Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
107492-0010
1074920010
NISSAN-DIESEL
1670029D10
1670029d10
Rating:
Service parts 107492-0010 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
16600-29D01
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
19.6{200}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
107492-0010
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
107492-0010
1074920010
NISSAN-DIESEL
1670029D10
1670029d10
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8250
Bosch type code
1 688 901 101
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
20.7
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
211
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131425-0520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407910-3
03*
Selector switch no.
02
PS/ACT control unit part no.
407980-2
24*
Digi switch no.
01
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
5.6
5.57
5.63
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.6
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
96.5
94.5
98.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.6+-0.0
5
PS407910-303*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407910-303*
mm
3.6+-0.0
5
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
7.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
510
510
510
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13
11.2
14.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
PS407980-224*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407980-224*
mm
5.5+-0.0
3
PS407910-303*
V
V1+0.05+
-0.01
PS407910-303*
mm
5.5+-0.0
3
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Refer to items regarding the pre-stroke actuator
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.6)
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
96.5
95.5
97.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
40
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
300
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.6+-0.0
5
PS407910-303*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407910-303*
mm
3.6+-0.0
5
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+2.25
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
111
107
115
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
40
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
300
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.6+-0.0
5
PS407910-303*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407910-303*
mm
3.6+-0.0
5
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R2-1
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69
65
73
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
PS407980-224*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407980-224*
mm
3.6+-0.0
5
PS407910-303*
V
2.25+-0.
01
PS407910-303*
mm
