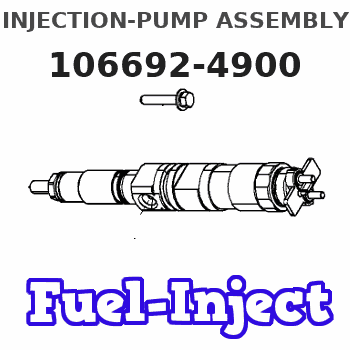
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 617 862
9400617862
ZEXEL
106692-4900
1066924900
KOMATSU
6211711352
6211711352
Rating:
Service parts 106692-4900 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6211-11-3101
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
24.5{250}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106692-4900
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 617 862
9400617862
ZEXEL
106692-4900
1066924900
KOMATSU
6211711352
6211711352
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106692-4900
9 400 617 862
6211711352 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S6D140 K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
S6D140 K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-3420
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.75
3.7
3.8
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
8.2
Pump speed
r/min
1050
1050
1050
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
154.2
152.2
156.2
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
3.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
365
365
365
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
14.2
12.7
15.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
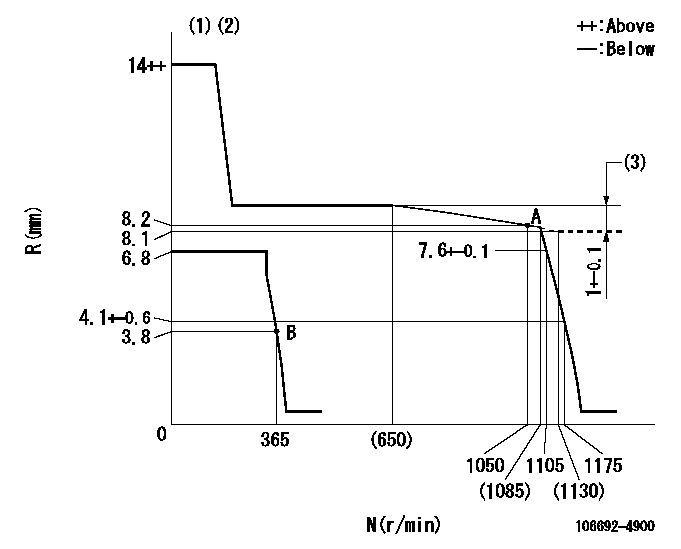
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=16 N1=1200r/min N2=400r/min
----------
----------
K=16 N1=1200r/min N2=400r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
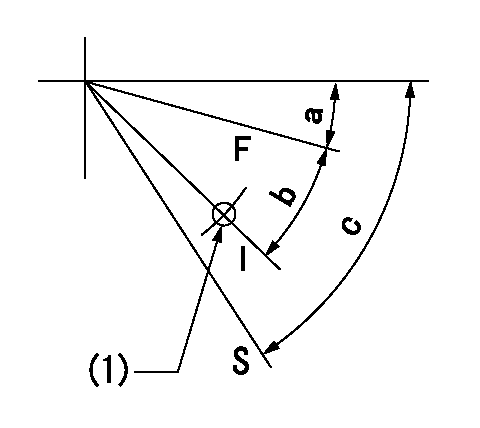
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
----------
aa=58mm
----------
a=14deg+-5deg b=25deg+-5deg c=53deg+-3deg
----------
aa=58mm
----------
a=14deg+-5deg b=25deg+-5deg c=53deg+-3deg
0000001501 LEVER
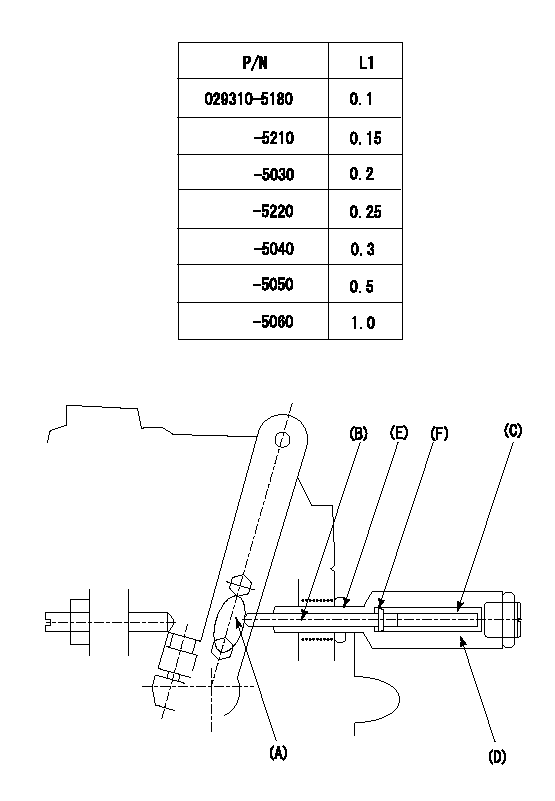
(F) P/N: Part number of the shim
L1:Thickness (mm)
1. Adjustment of the control lever
(1)Perform idling with the control lever (A) contacting the pushrod (B). At this time, confirm that the spring (C) is not compressed by control lever (A)'s operating torque.
