Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 618 567
9400618567
ZEXEL
106961-0101
1069610101
NISSAN-DIESEL
1679097012
1679097012

Rating:
Service parts 106961-0101 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
16600-97003
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
19.6{200}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106961-0101
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 618 567
9400618567
ZEXEL
106961-0101
1069610101
NISSAN-DIESEL
1679097012
1679097012
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106961-0101
9 400 618 567
1679097012 NISSAN-DIESEL
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
RD10 K 14CE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE10P PE
RD10 K 14CE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE10P PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle
105015-2780
Bosch type code
DLLA166S374NP6
Nozzle holder
105031-4190
Opening pressure
MPa
19.6
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
200
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-1050
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-1050
Overflow valve
132424-0620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
10-9-4-3
-6-5-8-7
-2-1
Pre-stroke
mm
3.65
3.6
3.7
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 10-9 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Cal 10-9 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 10-4 deg. 72 71.5 72.5
Cal 10-4 deg. 72 71.5 72.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 10-3 deg. 117 116.5 117.5
Cal 10-3 deg. 117 116.5 117.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 10-6 deg. 144 143.5 144.5
Cal 10-6 deg. 144 143.5 144.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 10-5 deg. 189 188.5 189.5
Cal 10-5 deg. 189 188.5 189.5
Difference between angles 6
Cal 10-8 deg. 216 215.5 216.5
Cal 10-8 deg. 216 215.5 216.5
Difference between angles 7
Cal 10-7 deg. 261 260.5 261.5
Cal 10-7 deg. 261 260.5 261.5
Difference between angles 8
Cal 10-2 deg. 288 287.5 288.5
Cal 10-2 deg. 288 287.5 288.5
Difference between angles 9
Cal 10-1 deg. 333 332.5 333.5
Cal 10-1 deg. 333 332.5 333.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.2
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
103
102
104
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
10.2
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
97
94
100
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
10.2
Pump speed
r/min
1150
1150
1150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
93.5
89.5
97.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
20
18
22
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
300+100
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
700
Advance angle
deg.
3
2.5
3.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1000
Advance angle
deg.
5.6
5.1
6.1
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1250+50
Advance angle
deg.
8
7.5
8.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
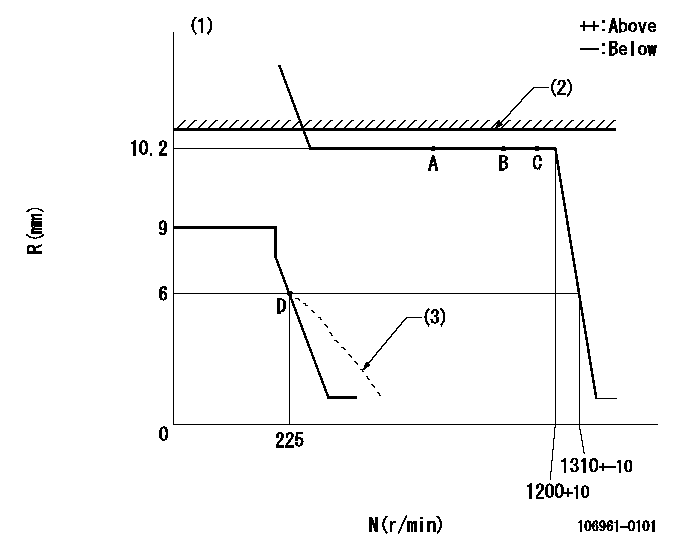
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)RACK LIMIT: RAL
(3)Beginning of damper spring operation: DL
----------
K=15 RAL=10.9+-0.1mm DL=6-0.5mm
----------
----------
K=15 RAL=10.9+-0.1mm DL=6-0.5mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
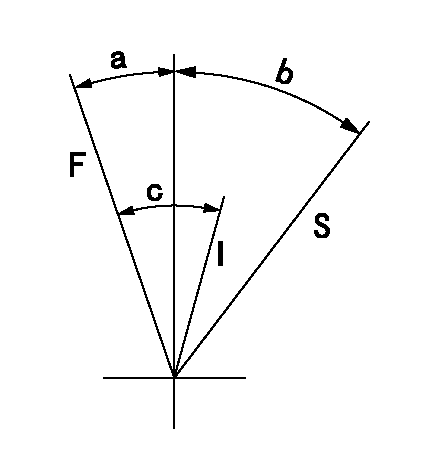
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
----------
----------
a=18deg+-5deg b=32deg+-3deg c=33deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=18deg+-5deg b=32deg+-3deg c=33deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
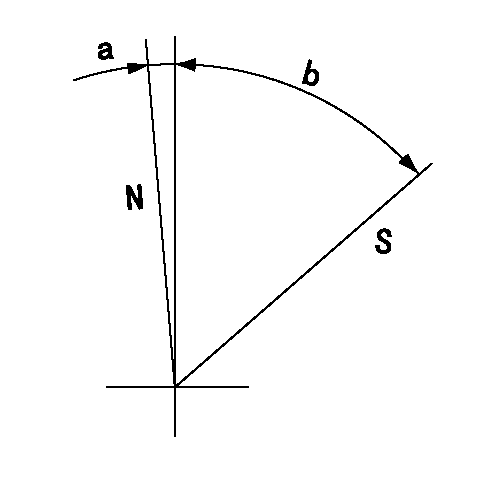
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=10.5deg+-5deg b=42.5deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=10.5deg+-5deg b=42.5deg+-5deg
Information:
Low power and engine response complaints can be caused by very different reasons and require different repairs, but are often the same complaint from the operator. A discussion with the operator is needed to help correctly diagnose whether to repair for low power or slow response. At times, full engine horsepower is available, but the operator still complains of low power. Repairs for low power would not provide a satisfactory result, and may consume many hours with expensive repairs. The actual complaint may be the engines ability to respond to a changing load or shifting gears.Normally, engine power can be measured to determine if it is within specifications. When troubleshooting a "low horsepower" complaint, if fuel consumption, timing, speeds, and manifold pressure are within specification, do not spend additional time looking for "low engine horsepower". If it is still believed that performance of the vehicle is below that expected, look for horsepower losses in the transmission, differential, clutches, parasitic loads (fan, air compressor, air conditioner, etc), tires, low fuel density or high temperatures, but not the engine.Owner/Operator Input
