Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106871-2580
1068712580
MITSUBISHI
ME066602
me066602

Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106871-2580
1068712580
MITSUBISHI
ME066602
me066602
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
132424-0620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-7-3-
4-5-6-8
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.75
4.85
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Difference between angles 7
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9.4
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
97
94.1
99.9
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
20
17
23
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(9.4)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
97
96
98
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1(9.4)
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
105.7
101.5
109.9
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
8.4
8.4
8.4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
135
115
155
Fixing the lever
*
Remarks
After startup boost setting
After startup boost setting
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
950--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1000
Advance angle
deg.
1.8
1.1
2.5
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
3.5
3.5
Timer adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1150
Advance angle
deg.
6.5
6
7
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
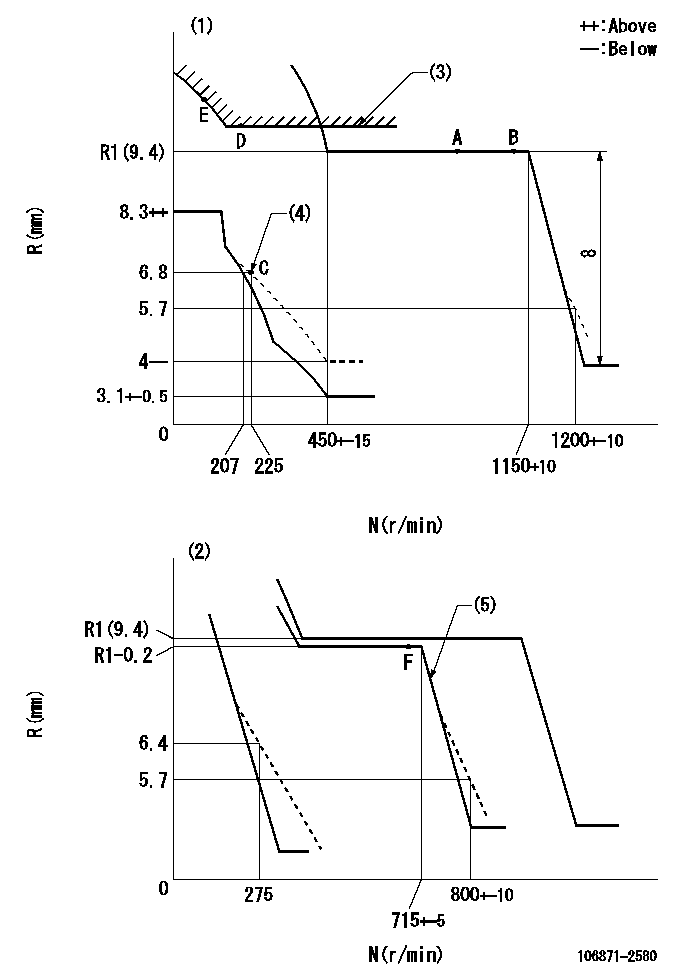
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Adjust with speed control lever at full position (minimum-maximum speed specification)
(2)Adjust with the load control lever in the full position (variable speed specification).
(3)Excess fuel setting for starting: SXL
(4)Damper spring setting
(5)When air cylinder is operating.
