
2.05
Output voltage
V
2.83
2.82
2.84
Adjustment
*
_05
CU407910-303*
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
5.1
5.07
5.13
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_06
CU407910-303*
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
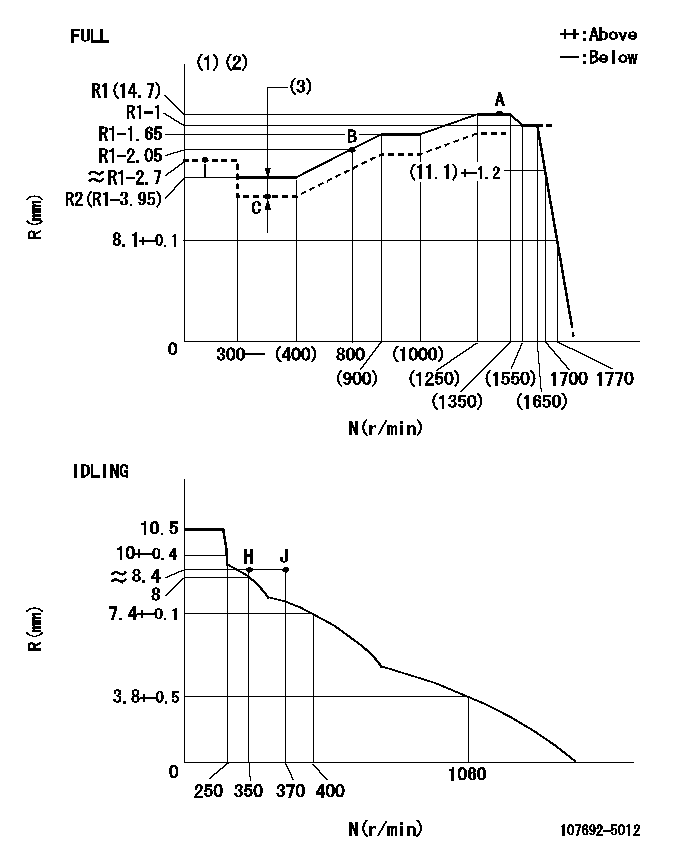
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=AF93 BCL=(0.7)mm
----------
----------
T1=AF93 BCL=(0.7)mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=93.5mm
----------
a=17deg+-5deg b=(37deg)+-3deg
----------
aa=93.5mm
----------
a=17deg+-5deg b=(37deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle
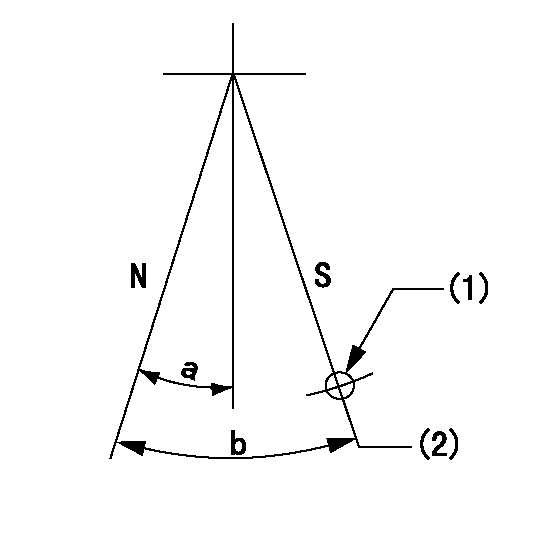
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
(2)Set the stopper bolt so that rack position = bb (speed = cc)
----------
aa=37mm bb=1.5+-0.3mm cc=0r/min
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=45deg+-5deg
----------
aa=37mm bb=1.5+-0.3mm cc=0r/min
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=45deg+-5deg
0000001301

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)Pre-stroke: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=5.1+-0.03mm
----------
a=(20deg)
----------
aa=5.1+-0.03mm
----------
a=(20deg)
0000001401
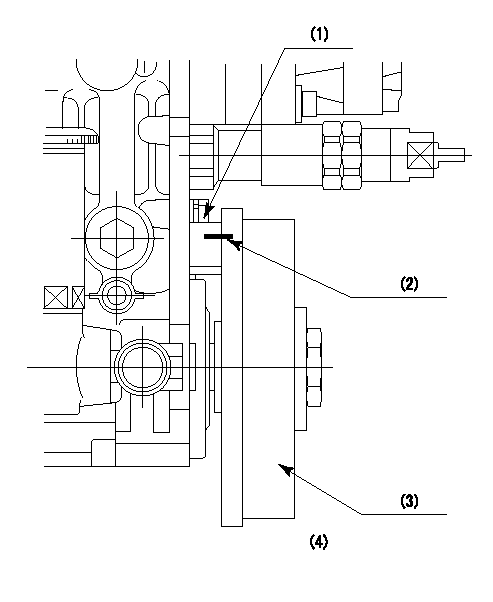
(1)Pointer
(2)Injection timing aligning mark
(3)Fly weight
(4)The actual shape and direction may be different from this illustration.
