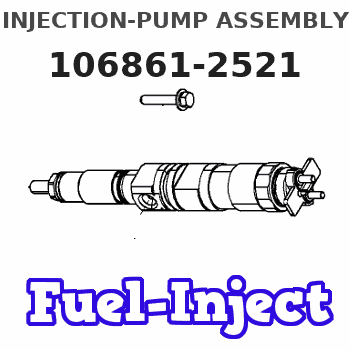
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 617 994
9400617994
ZEXEL
106861-2521
1068612521
MITSUBISHI
ME091890
me091890
Rating:
Service parts 106861-2521 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME060110
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7{180}/21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106861-2521
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 617 994
9400617994
ZEXEL
106861-2521
1068612521
MITSUBISHI
ME091890
me091890
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106861-2521
9 400 617 994
ME091890 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
8DC9T6 K 14CD INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE8P PE
8DC9T6 K 14CD INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE8P PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-4620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-7-3-
4-5-6-8
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.75
4.85
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-7 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 135 134.5 135.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 225 224.5 225.5
Difference between angles 6
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Difference between angles 7
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Cal 1-8 deg. 315 314.5 315.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
12.1+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
152
147.6
156.4
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
18.5
16
21
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(12.1)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
152
151
153
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
61.3
61.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
460
460
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1(12.1)
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
154
147.6
160.4
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
12.8
12.8
12.8
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
61.3
61.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
460
460
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
R2(11.2)
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
128
124.3
131.7
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
24
24
24
Boost pressure
mmHg
180
180
180
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
200
200
200
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
140
120
160
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
9.9
Boost pressure
kPa
2.7
2.7
2.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
20
20
20
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R2(11.2)
Boost pressure
kPa
24
22.7
25.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
180
170
190
Boost compensator adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R1(12.1)
Boost pressure
kPa
48
41.3
54.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
360
310
410
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
930
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
3
2.5
3.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
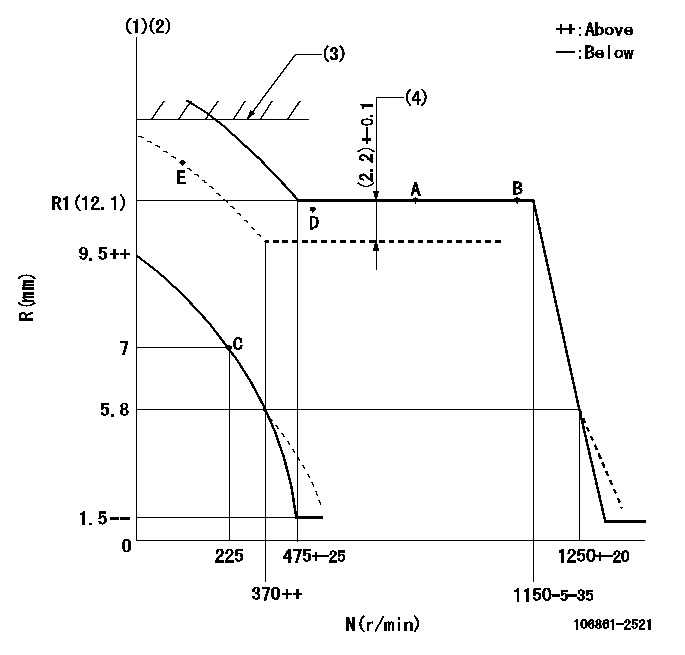
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Damper spring setting: DL
(2)Boost compensator cancel stroke: BSL
(3)Rack limit using the stop lever: R1
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
DL=5.8-0.2mm BSL=2.6mm R1=13+0.5mm BCL=(2.2)+-0.1mm
----------
----------
DL=5.8-0.2mm BSL=2.6mm R1=13+0.5mm BCL=(2.2)+-0.1mm
----------
0000000901

F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=14deg+-5deg b=(22deg)+-3deg
----------
----------
a=14deg+-5deg b=(22deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle
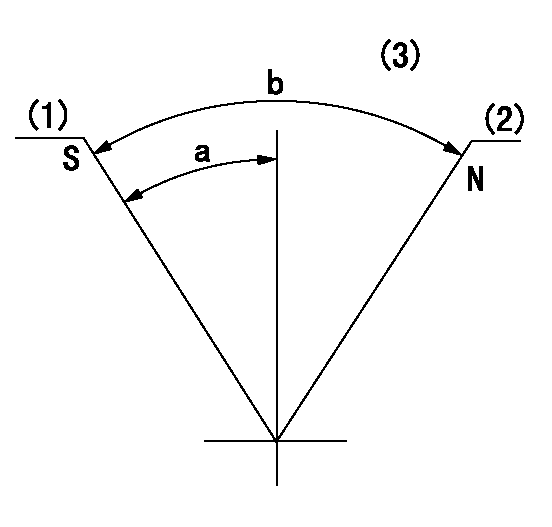
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa, stopper bolt setting
(2)Rack position bb
(3)Using reverse lever
----------
aa=4.7-0.5mm bb=13+0.5mm
----------
a=3deg+-6deg b=37deg+-6deg
----------
aa=4.7-0.5mm bb=13+0.5mm
----------
a=3deg+-6deg b=37deg+-6deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=325+-5r/min Ra=6.7mm
----------
----------
N1=325+-5r/min Ra=6.7mm
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
Information:
Adjustto conform and correspond to specifications.Checkto observe for satisfactory conditions, accuracy, safety or performance.Exchangeto trade a worn or failing component for a remanufactured or rebuilt component.Inspectto examine closely, in critical appraisal, while testing or evaluating components or systems.Inspect/Rebuild or Exchangeto examine closely, then making the decision on repair option (i.e. Rebuild or Exchange).Lubricateto apply a lubricant (oil, grease, etc.) as specified for reducing friction, heat and wear between solid surfaces.Protective Devicesindicators such as gauges, lights, emergency shutoffs, etc., that alert an operator that a potential problem may exist. Failure to respond to these indicators in a timely manner could result in serious engine damage.Rebuildto repair a worn or failing component with new parts, components and/or remanufactured components.Replaceto install something new, remanufactured or rebuilt in place of an existing worn or failing component.Service Hours (Electrical)records the time (clock hours) the engine is actually running but does not reflect variations in speed, load, etc. Some engines are equipped with mechanical service meters reading in Service Meter Units (SMU). The Maintenance Schedules are developed for clock hours or fuel consumption. For most users, clock hours are the standard interval for maintenance and SMU's can be roughly equal to clock hours. However, Caterpillar recommends that fuel consumption be used as the preferred method of determining intervals rather than SMU's or clock hours.Interval Categories
Engine components can generally be grouped into speed sensitive and load sensitive categories. The maintenance interval for each item listed in the Maintenance Schedule is based on either engine speed or load. Speed sensitive items such as water pumps and air compressors are not primarily affected by the operating load on your engine. The load on an engine will not significantly accelerate the repair or replacement cycle for speed sensitive items.The maintenance intervals established for speed sensitive items are based on service hours. Load sensitive items such as piston rings and cylinder liners are affected by the operating load on your engine. Generally speaking, the lower the load, the longer the engine life. Conversely, the higher the load, the shorter the engine life. A heavy load on an engine will accelerate the repair or replacement cycle for load sensitive items.Load sensitive items are normally internal engine components. The amount of fuel consumed is directly related to the load on your engine.The maintenance interval for load sensitive items includes fuel consumption, since the amount of fuel consumed is directly related to the load on your engine.Caterpillar recommends performing maintenance on load sensitive items at maintenance intervals based on the quantity of fuel consumed.
Engine components can generally be grouped into speed sensitive and load sensitive categories. The maintenance interval for each item listed in the Maintenance Schedule is based on either engine speed or load. Speed sensitive items such as water pumps and air compressors are not primarily affected by the operating load on your engine. The load on an engine will not significantly accelerate the repair or replacement cycle for speed sensitive items.The maintenance intervals established for speed sensitive items are based on service hours. Load sensitive items such as piston rings and cylinder liners are affected by the operating load on your engine. Generally speaking, the lower the load, the longer the engine life. Conversely, the higher the load, the shorter the engine life. A heavy load on an engine will accelerate the repair or replacement cycle for load sensitive items.Load sensitive items are normally internal engine components. The amount of fuel consumed is directly related to the load on your engine.The maintenance interval for load sensitive items includes fuel consumption, since the amount of fuel consumed is directly related to the load on your engine.Caterpillar recommends performing maintenance on load sensitive items at maintenance intervals based on the quantity of fuel consumed.
Have questions with 106861-2521?
Group cross 106861-2521 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
106861-2521
9 400 617 994
ME091890
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
8DC9T6
8DC9T6