Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
107692-1351
1076921351
ISUZU
8943922311
8943922311
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
107692-1351
1076921351
ISUZU
8943922311
8943922311
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8250
Bosch type code
1 688 901 101
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
20.7
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
211
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131425-1820
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407980-2
24*
Digi switch no.
17
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
5.1
5.07
5.13
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
13.7
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
121.5
119.9
123.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
7.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
435
435
435
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8.5
7.2
9.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407980-224*
mm
5+-0.03
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(13.7)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
121.5
120.5
122.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.1+-0.0
5
0000001601
CU407980-224*
*
Actuator retarding type
*
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
2
1.95
2.05
Output voltage
V
2.83
2.82
2.84
Adjustment
*
_02
CU407980-224*
*
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
5.1
5.07
5.13
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_03
CU407980-224*
*
Supply voltage
V
24
23.5
24.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
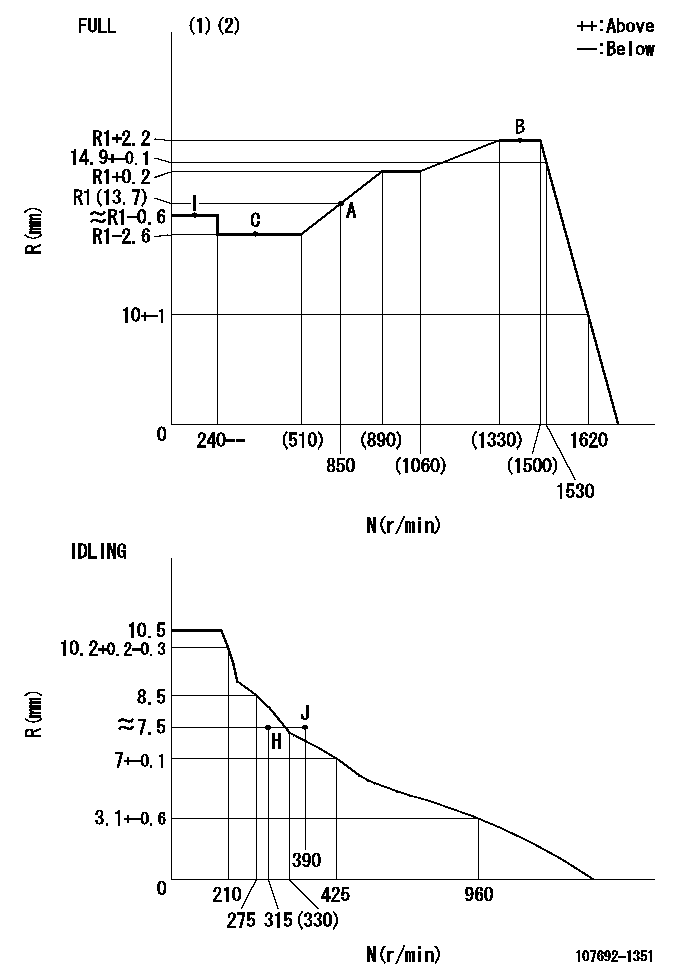
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
----------
T1=AF89
----------
----------
T1=AF89
----------
Speed control lever angle
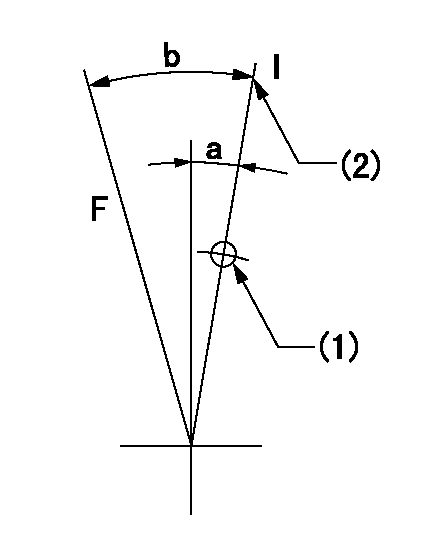
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=2.5deg+-5deg b=43.5deg+-3deg
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=2.5deg+-5deg b=43.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
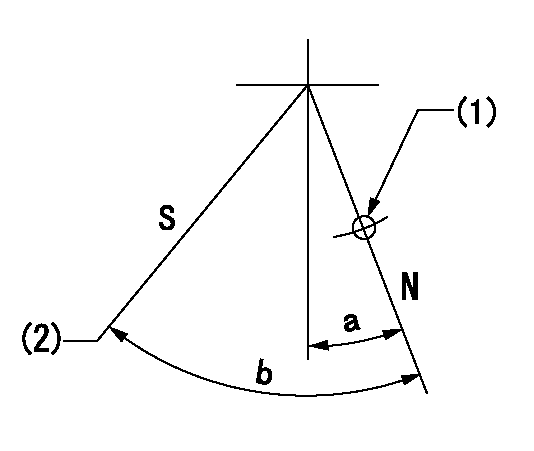
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
(2)Set the stopper bolt at speed = bb and rack position = cc (non-injection rack position).