(2)To set the stop position, compress spring (C) using the control lever (A) and adjust the rack so that it contacts the guide screw (D) at position L2. Then, set and fix using the lock nut (E). Adjust the rack position L2 at this time using the shim (F).
(3)Confirm that the control lever (A) returns to the idling position when pulled in the stop direction and then released.
----------
L2=0.2~2mm
----------
----------
L2=0.2~2mm
----------
Timing setting
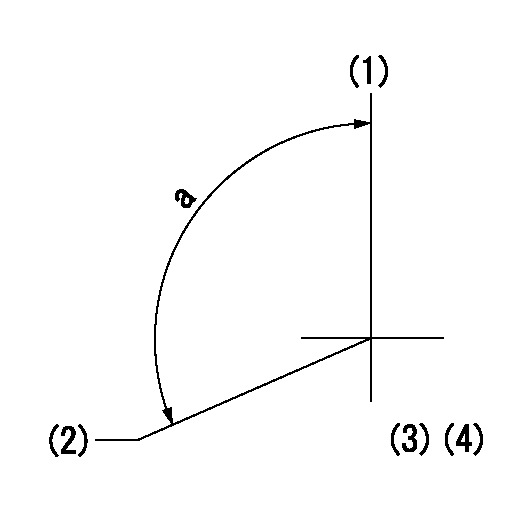
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(100deg)
----------
----------
a=(100deg)
Information:
Retrofit DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) System
This Retrofit DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) System must have the following components:
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
Silencer and/or housing
Clamp and gasket
Flow direction label
Engine tagEngine exhaust flows into the Retrofit DPF System reactor housing through the exhaust inlet. Exhaust flows through the DPF.Non-Unidirectional Requirements
(r) Directional Requirements for Diesel Emission Control Strategies
Every diesel emission control strategy must be installed as designed and specified by the manufacturer. For a diesel emission control strategy comprised of multiple exhaust aftertreatment parts, each aftertreatment part must be installed in the proper order relative to the exhaust flow.
Diesel emission control strategies installed between February 19, 2009, and January 1, 2010.
(A) The diesel emission control strategy must indicate the proper direction of exhaust flow. This exhaust flow indicator will allow the end user or installer to see how to install the device properly.
Diesel emission control strategies installed on or after January 1, 2010.
(A) The proper direction for exhaust to flow through the aftertreatment part of the diesel emission control strategy is to be clearly indicated on the outside surface of the aftertreatment part. The exhaust flow indicator consists of an arrow imprinted on or affixed to the aftertreatment part. The indicator arrow is to be clearly visible and durable.
(B) The aftertreatment part must be constructed such that the part can only be installed into the diesel emission control strategy in one unique direction relative to the exhaust flow. The aftertreatment part cannot be installed in the reversed direction.
(C) A diesel emission control strategy not meeting these requirements may be installed after January 1, 2010, if the diesel emission controls strategy: (1) Has a date of manufacture no later than December 31, 2009, (2) Complies with (r)(1) and (r)(2) above and (3) Is installed no later than December 31 2011.