----------
SXL=11.9+-0.1mm
----------
----------
SXL=11.9+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
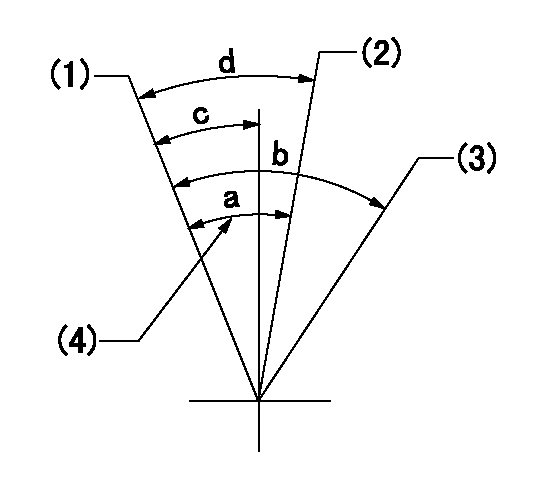
(1)Pump speed = aa
(2)Pump speed = bb
(3)Pump speed cc
(4)Possible adjusting range
----------
aa=1150r/min bb=275r/min cc=715r/min
----------
a=13deg b=23deg+-5deg c=8deg+-5deg d=13deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1150r/min bb=275r/min cc=715r/min
----------
a=13deg b=23deg+-5deg c=8deg+-5deg d=13deg+-5deg
0000000901
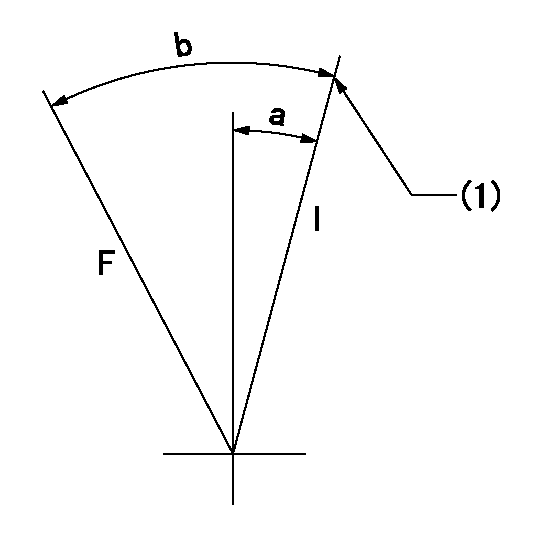
F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=23deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=23deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
(3)Rack position bb
(4)Free (at delivery)
----------
aa=4.7-0.5mm bb12.4mm
----------
a=43deg+7deg-5deg b=21.5deg+-5deg c=(10.5deg)
----------
aa=4.7-0.5mm bb12.4mm
----------
a=43deg+7deg-5deg b=21.5deg+-5deg c=(10.5deg)
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=325+-5r/min Ra=6.3mm
----------
----------
N1=325+-5r/min Ra=6.3mm
----------
0000001601 2-STAGE CHANGEOVER DEVICE

RFD governor 2 stage changeover mechanism adjustment outline
(A) Bolt
(B) bolt
(c) Nut
(D) Return spring
(E) Bolt
(F) Bolt
(G) Screw
(H) Bolt
(I) Load lever
(J) Speed lever
(K) Air cylinder
(M Air inlet
Figure 1 is only for reference. Lever shape, etc, may vary.
1. Minimum-maximum speed specification adjustment (when running)
(a) Without applying air to the air cylinder, loosen bolts (A) and (B).
(1)High speed return L setting
(a) In the speed range Nf~Nf - 300r/min, adjust using the speed adjusting bolt to determine the temporary beginning of high speed control speed.
(b) Determine the rack position in the vicinity of Rf using the full load lever.
(c) Increase speed and confirm return distance L.
(d) Adjust using the tension lever bolt to obtain L.
(2)Setting full load rack position Rf
(a) Move the load control lever to the full side.
(b) Adjust the full load adjusting bolt so that Rf can be obtained, then fix.
(3)Setting the beginning of high speed operation Nf
(a) Adjust using bolt (E) so that Nf can be obtained, and then fix.
(4)Idle control setting (Re, Ni, Rc)
(a) Set the speed at Ns + 200r/min and move the load control lever to the idle side.
(b) Fix the lever in the position where Re can be obtained.
(c) Next, decrease speed to Ni and screw in the idle spring.
(d) Adjust to obtain rack position Ri.
(e) Increase the speed and after confirming that the rack position is Re at Ns, set the speed at 0.
(f) Confirm protrusion position Rc at idle.
(5)Damper spring adjustment
(a) Increase speed and set the speed at the rack position Rd - 0.1 mm
(b) Set using the damper spring so that the rack position Rd can be obtained.
(c) When Rd is not specified, Rd = Ri - 0.5 mm.
(6)High speed droop confirmation
(a) Return the load control lever to the full load lever position.
(b) Increase the speed and confirm that Rf can be obtained at Nf r/min.
(c) Confirm that speed is Nh at rack position Rh.
2. Variable speed specification adjustment (at operation)
(a) Remove return spring (D).
(b) Apply air pressure of 245~294 kPa {2.5~3 kg/cm2} to the air cylinder.
