Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106871-9340
1068719340
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106871-9340
1068719340
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-4620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-7-3-
4-5-6-8
Pre-stroke
mm
3.4
3.35
3.45
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Difference between angles 7
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.8
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
161
156.2
165.8
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
5.9+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
17
14.4
19.6
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.8)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
161
160
162
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
127
127
Boost pressure
mmHg
950
950
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+1
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
183
179
187
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
127
127
Boost pressure
mmHg
950
950
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
115
75
155
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R1-2.8
Boost pressure
kPa
5.3
4
6.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
40
30
50
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R1(11.8)
Boost pressure
kPa
88
81.3
94.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
660
610
710
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
750--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
700
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
3
2.5
3.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
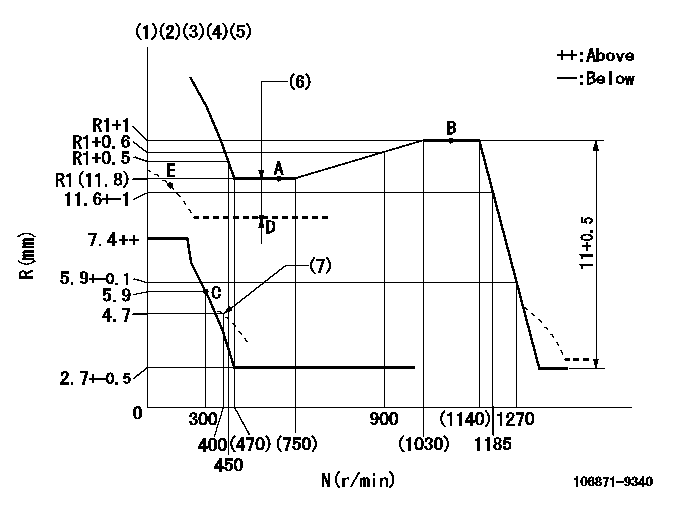
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Lever ratio: RT
(2)Target shim dimension: TH
(3)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(4)Microswitch not operating at delivery.
(5)Boost compensator cancel stroke: BSL
(6)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(7)Damper spring setting
----------
RT=1 TH=3.2mm BSL=2.8mm BCL=2.8+-0.1mm
----------
----------
RT=1 TH=3.2mm BSL=2.8mm BCL=2.8+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
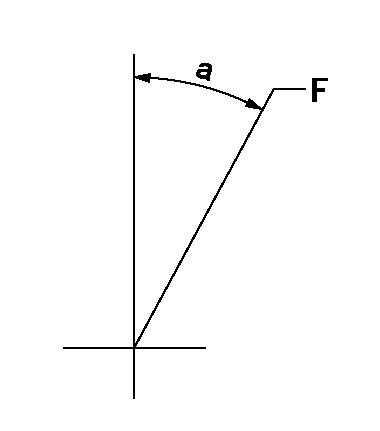
F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=(16.5deg)+-5deg
----------
----------
a=(16.5deg)+-5deg
0000000901

F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=33.5deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=33.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
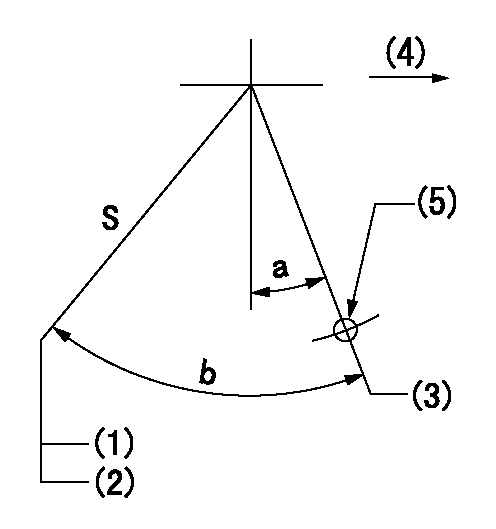
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
(3)Free (at delivery)
(4)Drive side
(5)Use the hole at R = bb
----------
aa=3.7-0.5mm bb=36mm
----------
a=10.5deg+-5deg b=57deg+7deg-5deg
----------
aa=3.7-0.5mm bb=36mm
----------
a=10.5deg+-5deg b=57deg+7deg-5deg
0000001501 GOVERNOR TORQUE CONTROL

Dr:Torque control stroke
(A): Without torque control spring capsule
1. Adjustment procedures
(1)Procedure is the same as that for the RFD (former type), except that the positive torque control stroke must be determined at the full lever setting.
2. Procedures for adjustment
(1)Remove the torque control spring capsule.
(2)Operate the pump at approximately N1. (End of idling spring operation < N1.)
(3)Tilt the lever to the full side.
(4)Set so that R = RF.
(5)Increase the speed by pushing in the screw (attached to the bracket on the rear of the tension lever) through the adjusting window.
(6)Adjust so that the torque control stroke Dr1 can be obtained.
(7)Align N2 and N3 with the torque control spring capsule.
3. Final confirmation
(1)After final confirmation, temporarily set the load lever to N = N1, R = idling position.
(2)From this condition, increase speed to N = N4.
(3)Confirm that positive torque control stroke is Dr2.