3.6+-0.0
5
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R2-1
Boost pressure
kPa
6.7
5.4
8
Boost pressure
mmHg
50
40
60
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R2(R1-1)
Boost pressure
kPa
26.7
26.7
26.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
200
200
200
0000001601
CU407980-224*
*
Actuator retarding type
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
2.5
2.45
2.55
Output voltage
V
2.83
2.82
2.84
Adjustment
*
_02
CU407980-224*
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
5.6
5.57
5.63
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_03
CU407980-224*
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
_04
CU407910-303*
*
Actuator retarding type
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
2.5
2.45
2.55
Output voltage
V
2.83
2.82
2.84
Adjustment
*
_05
CU407910-303*
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Pre-stroke
mm
5.6
5.57
5.63
Output voltage
V
1.2
1
1.4
Confirmation
*
Remarks
Output voltage V1
Output voltage V1
_06
CU407910-303*
*
Supply voltage
V
12
11.5
12.5
Ambient temperature
degC
23
18
28
Output voltage
V
3.05
3.05
Confirmation of operating range
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
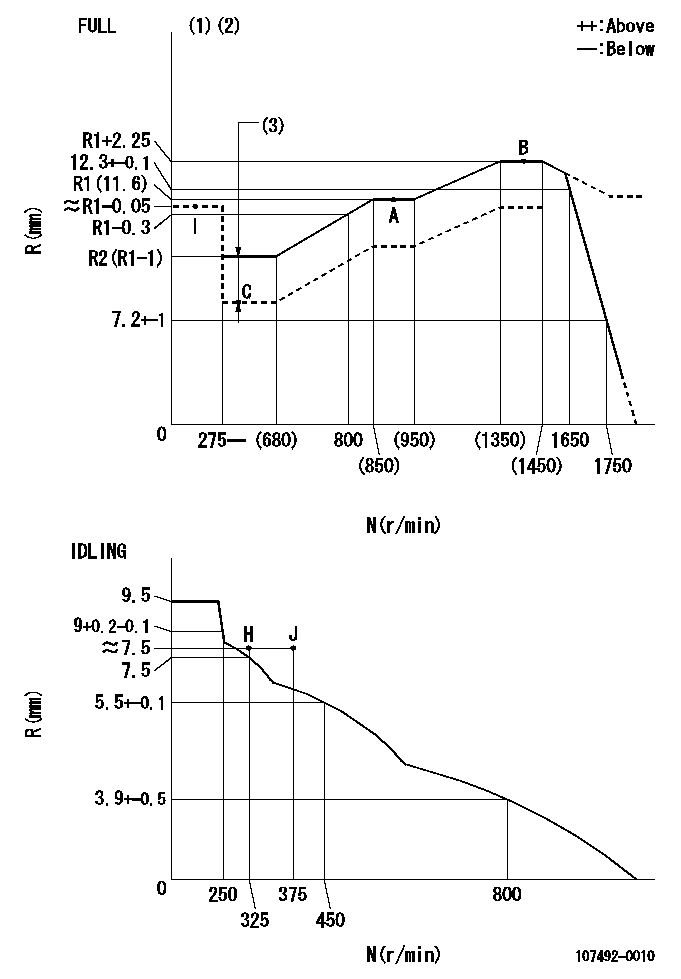
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=AF72 BCL=1+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=AF72 BCL=1+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=90.5mm
----------
a=22.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-3deg
----------
aa=90.5mm
----------
a=22.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
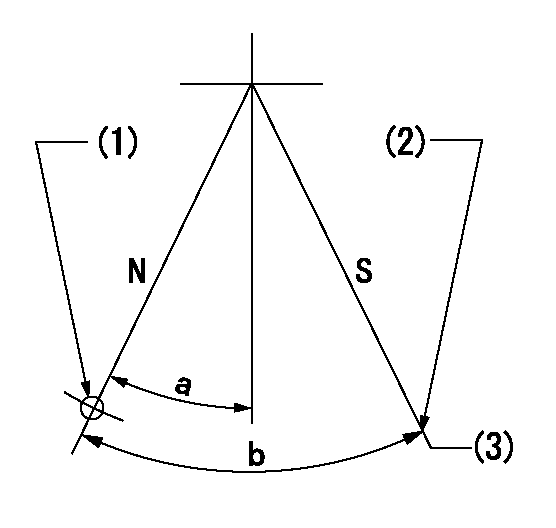
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
(3)Rack position = bb (speed = cc)
----------
aa=34mm bb=1.5+-0.3mm cc=0r/min
----------
a=22.5deg+-5deg b=45deg+-5deg
----------
aa=34mm bb=1.5+-0.3mm cc=0r/min
----------
a=22.5deg+-5deg b=45deg+-5deg
0000001301

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Positions of coupling's standard threaded holes at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)Pre-stroke: bb
----------
aa=3deg bb=5.6+-0.03mm
----------
a=(50deg)
----------
aa=3deg bb=5.6+-0.03mm
----------
a=(50deg)
0000001401
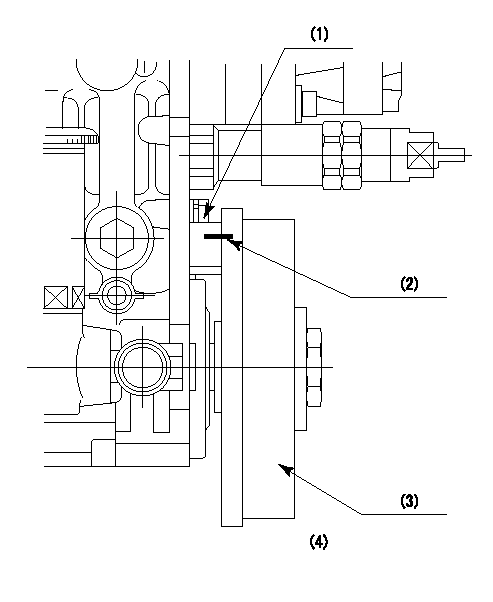
(1)Pointer
(2)Injection timing aligning mark
(3)Fly weight
(4)The actual shape and direction may be different from this illustration.
Operation sequence
1. Turn the prestroke actuator OFF.
2. Turn the camshaft as far as the No.1 cylinder's beginning of injection position.
3. Check that the pointer alignment mark of the injection pump and the alignment mark of the flywheel are matching.
4. If they are not matching, erase the alignment mark on the flywheel side, and stamp an alignment mark on the flywheel position that matches with the pointer side alignment mark.