----------
aa=40mm bb=0r/min cc=1.5+-0.3mm
----------
a=12deg+-5deg b=44deg+-5deg
----------
aa=40mm bb=0r/min cc=1.5+-0.3mm
----------
a=12deg+-5deg b=44deg+-5deg
0000001301
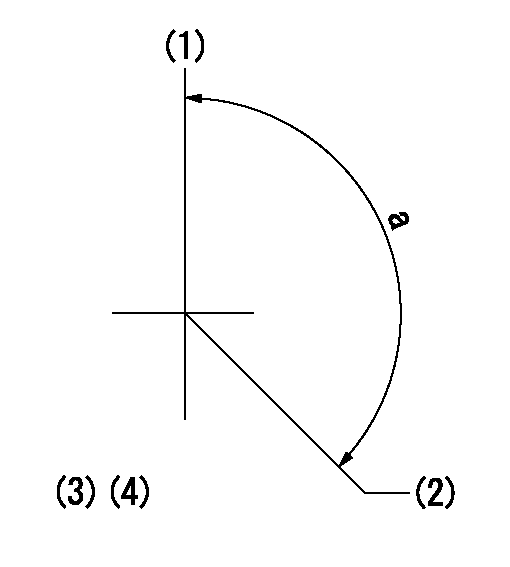
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Positions of coupling's threaded installation holes at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)Pre-stroke: bb
----------
aa=8deg bb=5.1+-0.03mm
----------
a=(140deg)
----------
aa=8deg bb=5.1+-0.03mm
----------
a=(140deg)
0000001401
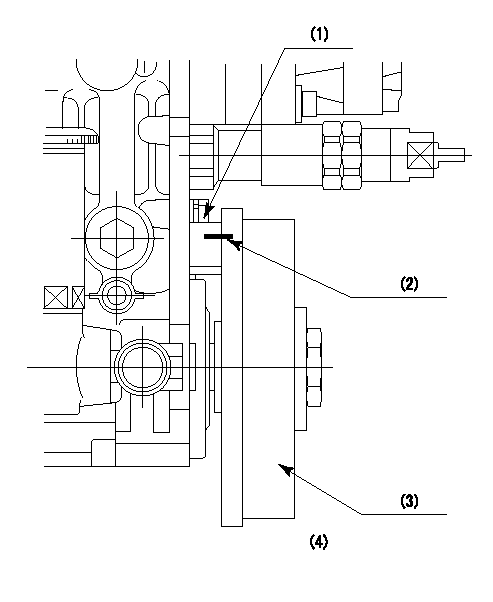
(1)Pointer
(2)Injection timing aligning mark
(3)Fly weight
(4)The actual shape and direction may be different from this illustration.
Operation sequence
1. Turn the prestroke actuator OFF.
2. Turn the camshaft as far as the No.1 cylinder's beginning of injection position.
3. Check that the pointer alignment mark of the injection pump and the alignment mark of the flywheel are matching.
4. If they are not matching, erase the alignment mark on the flywheel side, and stamp an alignment mark on the flywheel position that matches with the pointer side alignment mark.