Operation sequence
1. Turn the prestroke actuator OFF.
2. Turn the camshaft as far as the No.1 cylinder's beginning of injection position.
3. Check that the pointer alignment mark of the injection pump and the alignment mark of the flywheel are matching.
4. If they are not matching, erase the alignment mark on the flywheel side, and stamp an alignment mark on the flywheel position that matches with the pointer side alignment mark.
5. Check again that the coupling's key groove position is in the No.1 cylinder's beginning of injection position.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001701
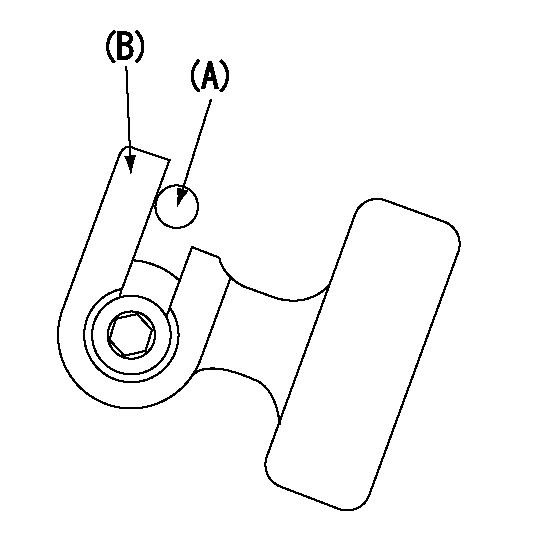
A : Stopper pin
B: Connector
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001801
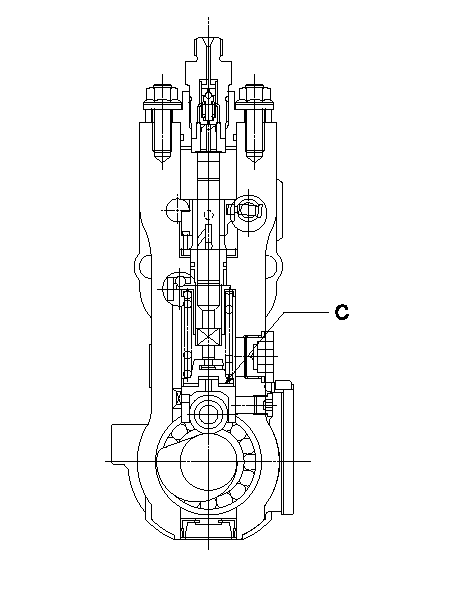
C:Shim
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001901
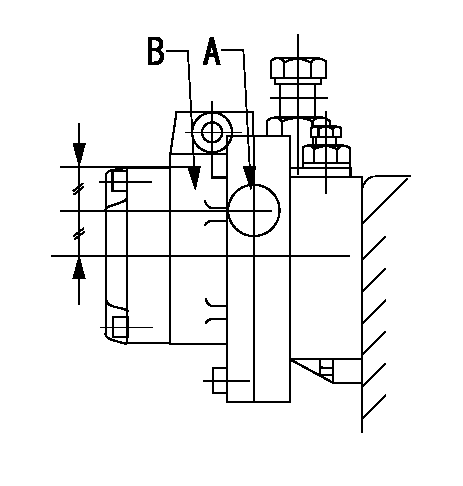
A:Sealing position
B:Pre-stroke actuator
1. When installing the pre-stroke actuator on the pump, first tighten the installation bolts loosely, then move the actuator fully counterclockwise (viewed from the drive side).
Temporary tightening torque: 1 - 1.5 N.m (0.1 - 0.15 kgf.m)
2. Move the actuator in the clockwise direction when viewed from the drive side, and adjust so that it becomes the adjustment point of the adjustment value. Then tighten it.