(c) Perform the following adjustment in this condition.
(1)Setting full load rack position Rf'
(a) Pull the load lever to the idle side.
(b) Obtain rack position Rf' using the nut (C). (Pump speed is Nf'-50 r/min.)
(2)Setting full speed Nf'
(a) Adjust using bolt (B) so that Nf can be obtained, and then fix.
(3)Low speed side setting
(a) At 350r/min, set bolt (F) at beginning of governor operation position, then fix.
3. Bolt (A) adjustment
(1)Install return spring (D) and perform the adjustments below at air pressure 0.
(a) Set at speed Nf using bolt (E).
(b) Screw in bolt (A).
(c) Screw in 1 more turn from the speed lever contact position
(d) Fix bolt (A).
(e) At this time confirm that the air cylinder's shaft moves approximately 1 mm towards the governor.
4. Lever operation confirmation using the air cylinder
(1)Apply 588 kPa {6 kg/cm2} air pressure to the air cylinder.
(2)Confirm that the cylinder piston is moved 50 mm by the spring (D).
----------
----------
----------
----------
Information:
Illustration 8 g00281837
Circuit breaker
(1) Reset button
(2) Disc in open position
(3) Contacts
(4) Disc in closed position
(5) Battery circuit terminals A circuit breaker is a switch that opens the circuit if the current in the electrical system is higher than the rating of the circuit breaker.A metal disc that is controlled with heat and a contact (3) will complete the circuit through the circuit breaker. If the current in the electrical system is too high, the metal disc becomes too hot. The heat causes a distortion of the metal disc which opens the contacts (2). Open contacts break the circuit. A circuit breaker that is open can be reset after the circuit breaker cools. Push the reset button (1) in order to close the contacts (4) and reset the circuit breaker.
Find and correct the problem that causes the circuit breaker to open.Correcting the problem before running the engine will help prevent damage to the circuit components caused by too much current.
Air Shutoff Solenoid (ASOS)
Illustration 9 g00281839
Air shutoff (Typical example)
(1) Air transfer pipe
(2) Valve assembly
(3) Shutoff shaft
(4) Governor control shaft
(5) Air shutoff solenoid
(6) O-ring seal
(7) Diode assembly
Illustration 10 g00293067
(5) Air shutoff solenoid that is mounted in the air intake pipe.
The air shutoff solenoid (5) is located in the air inlet system on the top of the engine. When the air shutoff solenoid ("ASOS") is energized, the inlet air to the engine is mechanically shut off. The ASOS can be energized in the following two ways:
The ASOS is energized by the overspeed switch (OS).
The ASOS is energized by the emergency stop switch (ES).Fuel Solenoid (FS)
Illustration 11 g00281970
Fuel solenoid (Typical example)
(1) Diode assembly
(2) Spring
(3) Governor drive
(4) Fuel solenoid
(5) Shaft
Illustration 12 g00293070
(4) Fuel solenoid (FS) that is mounted on the governor.
The fuel solenoid (FS) (4) is located on the governor or on the fuel injection pump of the engine. When the FS is energized, the spring (2) and the shaft (5) will cause the fuel rack to move directly or the fuel rack will move through the governor drive to the FUEL ON position. The FS must remain energized or the fuel flow will be stopped to the engine. 2301A Electric Governor Control
Illustration 13 g00293071
(1) 2301A Electric Governor Speed Control
Illustration 14 g00293069
Electric governor actuator (EGA) (2) and fuel solenoid (FS) (3). The components are mounted on the top of the engine.
The 2301A Electric Governor Control system consists of the following components:
2301A Control
Actuator (EGA)
Magnetic pickup (MPU)The 2301A Electric Governor Control system provides precision engine speed control. The 2301A Control constantly monitors the engine rpm. The control makes the necessary corrections to the engine fuel setting through an actuator that is connected to the fuel system.The engine rpm is measured by the magnetic pickup ("MU"). The magnetic pickup makes an AC voltage that is sent to the 2301A Control. The 2301A Control then sends a DC voltage signal to the actuator in order to adjust the fuel flow.The actuator changes the electrical signal from the 2301A Control to a mechanical output. The mechanical output of the actuator causes the linkage from the actuator