5. Check again that the coupling's key groove position is in the No.1 cylinder's beginning of injection position.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001701
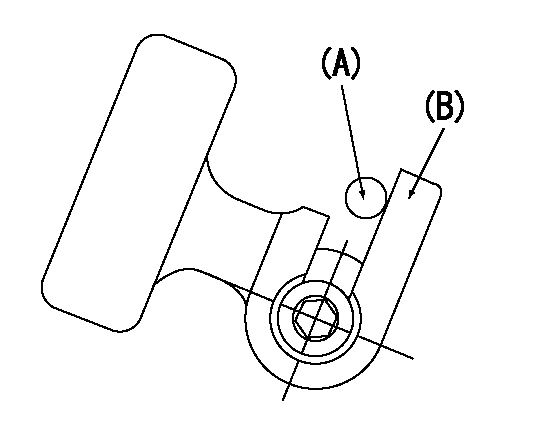
A : Stopper pin
B: Connector
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001801
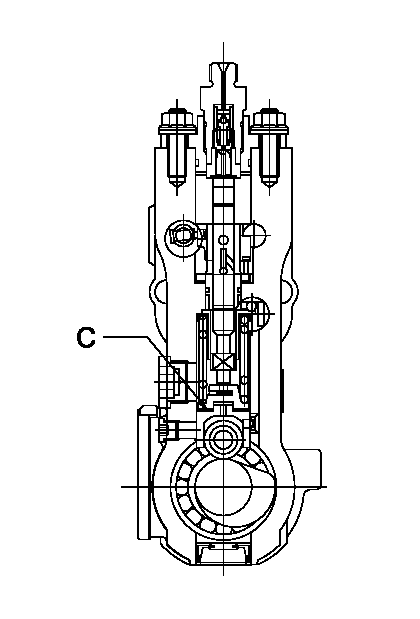
C:Shim
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001901
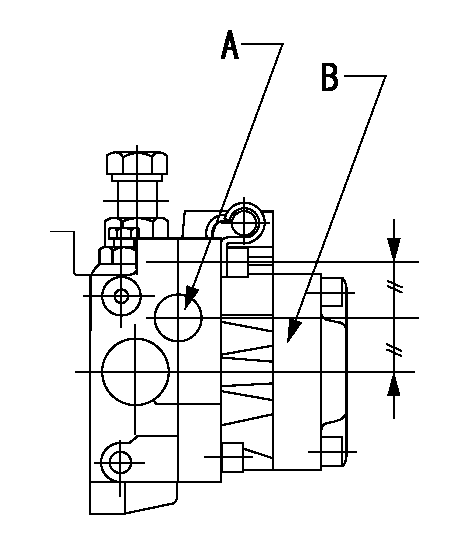
A:Sealing position
B:Pre-stroke actuator
1. When installing the pre-stroke actuator on the pump, first tighten the installation bolts loosely, then move the actuator fully clockwise (viewed from the drive side).
Temporary tightening torque: 1 - 1.5 N.m (0.1 - 0.15 kgf.m)
2. Move the actuator in the counterclockwise direction when viewed from the drive side, and adjust so that it becomes the adjustment point of the adjustment value. Then tighten it.
Tightening torque: 7^9 N.m (0.7^0.9 kgf.m)
3. After prestroke actuator installation adjustment, simultaneously stamp both the actuator side and housing side.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000002201 RACK SENSOR
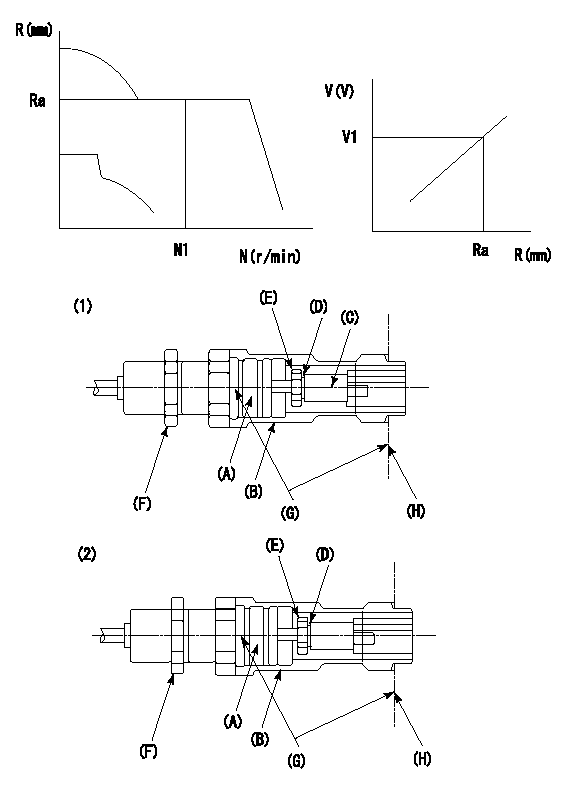
G:Red paint
H:Pump end face
P/N: part number of suitable shim
(1)Threaded type rack block
(2)Welded type rack block
Rack sensor adjustment
1. Threaded type rack sensor (-5*20, P type, no TICS rack limit).
(1)Screw in the bobbin (A) until it contacts the joint (B).
