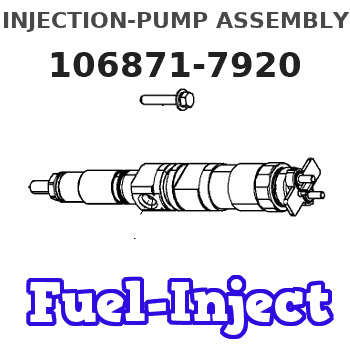
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 612 637
9400612637
ZEXEL
106871-7920
1068717920
MITSUBISHI
ME098573
me098573
Rating:
Service parts 106871-7920 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME066034
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106871-7920
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 612 637
9400612637
ZEXEL
106871-7920
1068717920
MITSUBISHI
ME098573
me098573
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106871-7920
9 400 612 637
ME098573 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
8DC9TC K 14CD INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE8P PE
8DC9TC K 14CD INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE8P PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-4620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-7-3-
4-5-6-8
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.75
4.85
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Difference between angles 7
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.9
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
151.8
148.8
154.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
61.3
61.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
460
460
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
5.6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15.5
12.9
18.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R1-0.7
Boost pressure
kPa
34.7
33.4
36
Boost pressure
mmHg
260
250
270
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R1(10.9)
Boost pressure
kPa
48
41.3
54.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
360
310
410
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
950--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
1
0.5
1.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
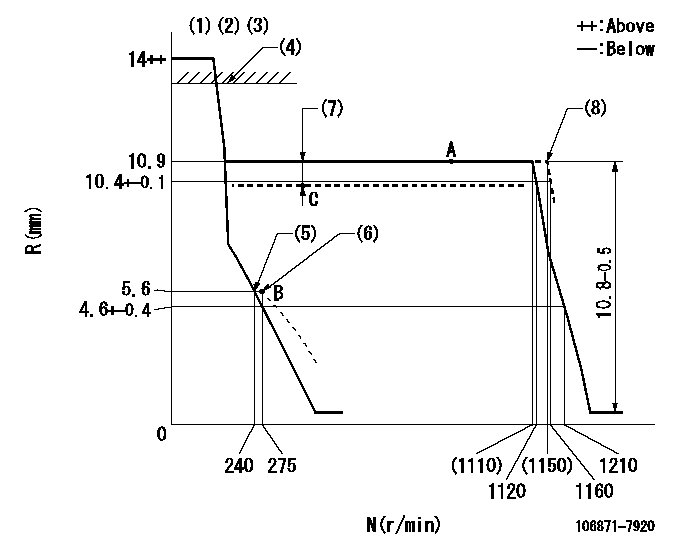
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Torque spring does not operate.
(4)Excess fuel lever setting: EXL or above (at boost pressure 0)
(5)Main spring setting
(6)Set idle sub-spring
(7)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(8)At delivery
----------
K=12 EXL=13mm BCL=0.7+-0.1mm
----------
----------
K=12 EXL=13mm BCL=0.7+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
(2)At delivery
----------
----------
a=7deg+-5deg b=27deg+-5deg c=(2deg)
----------
----------
a=7deg+-5deg b=27deg+-5deg c=(2deg)
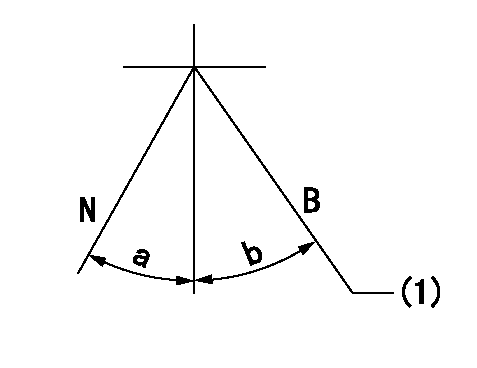
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Normal
----------
----------
a=19deg+-5deg b=46deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=19deg+-5deg b=46deg+-5deg
0000001101
N:Normal
B:When boosted
(1)Rack position = at least aa (speed = bb; at boost pressure 0)
----------
aa=13mm bb=0r/min
----------
a=(10deg) b=(15deg)
----------
aa=13mm bb=0r/min
----------
a=(10deg) b=(15deg)
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
Information:
This troubleshooting guide, when followed exactly as shown, can be an aid for the serviceman to find the cause of existing problems. The information from the measurements will also show proof if there is any basis for the complaint.Be sure to get a good description of the problem from the operator and/or the person who owns the vehicle. What they tell you about the problem can save you time and make the repair job faster and easier.Low Power And High Fuel Consumption Problems
