Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106873-2060
1068732060

Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106873-2060
1068732060
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106873-2060
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
132424-0620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-7-3-
4-5-6-8
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.75
4.85
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Difference between angles 7
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
10
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
129
125.1
132.9
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6.1+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
20
17
23
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(10)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
129
128
130
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1(10)
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
132
126
138
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
160
140
180
Fixing the lever
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
1
Load
3/4
Remarks
Q=121 (mm3/st) / N=700(r/min)
Q=121 (mm3/st) / N=700(r/min)
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Load
4/4
Remarks
Q=155 (mm3/st) / N=700 (r/min), end of advance
Q=155 (mm3/st) / N=700 (r/min), end of advance
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment

N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Damper spring setting: DL
(2)Excess fuel setting for starting: SXL (N = N1)
(3)Rack difference between N = N2 and N = N3
----------
DL=4.3-0.2mm SXL=10.8+-0.1mm N1=330r/min N2=700r/min N3=900r/min
----------
----------
DL=4.3-0.2mm SXL=10.8+-0.1mm N1=330r/min N2=700r/min N3=900r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
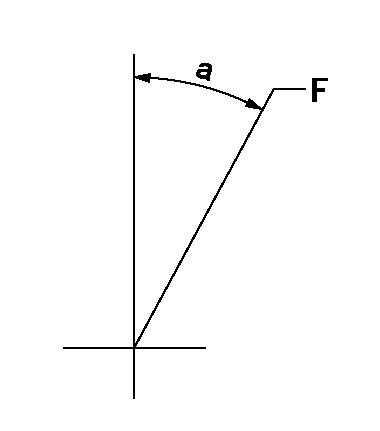
F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=18deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=18deg+-5deg
0000000901
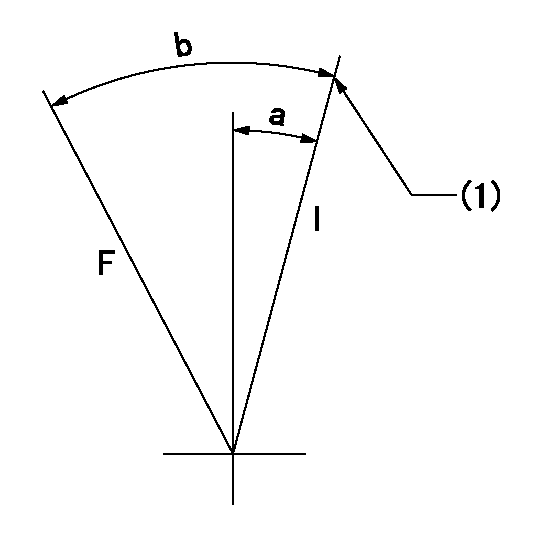
F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=28deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=28deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
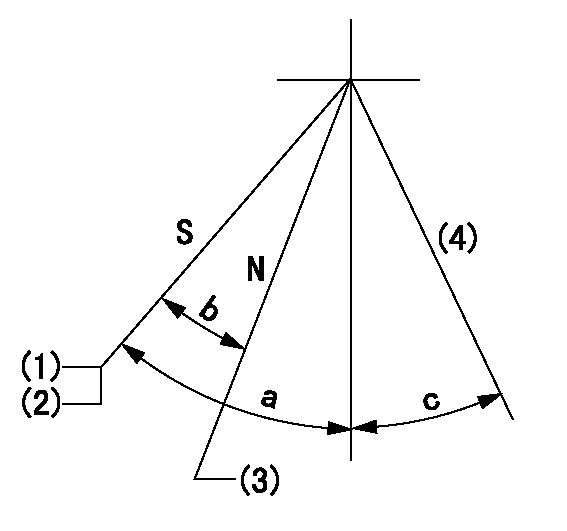
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
(3)Rack position bb
(4)Free (at shipping)
----------
aa=4-0.5mm bb=11.7mm
----------
a=43deg+7deg-5deg b=21.5deg+-5deg c=10.5deg+-5deg
----------
aa=4-0.5mm bb=11.7mm
----------
a=43deg+7deg-5deg b=21.5deg+-5deg c=10.5deg+-5deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=325+-5r/min Ra=5.6mm
----------
----------
N1=325+-5r/min Ra=5.6mm
----------
Timing setting
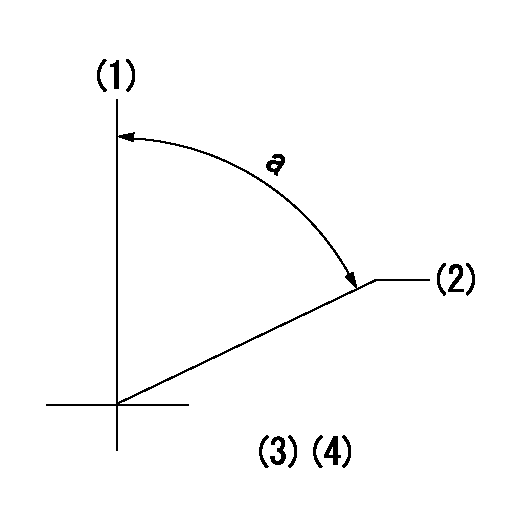
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
Information:
The problems in this section are problems that do come about and are normally called "low power". These problems are not necessarily more common than engine problems, but they are possible problems which you need to read and check before an engine is disassembled.Read all of the items but make sure the first three are checked completely before making any engine test. Possible Causes/Corrections Tachometer ErrorTo check, connect a tachometer of known accuracy to the engine. Run the engine and make a comparison of the readings of the vehicle and test tachometers. If vehicle tachometer is defective, make repairs as necessary or install a new tachometer. Engine Operated At High AltitudeLess oxygen at higher altitudes causes the engine horsepower to go down. There is no effect on the horsepower of the engine for the first 2280 m (7500 ft) above sea level of operation. Brakes Do Not Completely ReleaseCheck the brakes by feeling all the brake drums. If the brakes of a wheel do not completely release, the brake drum for that wheel will be hotter than the brake drums for the other wheels. With the truck lifted with a jack, the wheels must have free rotation when turned by hand. Extra Engine Driven EquipmentAir compressors, hydraulic pumps, alternator, and other engine driven equipment that has damage, or that was not installed correctly, or that is not in correct adjustment, can take more horsepower to drive than expected. If necessary, disconnect the equipment and test the engine. Speedometer ErrorA defective speedometer does not give the correct speed or the correct indication of fuel consumption. An indication of low speed can cause the operator to feel that he has a power problem. Speeds Too HighThe need for more horsepower is easy to see as the speed of the vehicle is increased. This is especially true if the front of the vehicle has a large surface area. Application personnel can give you the horsepower necessary for different vehicle designs at different speeds. Overload On VehicleApplication personnel can give you the horsepower needs for different vehicles. High Moving ResistanceSoft ground conditions cause a need for more horsepower. To see if the problem is the engine, test the vehicle on a surface known to be good, or test on a chassis dynamometer. High Wind ResistanceThe horsepower needs for a truck can be divided into two parts. Part of the horsepower is used to move the vehicle and part is used to get through the resistance of the wind. The horsepower necessary to get through the resistance of the wind will increase as the vehicle is used at higher speeds. Vehicles with a large front area have a higher wind resistance and take more horsepower than those with a small front area. Some types of trucks, for example those used for the transportation of automobiles and or boats have high wind resistance even if the front area is small. Moving against the wind has the same effect on wind resistance as does higher
Have questions with 106873-2060?
Group cross 106873-2060 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
106873-2060
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY