Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106873-3151
1068733151
HINO
220007980B
220007980b
Rating:
Service parts 106873-3151 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
23600-2480E
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
14.7{150}/24.5{250}
14.
NOZZLE
Include in #1:
106873-3151
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106873-3151
1068733151
HINO
220007980B
220007980b
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-0820
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-8-6-2-
7-5-4-3
Pre-stroke
mm
4.5
4.44
4.5
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-8 deg. 45 44.75 45.25
Cal 1-8 deg. 45 44.75 45.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-6 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 135 134.75 135.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 135 134.75 135.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-7 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-7 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.75 225.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.75 225.25
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-4 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Difference between angles 7
Cal 1-3 deg. 315 314.75 315.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 315 314.75 315.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.2
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
157.6
155.6
159.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
9.1
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
160.7
157.7
163.7
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
9.25+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
143.7
139.7
147.7
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
8.5
Pump speed
r/min
1200
1200
1200
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
129
126
132
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
F
Rack position
3.9+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12.6
9.6
15.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
G
Rack position
9.85+-0.
1
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
178.5
174.5
182.5
Fixing the lever
*
Remarks
Startup boost setting
Startup boost setting
Injection quantity adjustment_07
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
188
188
208
Fixing the lever
*
Remarks
After startup boost setting
After startup boost setting
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Load
1/4
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
550
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Load
1/4
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
700--
Advance angle
deg.
1
0.7
1.3
Load
4/4
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
900+50
Advance angle
deg.
1
0.7
1.3
Load
3/4
Timer adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1100-50
Advance angle
deg.
4.75
4.45
5.05
Load
4/4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
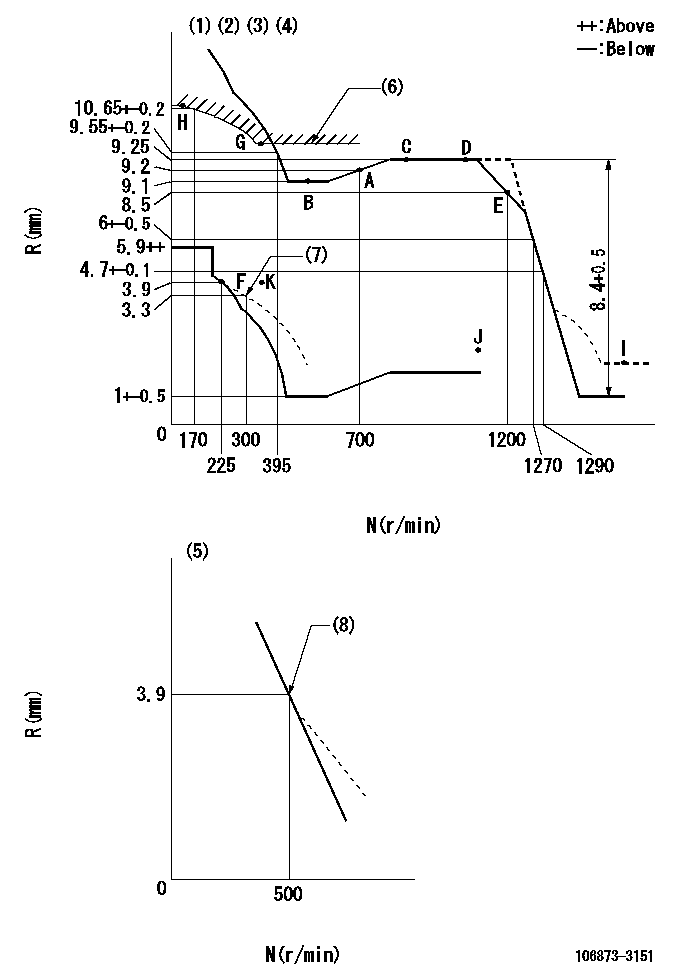
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Lever ratio: RT
(2)Target shim dimension: TH
(3)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(4)Set idle at point K (N = N1, R = R2) and confirm that the injection quantity does not exceed Q1 at point J (N = N2).
(5)Variable speed specification: idling adjustment
(6)Excess fuel setting for starting: SXL
(7)Damper spring setting
(8)Main spring setting
----------
RT=0.8 TH=2.9mm N1=300r/min R2=3.9mm N2=1150r/min Q1=3mm3/ST SXL=9.85+-0.1mm
----------
----------
RT=0.8 TH=2.9mm N1=300r/min R2=3.9mm N2=1150r/min Q1=3mm3/ST SXL=9.85+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
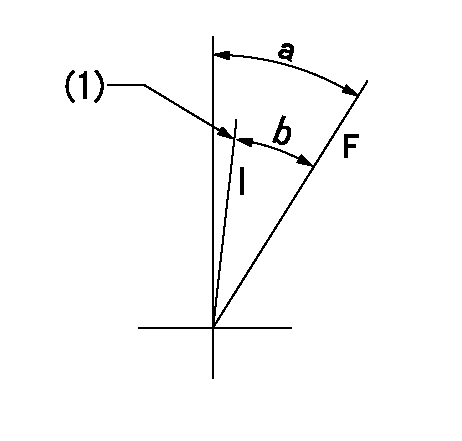
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=15.5deg+-5deg b=(14deg)+-5deg
----------
----------
a=15.5deg+-5deg b=(14deg)+-5deg
0000000901

F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=39mm
----------
a=39deg+-5deg b=43.5deg+-3deg
----------
aa=39mm
----------
a=39deg+-5deg b=43.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
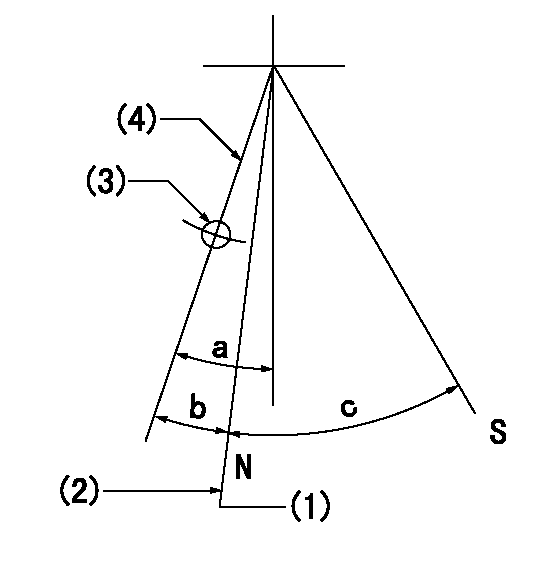
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa (at delivery), set before governor adjustment
(2)Set the stopper bolt (apply red paint).