----------
N1=500r/min N2=(750)r/min N3=(1030)r/min N4=1100r/min RF=11.8mm Dr1=1mm Dr2=0+0.3mm
----------
----------
N1=500r/min N2=(750)r/min N3=(1030)r/min N4=1100r/min RF=11.8mm Dr1=1mm Dr2=0+0.3mm
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
Information:
Possible Causes/Corrections
Air or Water in Fuel System/With air in the fuel system, the engine will normally be difficult to start, run rough and release a large amount of white smoke. If the engine will not start, loosen a fuel injection line nut and crank the engine until fuel comes out. Tighten the fuel line nut. Start the engine. If the engine does not run smooth or releases a large amount of white smoke, loosen the fuel line nuts one at a time until the fuel that comes out is free of air. Tighten the fuel lines nuts. If the air can not be removed in this way, put 35 kPa (5 psi) of air pressure to the fuel tank.
Do not use more than 55 kPa (8 psi) of air pressure in the fuel tank or damage to the tank may result.
Check for leaks at the connections between the fuel tank and the fuel transfer pump. If leaks are found, tighten the connections or replace the lines. If there are no visual leaks, remove the fuel supply line from the tank and connect it to an outside fuel supply. If this corrects the problem, the suction line (standpipe) inside the fuel tank has a leak.Water in the fuel can cause rough running and possible fuel system damage. Valve Adjustment Not Correct/Check and make necessary adjustments as in Testing and Adjusting section of this Service Manual. Intake valve clearance is 0.38 mm (.015 in.) and exhaust valve clearance is 0.64 mm (.025 in.). Also check for a bent or broken push rod. Bad Fuel Nozzle(s)/Find a bad nozzle by running engine at the rpm where it runs rough. Loosen the fuel line nut enough to stop fuel supply to that cylinder. Each cylinder must be checked this way. If a cylinder is found where loosening of the nut makes no difference in the rough running, test the nozzle for that cylinder. To test a nozzle, remove the nozzle from the engine and test as in Testing and Adjusting section of this Service Manual. Fuel Leakage From Fuel Injection Line Nut/Tighten nut to 40 7 N m (30 5 lb. ft.). Again check for leakage. Bad Fuel Injection Pump/An injection pump can have a good fuel flow coming from it but cause rough running because of slow timing that is caused by wear on the bottom end of the plunger. See the Testing and Adjusting section in this Service Manual for the correct specifications and procedure to check the plungers and lifters.Fuel pumps which are severely scored from debris can cause rough running, but fuel dilution usually occurs before horsepower is affected.Low installation torque on the fuel pump retaining nut can cause misfire, rough running and low power. Fuel Has a High "Cloud Point"/In cold weather operation this condition should be checked first. The fuel "cloud point" is the temperature at which wax begins to form in the fuel. If the atmospheric temperature is lower than the "cloud point"
Air or Water in Fuel System/With air in the fuel system, the engine will normally be difficult to start, run rough and release a large amount of white smoke. If the engine will not start, loosen a fuel injection line nut and crank the engine until fuel comes out. Tighten the fuel line nut. Start the engine. If the engine does not run smooth or releases a large amount of white smoke, loosen the fuel line nuts one at a time until the fuel that comes out is free of air. Tighten the fuel lines nuts. If the air can not be removed in this way, put 35 kPa (5 psi) of air pressure to the fuel tank.
Do not use more than 55 kPa (8 psi) of air pressure in the fuel tank or damage to the tank may result.
Check for leaks at the connections between the fuel tank and the fuel transfer pump. If leaks are found, tighten the connections or replace the lines. If there are no visual leaks, remove the fuel supply line from the tank and connect it to an outside fuel supply. If this corrects the problem, the suction line (standpipe) inside the fuel tank has a leak.Water in the fuel can cause rough running and possible fuel system damage. Valve Adjustment Not Correct/Check and make necessary adjustments as in Testing and Adjusting section of this Service Manual. Intake valve clearance is 0.38 mm (.015 in.) and exhaust valve clearance is 0.64 mm (.025 in.). Also check for a bent or broken push rod. Bad Fuel Nozzle(s)/Find a bad nozzle by running engine at the rpm where it runs rough. Loosen the fuel line nut enough to stop fuel supply to that cylinder. Each cylinder must be checked this way. If a cylinder is found where loosening of the nut makes no difference in the rough running, test the nozzle for that cylinder. To test a nozzle, remove the nozzle from the engine and test as in Testing and Adjusting section of this Service Manual. Fuel Leakage From Fuel Injection Line Nut/Tighten nut to 40 7 N m (30 5 lb. ft.). Again check for leakage. Bad Fuel Injection Pump/An injection pump can have a good fuel flow coming from it but cause rough running because of slow timing that is caused by wear on the bottom end of the plunger. See the Testing and Adjusting section in this Service Manual for the correct specifications and procedure to check the plungers and lifters.Fuel pumps which are severely scored from debris can cause rough running, but fuel dilution usually occurs before horsepower is affected.Low installation torque on the fuel pump retaining nut can cause misfire, rough running and low power. Fuel Has a High "Cloud Point"/In cold weather operation this condition should be checked first. The fuel "cloud point" is the temperature at which wax begins to form in the fuel. If the atmospheric temperature is lower than the "cloud point"