5. Check again that the coupling's key groove position is in the No.1 cylinder's beginning of injection position.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001701
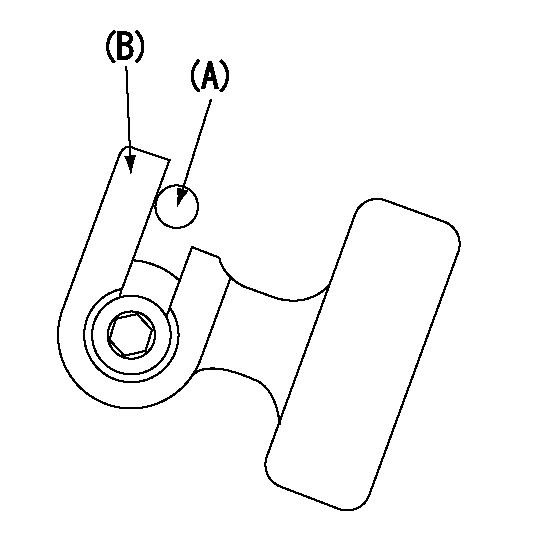
A : Stopper pin
B: Connector
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001801
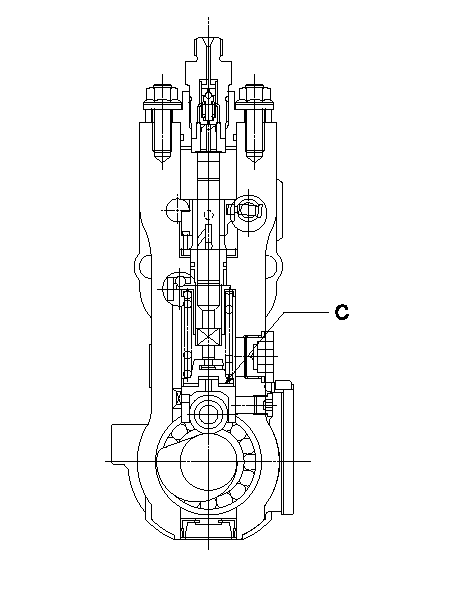
C:Shim
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001901
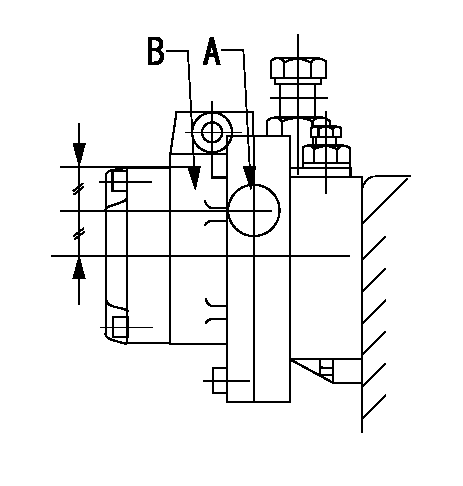
A:Sealing position
B:Pre-stroke actuator
1. When installing the pre-stroke actuator on the pump, first tighten the installation bolts loosely, then move the actuator fully counterclockwise (viewed from the drive side).
Temporary tightening torque: 1 - 1.5 N.m (0.1 - 0.15 kgf.m)
2. Move the actuator in the clockwise direction when viewed from the drive side, and adjust so that it becomes the adjustment point of the adjustment value. Then tighten it.
Tightening torque: 7^9 N.m (0.7^0.9 kgf.m)
3. After prestroke actuator installation adjustment, simultaneously stamp both the actuator side and housing side.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000002201 RACK SENSOR
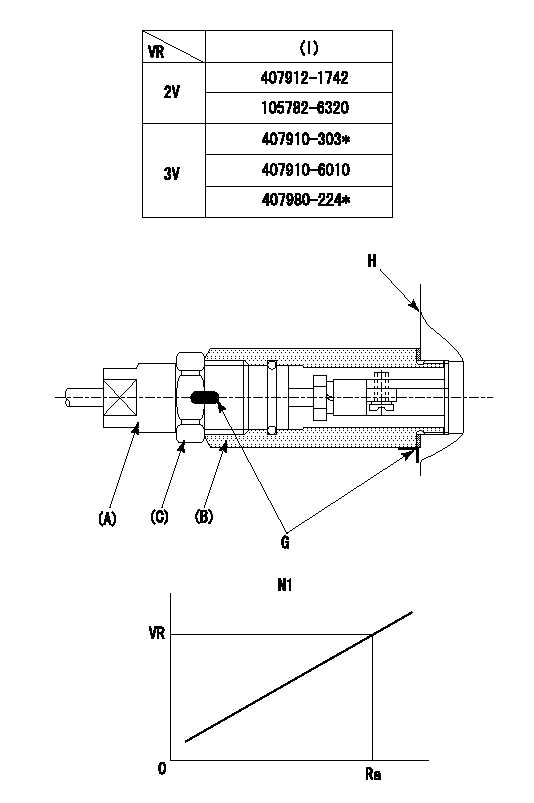
(VR) measurement voltage
(I) Part number of the control unit
(G) Apply red paint.
(H): End surface of the pump
1. Rack sensor adjustment (-0620)
(1)Fix the speed control lever at the full position
(2)Set the speed to N1 r/min.
(If the boost compensator is provided, apply boost pressure.)
(3)Adjust the bobbin (A) so that the rack sensor's output voltage is VR+-0.01.
(4)At that time, rack position must be Ra.
(5)Apply G at two places.
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the nut (F)
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the end surface of the pump (H)
----------
N1=1400r/min Ra=R1(11.6)+2.25mm
----------
----------
N1=1400r/min Ra=R1(11.6)+2.25mm
----------
0000002301 POTENTIO METER
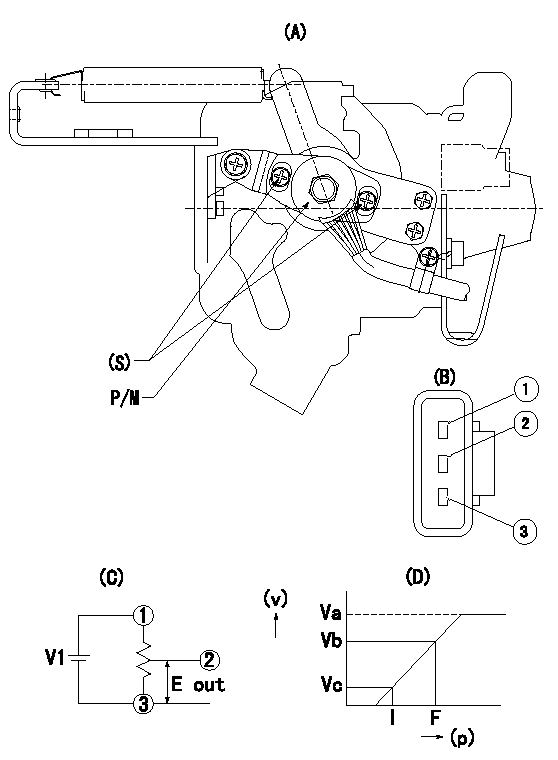
(A) : Governor plan view
(B): Potentiometer harness terminal
(C): Potentiometer connection diagram
(D) : Output voltage standard value
(S): Voltage
P/M: potentiometer
(v): output voltage (V)
(p): direction of potentiometer rotation
1. Adjustment procedures
(1)Apply DCV1 to potentiometer harness terminal (B) to obtain the specified output voltage.
(2)Fix the speed lever at the full side.
(3)Loosen the bolt (S), and move the potentiometer from left and right.
(4)Adjust so that the output voltage at full is within the standard values.
(5)Fix bolt (S).
(6)Repeatedly move the speed lever from the full side to the idle side.
(7)Check that it is within the standard values at full and idle.
----------
V1=5+-0.02V
----------
V1=5+-0.02V Va=(5)V Vb=4+-0.2V Vc=-
----------
V1=5+-0.02V
----------
V1=5+-0.02V Va=(5)V Vb=4+-0.2V Vc=-
Information:
To avoid possible engine damage or another immediate shutdown, the water temperature fault must be corrected before attempting to restart the engine.
Even though the starter motor circuit can now be engaged, there is no fuel flow to the engine. The fuel flow to the engine is stopped until the coolant temperature falls below the rating for the water temperature contactor switch (WTS). When the coolant temperature falls below the rating for the water temperature contactor switch (WTS), the contactor switch opens again. The fuel shutoff solenoid is de-energized when the switch reopens. This allows fuel flow to the engine. The engine can then be restarted.When the coolant temperature decreases below the rating of the water temperature contactor switch, the switch opens again. The time delay relay also causes a delay of 70 seconds before the fuel shutoff solenoid (FSOS) is de-energized. The engine can then be restarted.
Accidental engine starting can cause injury or death to personnel working on the equipment.To avoid accidental engine starting, disconnect the battery cable from the negative (-) battery terminal. Completely tape all metal surfaces of the disconnected battery cable end in order to prevent contact with other metal surfaces which could activate the engine electrical system.Place a Do Not Operate tag at the Start/Stop switch location to inform personnel that the equipment is being worked on.
2301A Electric Governor Control
The 2301A Electric Governor Control activates all of the components that are in the electric protection system. The components are activated in the same manner when the nonelectric governor is used. One difference exists in the main circuit. The fuel shutoff solenoid (FSOS) (line 34) is not used.When the electric governor control is used, the engine must run in a normal condition in order for the electric circuit to operate in the manner that is described below.
Current flows from terminal (TS-28) (line 27) and current flows from terminal (TS-31) (line 35), which are located on the terminal strip in the junction box.
Current from terminals (TS-28) (line 27) and (TS-31) (line 35) flows through the preregulator (PR) (line 38) or the fuse (F4) to the electric governor control.
When the engine flywheel is rotating, the current also flows through the electric governor actuator (EGA) (line 52). When a fault in the system causes the current to energize the slave relay (SR1), the following events occur in the electric circuit in order to stop the engine.
The slave relay (SR1) opens across the contacts (SR1-30) and (SR1-87a) (line 45). The relay closes across the contacts (SR1-30) and (SR1-87) (line 43).
When the circuit opens across contacts (SR1-30) and (SR1-87a), the current is stopped to the electric governor control.
Current to the electric governor actuator (EGA) is also stopped.
The mechanical spring load in the electric governor actuator (EGA) will now move the fuel control rod in order to stop fuel flow to the engine.Note: With the exception of the differences that are described in this section of the manual, all of the fault circuits in the electric protection system are identical