Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 618 120
9400618120
ZEXEL
106871-3881
1068713881
HINO
220004871A
220004871a

Rating:
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 618 120
9400618120
ZEXEL
106871-3881
1068713881
HINO
220004871A
220004871a
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106871-3881
9 400 618 120
220004871A HINO
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
EF750 K
EF750 K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-0820
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-8-6-2-
7-5-4-3
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.74
4.8
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-8 deg. 45 44.75 45.25
Cal 1-8 deg. 45 44.75 45.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-6 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 135 134.75 135.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 135 134.75 135.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-7 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-7 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.75 225.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.75 225.25
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-4 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Difference between angles 7
Cal 1-3 deg. 315 314.75 315.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 315 314.75 315.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
10.7
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
123
121
125
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
8.1+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12.6
9.6
15.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(10.7)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
123
121
125
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.5
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
141
135
147
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
(R1+0.2)
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
137
131
143
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
R2(10.6)
Pump speed
r/min
1175
1175
1175
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
126
121
131
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_07
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
13.3+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
155
150
160
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Injection quantity adjustment_08
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
R1(10.7)
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
124
118
130
Fixing the lever
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
(860)
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
4.75
4.45
5.05
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
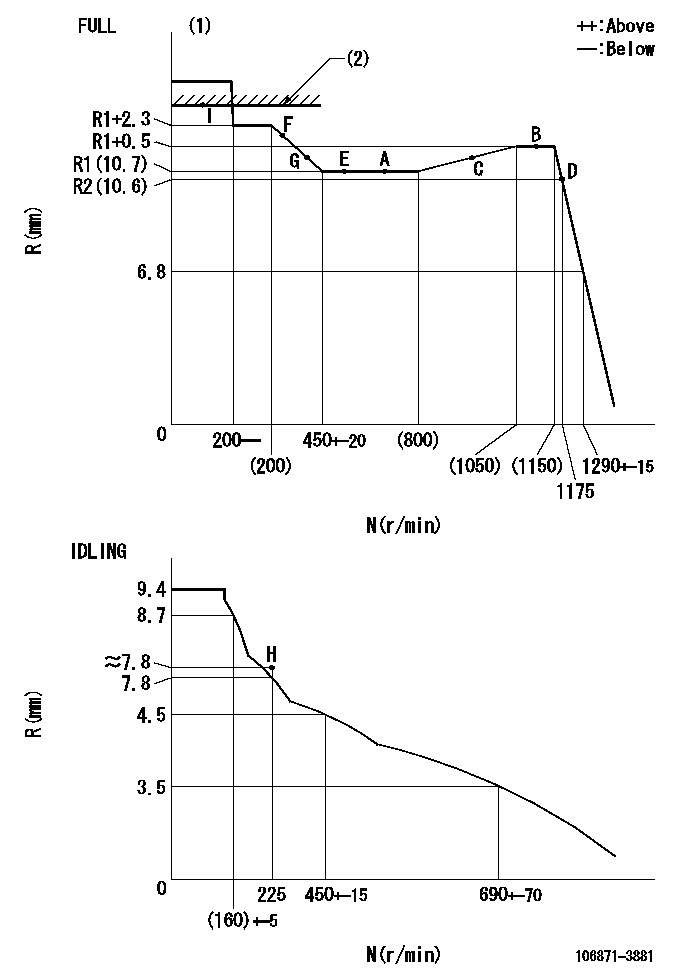
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=B75
----------
----------
T1=B75
----------
Speed control lever angle
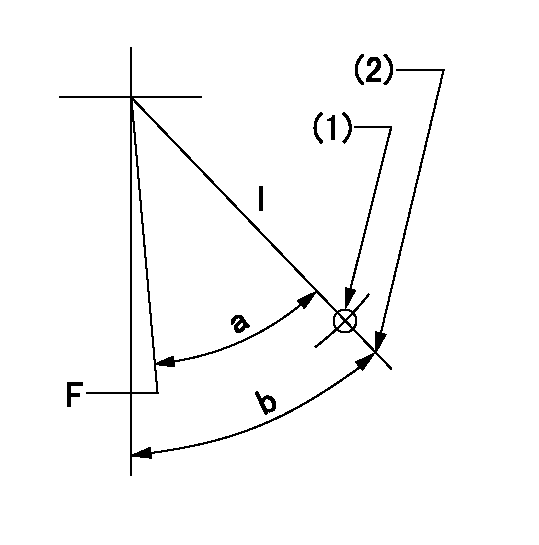
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=38mm
----------
a=(36deg)+-3deg b=38deg+-5deg
----------
aa=38mm
----------
a=(36deg)+-3deg b=38deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
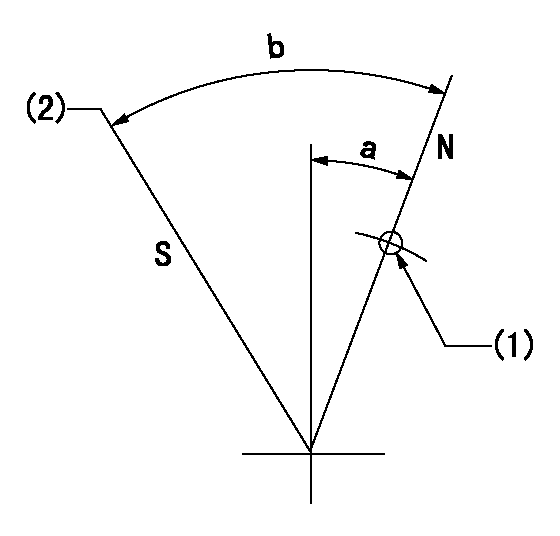
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Set the stopper screw at rack position = bb
----------
aa=45mm bb=4mm
----------
a=19deg+-5deg b=(37.5deg)+-5deg
----------
aa=45mm bb=4mm
----------
a=19deg+-5deg b=(37.5deg)+-5deg
Timing setting
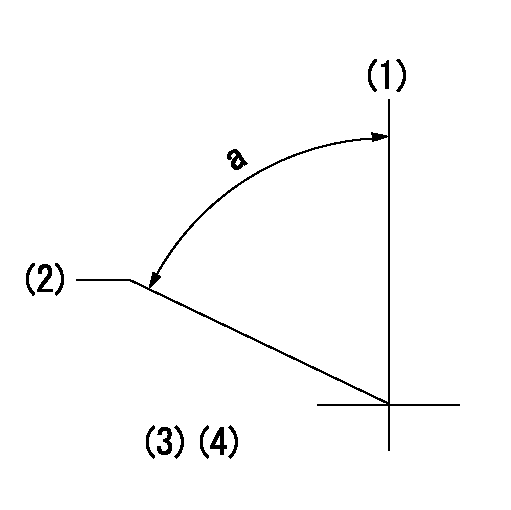
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(80deg)
----------
----------
a=(80deg)
Information:
The following topics describe care and maintenance of the electrical system components. These components functioning together produce the energy needed for operating the electrical equipment on the truck and each is dependent upon the other for satisfactory operation. In the event of failure or improper operation, it is essential to check the entire electrical system as a defect in one component can cause damage to another.Many electrical system problems can be traced to loose or corroded connections. Keep connections tight and make sure the wiring insulation is in satisfactory condition. Most of electrical system testing can be performed on the vehicle. (It should be remembered, if a malfunction is found on a vehicle test, the component may need further testing, repair or replacement.) Installations will have electrical components not furnished by Caterpillar. Consult the vehicle manufacturer's manual for maintenance procedures.Check the electrolyte level of each cell and the general condition of the battery. Maintain the electrolyte level to the base of each vent well. The make-up water must be one of the following (in order of preference): 1. Distilled water.2. Odorless, tasteless drinking water.3. Iron free water.4. Any available water.