(2)Fix the pump lever.
(3)At speed N1 and rack position Ra, adjust the amount that the bobbin is screwed in so that the amp's output voltage is V1.
(4)Fix using the nut (F).
(5)Affix the caution plate to the upper part of the joint (B).
(6)Apply (G) at two places.
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the nut (F)
Connecting part between the end surface of the pump (H) and the joint (B)
2. Range for screw-in adjustment between the bobbin (A) and the joint (B) is 9 threads.
Screw in to the end from (the position where the bobbin (A) is rotated 9 turns).
Speed N1, rack position Ra, output voltage V1, rack sensor supply voltage 5+-0.01 (V)
----------
Ra=R1(13.7)+2.2mm N1=1400r/min V1=3+-0.01V
----------
----------
Ra=R1(13.7)+2.2mm N1=1400r/min V1=3+-0.01V
----------
Information:
Starting From External Electrical Source
Always wear protective glasses when working with batteries.Do not allow the free end of booster cables to make contact with each other or touch the engine. This will help prevent sparks near the batteries.Batteries give off flammable fumes that can explode.Do not smoke when observing the battery electrolyte levels.Electrolyte is an acid and can cause personal injury if it contacts skin or eyes.
Be sure the main power switch is in the OFF position before attaching the booster cables to the engine being started. When using booster cables, be sure to connect in parallel: POSITIVE (+) to POSITIVE (+) and NEGATIVE (-) to NEGATIVE (-).Use only equal voltage for boost starting. The use of a welder or higher voltage will damage the electrical system.
Engines without engine-to-frame ground straps can be damaged by electrical discharge.To prevent electrical discharge damage, check to make sure there is an engine-to-frame ground strap. For engines which have the alternator connected to an engine component, the ground strap must connect that component to the frame.Some engines have starter-to-frame ground straps. But, many of these starters are not electrically grounded to the engine. They have electrical insulation systems. For this reason, the starter-to-frame ground strap may not be an acceptable ground.Connect one end of cable to the POSITIVE (+) (ungrounded) terminal of the battery on the engine being started. Connect the other end to the POSITIVE (+) terminal of the power source.Connect one end of the second cable to the NEGATIVE (-) terminal of the power source. Connect the other end to the frame of the engine to be started.Turn the start switch on and start the engine.Disconnect the cable from the frame first. Disconnect the other end from the NEGATIVE (-) terminal of the power source. Disconnect the cable from the POSITIVE (+) terminal of the battery. Disconnect the other end from the POSITIVE (+) terminal of the power source.
Always wear protective glasses when working with batteries.Do not allow the free end of booster cables to make contact with each other or touch the engine. This will help prevent sparks near the batteries.Batteries give off flammable fumes that can explode.Do not smoke when observing the battery electrolyte levels.Electrolyte is an acid and can cause personal injury if it contacts skin or eyes.
Be sure the main power switch is in the OFF position before attaching the booster cables to the engine being started. When using booster cables, be sure to connect in parallel: POSITIVE (+) to POSITIVE (+) and NEGATIVE (-) to NEGATIVE (-).Use only equal voltage for boost starting. The use of a welder or higher voltage will damage the electrical system.
Engines without engine-to-frame ground straps can be damaged by electrical discharge.To prevent electrical discharge damage, check to make sure there is an engine-to-frame ground strap. For engines which have the alternator connected to an engine component, the ground strap must connect that component to the frame.Some engines have starter-to-frame ground straps. But, many of these starters are not electrically grounded to the engine. They have electrical insulation systems. For this reason, the starter-to-frame ground strap may not be an acceptable ground.Connect one end of cable to the POSITIVE (+) (ungrounded) terminal of the battery on the engine being started. Connect the other end to the POSITIVE (+) terminal of the power source.Connect one end of the second cable to the NEGATIVE (-) terminal of the power source. Connect the other end to the frame of the engine to be started.Turn the start switch on and start the engine.Disconnect the cable from the frame first. Disconnect the other end from the NEGATIVE (-) terminal of the power source. Disconnect the cable from the POSITIVE (+) terminal of the battery. Disconnect the other end from the POSITIVE (+) terminal of the power source.