Tightening torque: 7^9 N.m (0.7^0.9 kgf.m)
3. After prestroke actuator installation adjustment, simultaneously stamp both the actuator side and housing side.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000002201 RACK SENSOR
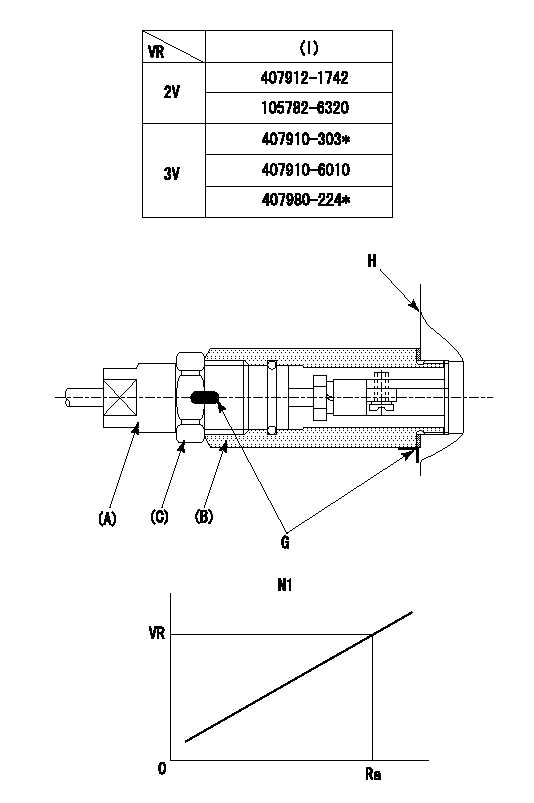
(VR) measurement voltage
(I) Part number of the control unit
(G) Apply red paint.
(H): End surface of the pump
1. Rack sensor adjustment (-0620)
(1)Fix the speed control lever at the full position
(2)Set the speed to N1 r/min.
(If the boost compensator is provided, apply boost pressure.)
(3)Adjust the bobbin (A) so that the rack sensor's output voltage is VR+-0.01.
(4)At that time, rack position must be Ra.
(5)Apply G at two places.
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the nut (F)
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the end surface of the pump (H)
----------
N1=1300r/min Ra=R1(14.7)mm
----------
----------
N1=1300r/min Ra=R1(14.7)mm
----------
0000002301 ACS
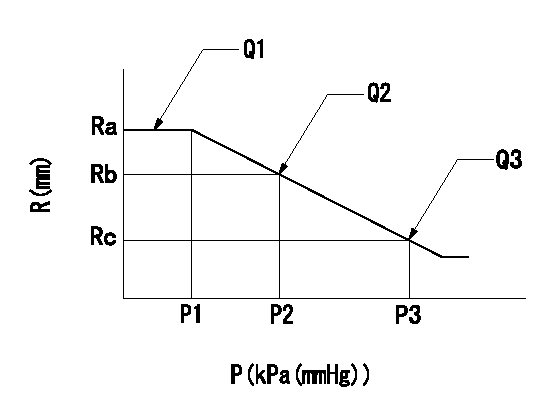
(P) Absolute pressure
(R) Rack position (mm)
1. Adjustment of the aneroid compensator
(1)Screw in the aneroid compensator body and attach the pushrod to the compensator lever so that the performance in the above graph can be obtained. The control lever must be at the full set position N = N1.
----------
N1=1300r/min
----------
Ra=R1(14.7)mm Rb=- Rc=(R1-0.65)mm P1=(86)+-2.7kPa((645)+-20mmHg) P2=- P3=57.7+-0.7kPa(433+-5mmHg) Q1=110.5+-1cm3/1000st Q2=- Q3=100.5+-2cm3/1000st
----------
N1=1300r/min
----------
Ra=R1(14.7)mm Rb=- Rc=(R1-0.65)mm P1=(86)+-2.7kPa((645)+-20mmHg) P2=- P3=57.7+-0.7kPa(433+-5mmHg) Q1=110.5+-1cm3/1000st Q2=- Q3=100.5+-2cm3/1000st
Information:
Rating Conditions
Unless otherwise specified, all ratings are based on SAE J1349 standard ambient conditions:* 100 kPa (29.6 inches of Hg) of pressure* 30 percent relative humidity, and* a temperature of 26°C (77°F)Ratings also apply at ISO8665, ISO3046/1, DIN6271, and BS5514 standard conditions.Power for diesel engines is based on:* API gravity of 35 at 15°C (60°F)* fuel LHV of 42,780 kJ/g (18390 Btu/lb) at 29°C (84°F)* fuel density of 839 g/L (7 lb/US gal)Ratings are gross output ratings- the total output capability of the engine equipped with standard accessories. Standard accessories include pumps for lubrication oil, fuel, and jacket water. The gross output, minus the power required to drive auxiliary components, equals the net power available for the external (flywheel) load. Typical auxiliary components include cooling fans, air compressors, and charging alternators.Rating Definitions
It is important to know how the vessel will be operating, so that the rating can match the operating profile. Additionally, proper rating selection is important so that customer perception of price/value is realized. In selecting a rating for a specific application, the most important consideration is time spent at full throttle. These rating definitions identify the percent of time at full throttle and corresponding times below rated rpm. A (Continuous): For heavy-duty service in ocean-going displacement hull vessels such as freighters, tugboats, bottom drag trawlers, and deep river towboats when the engine is operated at rated load and speed up to 100 percent of the time without interruption or load cycling. Typical use is 5000 to 8000 hours per year. B (Medium Duty): For displacement hull vessels such as mid-water trawlers, purse seiners, crew and supply boats, ferries, and towboats where locks, sandbars and curves dictate frequent slowing when engine load and speed are constant with some cycling. The engine may be operated up to 80 percent load factor and at rated load and speed for up to 80 percent of the duty cycle, or 10 hours out of every 12 hours. Typical use is 3000 to 5000 hours per year. C (Intermittent): For planing hull vessels such