Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
F 01G 09U 09N
f01g09u09n
ZEXEL
106871-1182
1068711182
ISUZU
1156031892
1156031892

Rating:
Cross reference number
BOSCH
F 01G 09U 09N
f01g09u09n
ZEXEL
106871-1182
1068711182
ISUZU
1156031892
1156031892
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8250
Bosch type code
1 688 901 101
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
20.7
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
211
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-4320
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
RED3 control unit part number
407910-3
960
RED3 rack sensor specifications
mm
19
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-8-7-3-
6-5-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
5.5
5.47
5.53
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-8 deg. 45 44.75 45.25
Cal 1-8 deg. 45 44.75 45.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.75 135.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.75 135.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.75 225.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.75 225.25
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-4 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Difference between angles 7
Cyl.1-2 deg. 315 314.75 315.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 315 314.75 315.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Rack position
(11.4)
Vist
V
2.14
2.14
2.14
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
142.5
141.5
143.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Remarks
Point A
Point A
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Rack position
(6.1)
Vist
V
2.9
2.8
3
Pump speed
r/min
490
490
490
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13.5
11.5
15.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-13
13
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
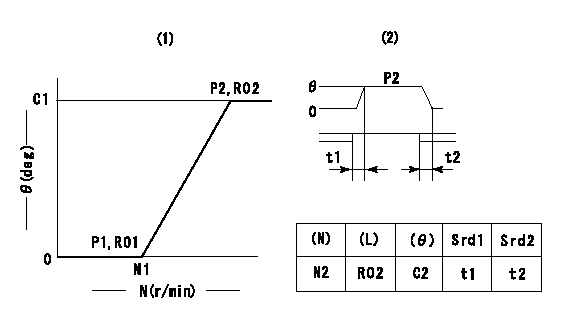
(1)Adjusting range
(2)Step response time
(N): Speed of the pump
(L): Load
(theta) Advance angle
(Srd1) Step response time 1
(Srd2) Step response time 2
1. Adjusting conditions for the variable timer
(1)Adjust the clearance between the pickup and the protrusion to L.
----------
L=1-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(8)deg t1=1.5--sec. t2=1.5--sec.
----------
N1=950++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=8+-0.3deg R01=0/4load R02=4/4load
----------
L=1-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(8)deg t1=1.5--sec. t2=1.5--sec.
----------
N1=950++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=8+-0.3deg R01=0/4load R02=4/4load
Speed control lever angle
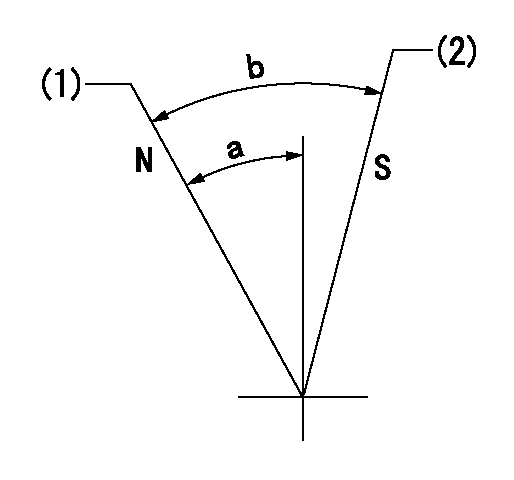
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Rack position bb
----------
aa=20mm bb=1mm
----------
a=37deg+-5deg b=37deg+-5deg
----------
aa=20mm bb=1mm
----------
a=37deg+-5deg b=37deg+-5deg
0000000901
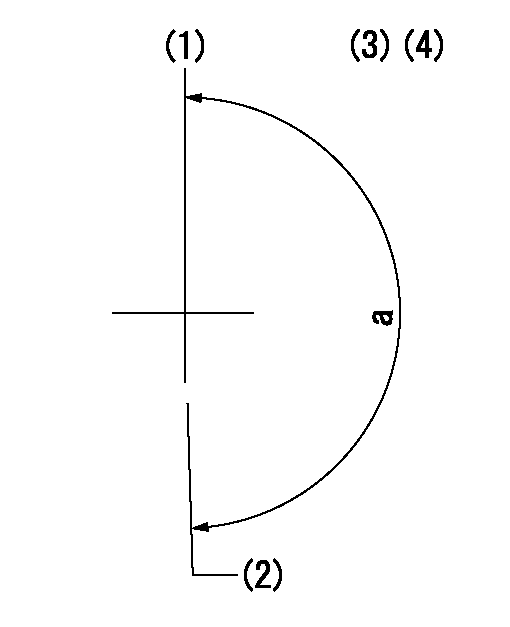
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of "Z" mark at the No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection (governor side)
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=4deg
----------
a=(180deg)
----------
aa=4deg
----------
a=(180deg)
Stop lever angle
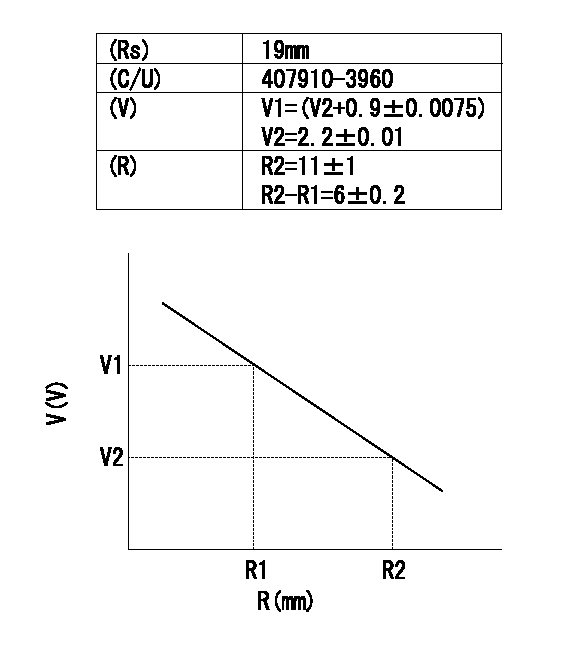
(Rs) rack sensor specifications
(C/U) control unit part number
(V) Rack sensor output voltage
(R) Rack position (mm)
1. Confirming governor output characteristics (rack 19 mm, span 6 mm)
(1)When the output voltages of the rack sensor are V1 and V2, check that the rack positions R1 and R2 in the table above are satisfied.