The following are some of the questions which should be asked before beginning any diagnosis or repair for an engine performance complaint. There Are No Hard And Fast Answers For These Questions. There are many different truck engine specifications and truck vehicle specifications which will provide acceptable results. There are also a variety of customer expectations which are acceptable. The answers to these questions will give you a better understanding and perspective on the complaint and may identify characteristics which will help pinpoint the cause of the complaint quickly. 1. Is there a particular operating condition when the complaint occurs?Low power and response complaints require different repairs. Complaints during shifting will be different from complaints of low power in certain speed ranges or in certain terrains. 2. What are the customer's expectations for fuel mileage and power and why does he have those expectations?Comparisons to other trucks on the road often have many unseen variables. If comparison to others is the basis for the complaint, you must insure that the comparison is valid. 3. What are the normal upshift and downshift rpm's?If the shift points are too high, find out why. If the driver is operating this way out of habit or because he is taught to drive that way, arrange for him to receive the Caterpillar driver training information. If his shift points are too high because of poor performance, you may be able to correct this in the engine. 4. What are the normal routes and loads for the truck?You should be looking for the amount of city versus highway driving, versus mountainous, heavy versus light loads, and cold climate versus warm climate. 5. Can the operator detect a misfire?This can lead you to a diagnosis of just one cylinder rather than an entire engine system. 6. Does the engine smoke excessively, and if so, under what conditions?Excessive smoke can give indications about engine settings and engine internal conditions.
The following are some of the questions which should be asked before beginning any diagnosis or repair for an engine performance complaint. There Are No Hard And Fast Answers For These Questions. There are many different truck engine specifications and truck vehicle specifications which will provide acceptable results. There are also a variety of customer expectations which are acceptable. The answers to these questions will give you a better understanding and perspective on the complaint and may identify characteristics which will help pinpoint the cause of the complaint quickly. 1. Is there a particular operating condition when the complaint occurs?Low power and response complaints require different repairs. Complaints during shifting will be different from complaints of low power in certain speed ranges or in certain terrains. 2. What are the customer's expectations for fuel mileage and power and why does he have those expectations?Comparisons to other trucks on the road often have many unseen variables. If comparison to others is the basis for the complaint, you must insure that the comparison is valid. 3. What are the normal upshift and downshift rpm's?If the shift points are too high, find out why. If the driver is operating this way out of habit or because he is taught to drive that way, arrange for him to receive the Caterpillar driver training information. If his shift points are too high because of poor performance, you may be able to correct this in the engine. 4. What are the normal routes and loads for the truck?You should be looking for the amount of city versus highway driving, versus mountainous, heavy versus light loads, and cold climate versus warm climate. 5. Can the operator detect a misfire?This can lead you to a diagnosis of just one cylinder rather than an entire engine system. 6. Does the engine smoke excessively, and if so, under what conditions?Excessive smoke can give indications about engine settings and engine internal conditions.
Have questions with 106961-0101?
Group cross 106961-0101 ZEXEL
Nissan-Diesel
106961-0101
9 400 618 567
1679097012
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
RD10
RD10