(D) Except for an aftertreatment part that reduces PM through a physical trapping mechanism, such as a diesel particulate filter, the applicant may request that the Executive Officer waives the requirements that an aftertreatment part indicates the flow direction and have unidirectional construction. In reviewing the request, the Executive Officer may consider all relevant information including, but not limited to, the symmetry of the aftertreatment part, potential for impaired performance as a result of different orientations relative to exhaust flow, and interaction with other parts.Diesel Particulate Filter Operation
The Cat DPF is a catalyzed diesel particulate filter that is designed to reduce emissions of particulate (smoke), carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC), from diesel engines. Carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon reductions are achieved when the exhaust gases interact with the catalyst on the ceramic filter. The catalyst is impregnated on the walls of the ceramic substrate. As the exhaust gases come in contact with the catalyst, a chemical reaction takes place that oxidizes the gases. The oxidation process turns carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons into water and carbon dioxide.Reduction of Emissions
The Cat DPF is a complete product for reducing carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and PM. The filter is catalyzed with a precious-metal catalyst. For CO
This Retrofit DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) System must have the following components:
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
Silencer and/or housing
Clamp and gasket
Flow direction label
Engine tagEngine exhaust flows into the Retrofit DPF System reactor housing through the exhaust inlet. Exhaust flows through the DPF.Non-Unidirectional Requirements
(r) Directional Requirements for Diesel Emission Control Strategies
Every diesel emission control strategy must be installed as designed and specified by the manufacturer. For a diesel emission control strategy comprised of multiple exhaust aftertreatment parts, each aftertreatment part must be installed in the proper order relative to the exhaust flow.
Diesel emission control strategies installed between February 19, 2009, and January 1, 2010.
(A) The diesel emission control strategy must indicate the proper direction of exhaust flow. This exhaust flow indicator will allow the end user or installer to see how to install the device properly.
Diesel emission control strategies installed on or after January 1, 2010.
(A) The proper direction for exhaust to flow through the aftertreatment part of the diesel emission control strategy is to be clearly indicated on the outside surface of the aftertreatment part. The exhaust flow indicator consists of an arrow imprinted on or affixed to the aftertreatment part. The indicator arrow is to be clearly visible and durable.
(B) The aftertreatment part must be constructed such that the part can only be installed into the diesel emission control strategy in one unique direction relative to the exhaust flow. The aftertreatment part cannot be installed in the reversed direction.
(C) A diesel emission control strategy not meeting these requirements may be installed after January 1, 2010, if the diesel emission controls strategy: (1) Has a date of manufacture no later than December 31, 2009, (2) Complies with (r)(1) and (r)(2) above and (3) Is installed no later than December 31 2011.
(D) Except for an aftertreatment part that reduces PM through a physical trapping mechanism, such as a diesel particulate filter, the applicant may request that the Executive Officer waives the requirements that an aftertreatment part indicates the flow direction and have unidirectional construction. In reviewing the request, the Executive Officer may consider all relevant information including, but not limited to, the symmetry of the aftertreatment part, potential for impaired performance as a result of different orientations relative to exhaust flow, and interaction with other parts.Diesel Particulate Filter Operation
The Cat DPF is a catalyzed diesel particulate filter that is designed to reduce emissions of particulate (smoke), carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC), from diesel engines. Carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon reductions are achieved when the exhaust gases interact with the catalyst on the ceramic filter. The catalyst is impregnated on the walls of the ceramic substrate. As the exhaust gases come in contact with the catalyst, a chemical reaction takes place that oxidizes the gases. The oxidation process turns carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons into water and carbon dioxide.Reduction of Emissions
The Cat DPF is a complete product for reducing carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and PM. The filter is catalyzed with a precious-metal catalyst. For CO
Have questions with 106692-4900?
Group cross 106692-4900 ZEXEL
Komatsu
106692-4900
9 400 617 862
6211711352
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S6D140
S6D140