----------
----------
----------
----------
Information:
(4) VOP (Valve Opening Pressure) Test A. Open the gauge protector valve [0-34500 kPa (0-5000 psi) gauge].B. Increase the pressure until test oil flows from the nozzle tip.C. Write down the VOP. (5) Pressure Loss Test A. Increase the pressure to 690 kPa (100 psi) less than the VOP.B. Close the pump isolator valve (6).C. Use the gauge protector valve (3), [0-34500 kPa (0-5000 psi) gauge] to adjust pressure to 690 kPa (100 psi) less than the VOP.D. After 30 seconds, write down the pressure loss. (6) Adjustment of Valve Opening Pressure If spray characteristics are satisfactory, adjust the valve unseating pressure: Use 7B2591 Cap Wrench (7) to remove the cap. Remove lift screw locknut (8) and loosen lift adjustment screw (9) approximately three turns, so it does not interfere with the pressure adjustment. Loosen pressure adjustment locknut (10).E. Install the nozzle on the 5P4150 Nozzle Tester. F. Use 7B2601 Wrench (11) and adjust the VOP. G. Remove the valve from the nozzle tester and put it in a vise. Install lift adjustment screw locknut (8).H. Use the 6B1655 Wrench to turn lift adjusting screw (9) down lightly against the stem of the fuel valve spring.I. Clamp the needle lift adjustment fixture to the fuel valve body.J. Use a thickness gauge and adjust screw (12) until there is a clearance of 0.43 (.017") between screw (12) and lift adjustment screw (9).K. Hold screw (12) in position with clamping screw (13).L. Remove the thickness gauge and loosen lift adjustment screw (9) until there is 0.3 (.010") clearance between screw (9) and screw (12), after lift screw locknut (8) is tightened with the 7B2587 Wrench. The correct needle lift setting for all valves is 0.177 (.007").Cleaning Needle, Nozzle And Nozzle End Of Flat Seat Valves (Except 1P1795 Master Valves)
(1) Remove cap (1), bonnet (2) or unseating pressure adjusting screw, spring retainer, spring (3) and spring stem (4). Put the correct needle extracting tool (5) through the valve body and tighten over the end of the needle. If the needle is tight, install a new valve service group, or disassemble and clean the valve according to the procedure that follows. (2) If a fuel valve has a chip of scale, metal or foreign material on the seat, this will prevent the needle, from seating on the spray valve nozzle end, and cause the inner surface of the nozzle end and the needle end to become coated with carbon. Put carbon scraper (6) in the needle extracting tool and insert it into the nozzle bore and against the nozzle end; carefully turn the tool one revolution, with a slight pressure to remove the carbon. The cutting surface of scraper (6) has been lapped as perfectly flat and square with the center line of the tool as possible. Unless it remains so, it cannot effectively remove carbon. Handle this tool with care. Two scrapers are provided, so if one becomes marred, the second can be used while another is being obtained.
(1) Remove cap (1), bonnet (2) or unseating pressure adjusting screw, spring retainer, spring (3) and spring stem (4). Put the correct needle extracting tool (5) through the valve body and tighten over the end of the needle. If the needle is tight, install a new valve service group, or disassemble and clean the valve according to the procedure that follows. (2) If a fuel valve has a chip of scale, metal or foreign material on the seat, this will prevent the needle, from seating on the spray valve nozzle end, and cause the inner surface of the nozzle end and the needle end to become coated with carbon. Put carbon scraper (6) in the needle extracting tool and insert it into the nozzle bore and against the nozzle end; carefully turn the tool one revolution, with a slight pressure to remove the carbon. The cutting surface of scraper (6) has been lapped as perfectly flat and square with the center line of the tool as possible. Unless it remains so, it cannot effectively remove carbon. Handle this tool with care. Two scrapers are provided, so if one becomes marred, the second can be used while another is being obtained.