(3)Use the pin at R = bb
(4)Lever free
----------
aa=12+-0.1mm bb=37mm
----------
a=(9deg)+-5deg b=9deg+-5deg c=35deg+-5deg
----------
aa=12+-0.1mm bb=37mm
----------
a=(9deg)+-5deg b=9deg+-5deg c=35deg+-5deg
Timing setting
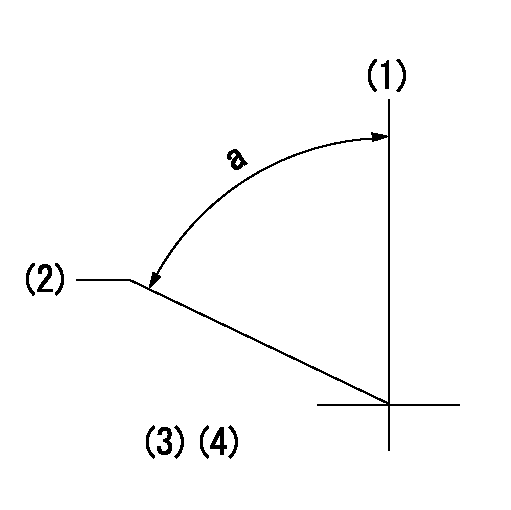
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(80deg)
----------
----------
a=(80deg)
Information:
Exhaust brakes should not be used as a primary or service brake.
Auxiliary engine braking devices are approved for use on the 3406B Engine.Compression Brake
Operation (Jacobs Brake or Pacific Brake)
The Jacobs Engine Brake should not be used as a primary or service brake. Do not allow the engine to exceed 2300 rpm. However, engines equipped with a Jacobs Engine Brake should not normally be operated above 2100 rpm.
The Jacobs Engine Brake is an engine attachment that converts a diesel engine into an air compressor. Its function is to slow the vehicle and reduce brake wear.Operating Controls-Compression Brake
The Jacobs Engine Brake controls may include a dash mounted module or an ON/OFF switch and a three position switch with "Lo," "Med" and "Hi" depending on how many cylinders of braking desired.On some applications a multiposition switch is used to provide variable retarding capability. Operators should become familiar with the controls used on their vehicles. Refer to the OEM vehicle manual for the type of operating controls that your vehicle is equipped with.Since the Jacobs Engine Brake is most effective at rated engine rpm, gear selection is very important. Gearing down the vehicle, within the limits of rated engine rpm, makes the engine brake a more effective retarder. Maximum retarding occurs at higher engine rpm.For information on adjustment to Jacobs Brake slave piston lash, refer to PM Level 2-Engine Valve Lash. Refer to Jacobs Brake Troubleshooting Manual, Form SENR4251 for information regarding this auxiliary braking system.There are differences in exhaust braking devices from those with little or no leakage when activated to those with a great deal of leakage.Sliding Gate Type (Williams Blue Ox)
This type of exhaust brake allows minimal leakage and must have a relief orifice to limit the maximum exhaust manifold back pressure to 50 psi (345 kPa) at maximum engine braking rpm. Flapper Type (Pacific)
With this type of exhaust brake, there is usually leakage around the movable plate. To obtain 50 psi (345 kPa) or 70 psi (485 kPa) performance level braking, a small hole would likely be required. The maximum permissible exhaust back pressure at maximum engine braking rpm is measured at the 1/4 NPT hole in the exhaust manifold below the turbocharger.Refer to the April, 1988 "Truck Engine Application and Installation Guide," Form LEBT8121 for more information.Exhaust Brake Option-70 psi (485 kPa) (flapper or sliding gate type)
This auxiliary brake has been approved for use with 3406B Truck engines, but because of the higher exhaust back pressure of 70 psi (485 kPa), larger exhaust valve springs and associated parts must be used when installed.The recommended orifice size for this braking device is .688 in. (17.48 mm), and it applies to a maximum braking rpm of 2200 rpm. A smaller orifice and/or higher operating speed will cause excessive back pressure and may shorten valve train life.
Due to interference with the larger valve rotators, the 70 psi (485 kPa) type exhaust brake cannot be used in addition to compression type brakes to obtain additional braking capacity.
Refer to the Service Manual