as ferries, fishing boats moving at higher speeds out and back (i.e. lobster, crayfish and tuna) offshore service boats, and also displacement hull yachts and short trip coastal freighters where engine load and speed are cyclical. The engine may be operated at up to 80 percent load factor and at rated load and speed for up to 50 percent of the duty cycle, or 6 hours out of every 12 hours. Typical use is 2000 to 4000 hours per year. D (Patrol Craft): For planning hull vessels such as offshore patrol boats, customs, police, and some fire and fishing boats. Also used for bow and stern thursters. The engine may be operated at up to 50 percent load factor and at rated load and speed for up to 16 percent of the duty cycle or 2 hours out of every 12 hours. Typical use is 1000 to 3000 hours per year. E (High Performance): For planning hull vessels
Unless otherwise specified, all ratings are based on SAE J1349 standard ambient conditions:* 100 kPa (29.6 inches of Hg) of pressure* 30 percent relative humidity, and* a temperature of 26°C (77°F)Ratings also apply at ISO8665, ISO3046/1, DIN6271, and BS5514 standard conditions.Power for diesel engines is based on:* API gravity of 35 at 15°C (60°F)* fuel LHV of 42,780 kJ/g (18390 Btu/lb) at 29°C (84°F)* fuel density of 839 g/L (7 lb/US gal)Ratings are gross output ratings- the total output capability of the engine equipped with standard accessories. Standard accessories include pumps for lubrication oil, fuel, and jacket water. The gross output, minus the power required to drive auxiliary components, equals the net power available for the external (flywheel) load. Typical auxiliary components include cooling fans, air compressors, and charging alternators.Rating Definitions
It is important to know how the vessel will be operating, so that the rating can match the operating profile. Additionally, proper rating selection is important so that customer perception of price/value is realized. In selecting a rating for a specific application, the most important consideration is time spent at full throttle. These rating definitions identify the percent of time at full throttle and corresponding times below rated rpm. A (Continuous): For heavy-duty service in ocean-going displacement hull vessels such as freighters, tugboats, bottom drag trawlers, and deep river towboats when the engine is operated at rated load and speed up to 100 percent of the time without interruption or load cycling. Typical use is 5000 to 8000 hours per year. B (Medium Duty): For displacement hull vessels such as mid-water trawlers, purse seiners, crew and supply boats, ferries, and towboats where locks, sandbars and curves dictate frequent slowing when engine load and speed are constant with some cycling. The engine may be operated up to 80 percent load factor and at rated load and speed for up to 80 percent of the duty cycle, or 10 hours out of every 12 hours. Typical use is 3000 to 5000 hours per year. C (Intermittent): For planing hull vessels such as ferries, fishing boats moving at higher speeds out and back (i.e. lobster, crayfish and tuna) offshore service boats, and also displacement hull yachts and short trip coastal freighters where engine load and speed are cyclical. The engine may be operated at up to 80 percent load factor and at rated load and speed for up to 50 percent of the duty cycle, or 6 hours out of every 12 hours. Typical use is 2000 to 4000 hours per year. D (Patrol Craft): For planning hull vessels such as offshore patrol boats, customs, police, and some fire and fishing boats. Also used for bow and stern thursters. The engine may be operated at up to 50 percent load factor and at rated load and speed for up to 16 percent of the duty cycle or 2 hours out of every 12 hours. Typical use is 1000 to 3000 hours per year. E (High Performance): For planning hull vessels