Never add acid or electrolyte.
CLEANING BATTERY: Mix a weak solution of baking soda and water. Be careful not to get cleaning solution into battery. Apply the solution with a soft bristle brush.
CLEANING BATTERY TERMINALSThoroughly rinse the battery and battery tray with clean water. Apply grease to the battery cable clamps and terminals and to all threads. Testing The Electrolyte Solution: The general condition of a battery can be determined by measuring the specific gravity of the electrolyte solution and adjusting the reading to 80°F (27°C). If the electrolyte level is too low to allow taking a hydrometer reading, add make-up water to the correct level and then charge the battery 2 to 4 hours before taking a reading.
TESTING ELECTROLYTE SOLUTION1. Insert the hydrometer into a cell. Fill the hydrometer barrel while holding it vertically. The float must not drag on the wall of the barrel.2. Read the hydrometer: 1.250 or above - fully charged battery cell1.250-1.225 - full to half charged battery cell1.225-1.150 - half to low charged battery cellBelow 1.150 - dead cell1.000 - water3. Test each cell in the same manner.4. If there is more than .050 (50 gravity points) variation between the highest and lowest reading, the battery may need to be replaced.5. Adjust the readings to 80°F (27°C). a. For every 10F° (5.5C°) the electrolyte temperature is above 80°F (27°C), add .004 (4 gravity points) to the specific gravity readings.b. For every 10F°(5.5C°) the electrolyte temperature is below 80°F (27°C), subtract .004 (4 gravity points) from the specific gravity reading.The corrected reading is of most importance during cold weather when the hydrometer reading is always corrected to a lower specific gravity reading. A low reading signifies the battery has less available power to crank the engine and that booster batteries may be required. Voltage Test (After Load): A load test should be made on a
Never add acid or electrolyte.
CLEANING BATTERY: Mix a weak solution of baking soda and water. Be careful not to get cleaning solution into battery. Apply the solution with a soft bristle brush.
CLEANING BATTERY TERMINALSThoroughly rinse the battery and battery tray with clean water. Apply grease to the battery cable clamps and terminals and to all threads. Testing The Electrolyte Solution: The general condition of a battery can be determined by measuring the specific gravity of the electrolyte solution and adjusting the reading to 80°F (27°C). If the electrolyte level is too low to allow taking a hydrometer reading, add make-up water to the correct level and then charge the battery 2 to 4 hours before taking a reading.
TESTING ELECTROLYTE SOLUTION1. Insert the hydrometer into a cell. Fill the hydrometer barrel while holding it vertically. The float must not drag on the wall of the barrel.2. Read the hydrometer: 1.250 or above - fully charged battery cell1.250-1.225 - full to half charged battery cell1.225-1.150 - half to low charged battery cellBelow 1.150 - dead cell1.000 - water3. Test each cell in the same manner.4. If there is more than .050 (50 gravity points) variation between the highest and lowest reading, the battery may need to be replaced.5. Adjust the readings to 80°F (27°C). a. For every 10F° (5.5C°) the electrolyte temperature is above 80°F (27°C), add .004 (4 gravity points) to the specific gravity readings.b. For every 10F°(5.5C°) the electrolyte temperature is below 80°F (27°C), subtract .004 (4 gravity points) from the specific gravity reading.The corrected reading is of most importance during cold weather when the hydrometer reading is always corrected to a lower specific gravity reading. A low reading signifies the battery has less available power to crank the engine and that booster batteries may be required. Voltage Test (After Load): A load test should be made on a
Have questions with 106871-3881?
Group cross 106871-3881 ZEXEL
Hino
106871-3881
9 400 618 120
220004871A
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
EF750
EF750