The troubleshooting charts that follow provide a definite sequence to be l followed for a logical, one by one elimination of many variables. The encircled numbers do not designate steps, but are references to detailed instructions that can not be shown on the chart. Always read the written material that corresponds with the encircled numbers on the charts.The PRIMARY ENGINE TESTS consist of quick and easy procedures that could identify the problem with a minimum loss of time. Always make these tests before starting the more involved troubleshooting charts.The necessary instruments to check each problem in sequence are shown on the chart. If the correct instrument is not available for the test, do not continue. The vehicle must be sent to a shop where the necessary tools are available.Whenever a problem is found and corrected, always run the test again to that point to be sure there is not a combination of problems. When the problem has been corrected and the complaint resolved, stop the test. Do not continue through the complete procedure just because it is there.When investigating possible causes, follow the letter sequence shown. Possible causes are arranged in order from more probable/easiest to check to less probable/more complex to check. OTHER PROBLEMS: VEHICLE OR VEHICLE OPERATION, MISFIRING AND RUNNING ROUGH, TOO MUCH EXHAUST SMOKE, DIFFICULT STARTING, COOLING SYSTEM, LOSS OF COOLANT, OR FUEL IN CRANKCASE OIL.The probable causes of a problem are given in the order they most commonly take place. Check the probable causes in the same order that they are given. When troubleshooting, use the section on recommended procedures which follow each chart to check and make the necessary corrections for each probable cause.Engine Vibration Problem
The troubleshooting chart provides a definite sequence to be followed for a logical procedure to determine the frequency and amplitude of vibration so that the source of the vibration can be located and corrected.
The troubleshooting charts that follow provide a definite sequence to be l followed for a logical, one by one elimination of many variables. The encircled numbers do not designate steps, but are references to detailed instructions that can not be shown on the chart. Always read the written material that corresponds with the encircled numbers on the charts.The PRIMARY ENGINE TESTS consist of quick and easy procedures that could identify the problem with a minimum loss of time. Always make these tests before starting the more involved troubleshooting charts.The necessary instruments to check each problem in sequence are shown on the chart. If the correct instrument is not available for the test, do not continue. The vehicle must be sent to a shop where the necessary tools are available.Whenever a problem is found and corrected, always run the test again to that point to be sure there is not a combination of problems. When the problem has been corrected and the complaint resolved, stop the test. Do not continue through the complete procedure just because it is there.When investigating possible causes, follow the letter sequence shown. Possible causes are arranged in order from more probable/easiest to check to less probable/more complex to check. OTHER PROBLEMS: VEHICLE OR VEHICLE OPERATION, MISFIRING AND RUNNING ROUGH, TOO MUCH EXHAUST SMOKE, DIFFICULT STARTING, COOLING SYSTEM, LOSS OF COOLANT, OR FUEL IN CRANKCASE OIL.The probable causes of a problem are given in the order they most commonly take place. Check the probable causes in the same order that they are given. When troubleshooting, use the section on recommended procedures which follow each chart to check and make the necessary corrections for each probable cause.Engine Vibration Problem
The troubleshooting chart provides a definite sequence to be followed for a logical procedure to determine the frequency and amplitude of vibration so that the source of the vibration can be located and corrected.
Have questions with 106871-7920?
Group cross 106871-7920 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
106871-7920
9 400 612 637
ME098573
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
8DC9TC
8DC9TC
