Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106691-2081
1066912081

Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106691-2081
1066912081
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-4620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.75
4.85
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.6
Pump speed
r/min
1050
1050
1050
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
132.3
129.3
135.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
49.3
49.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
370
370
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
4+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9.9
8.4
11.4
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
4.9+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12.7
10.8
14.6
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Remarks
(check)
(check)
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
9.6
Boost pressure
kPa
6.7
5.4
8
Boost pressure
mmHg
50
40
60
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
10.6
Boost pressure
kPa
36
32
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
270
240
300
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1050--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1000
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
1.5
1
2
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
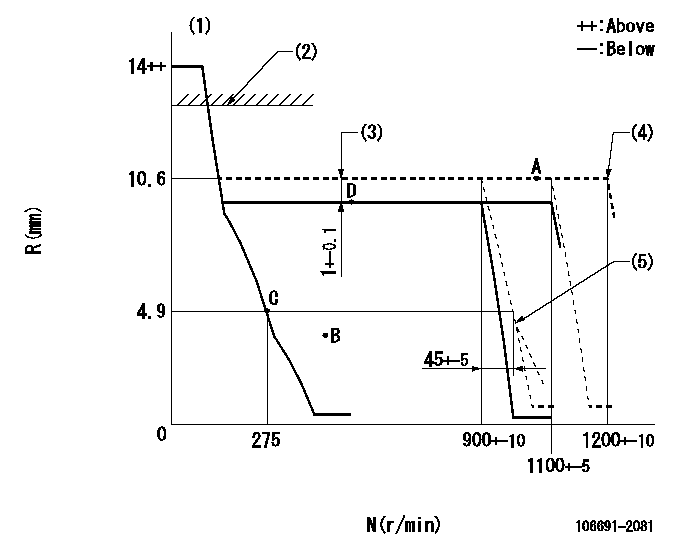
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)RACK LIMIT: RAL
(3)Boost compensator stroke
(4)At shipping
(5)Idle sub spring setting: L1.
----------
K=12 RAL=14+0.2mm L1=4.8+-0.1mm
----------
----------
K=12 RAL=14+0.2mm L1=4.8+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
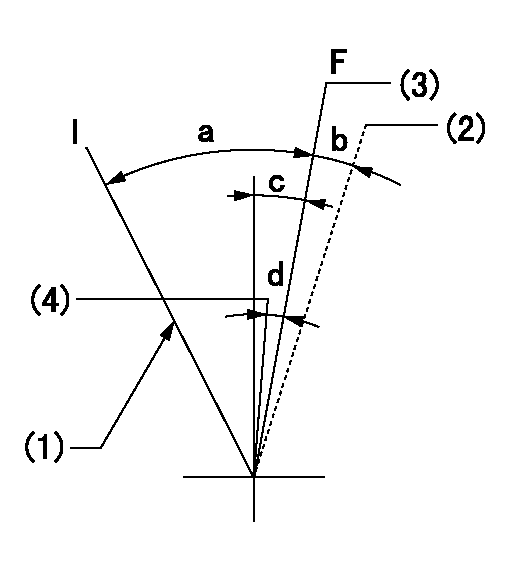
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
(2)At shipping
(3)Pump speed = aa
(4)Pump speed = bb
----------
aa=1100r/min bb=900r/min
----------
a=32deg+-5deg b=(5deg) c=9deg+-5deg d=8deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1100r/min bb=900r/min
----------
a=32deg+-5deg b=(5deg) c=9deg+-5deg d=8deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
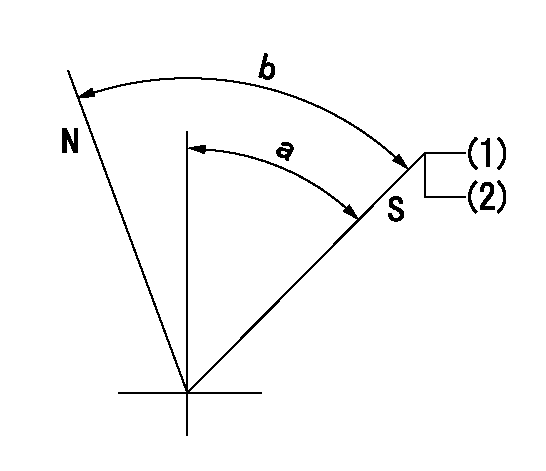
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Pump speed aa, rack position bb
(2)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.2mm
----------
a=50deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.2mm
----------
a=50deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
Timing setting
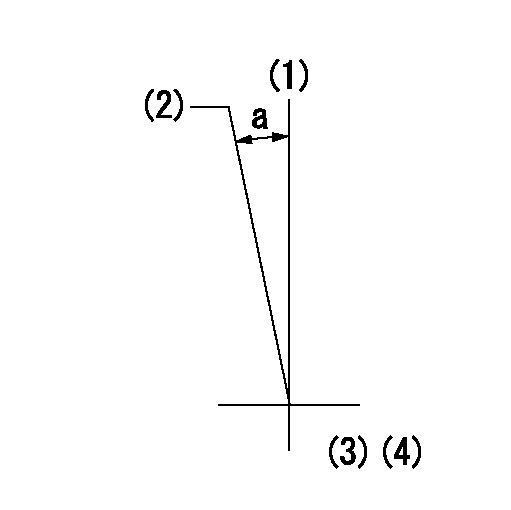
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(7deg)
----------
----------
a=(7deg)
Information:
Introduction
The problem that is identified below does not have a permanent solution. Until a permanent solution is known, use the solution that is listed below.Problem
A significant amount of HEUI pumps and injectors have been returned, but no cause of failure can be determined.Solution
Diagnostic procedures have been updated and have been incorporated into the following publications:
Special Instruction, REHS3819, "Procedure for Troubleshooting and Cleaning the Oil Rail System for the Hydraulic Electronic Unit Injector (HEUI)"
Troubleshooting, "Injection Actuation Pressure - Test"Note: These publications have been translated into Mandarin and Spanish.In addition, a new troubleshooting checklist is included with all service repair for HUEI pumps and HEUI injectors. The checklist is a summary of the diagnostic procedure steps to be confirmed before a suspect component is replaced. The checklist must be completed and returned with the suspect components in order to aid engineering to determine the cause of failure.Following the instructions step-by-step is critical in order to diagnose the failed component correctly. Do not skip steps in the procedures. Skipping steps in the procedure will lead to incorrect diagnosis of the problem.
The problem that is identified below does not have a permanent solution. Until a permanent solution is known, use the solution that is listed below.Problem
A significant amount of HEUI pumps and injectors have been returned, but no cause of failure can be determined.Solution
Diagnostic procedures have been updated and have been incorporated into the following publications:
Special Instruction, REHS3819, "Procedure for Troubleshooting and Cleaning the Oil Rail System for the Hydraulic Electronic Unit Injector (HEUI)"
Troubleshooting, "Injection Actuation Pressure - Test"Note: These publications have been translated into Mandarin and Spanish.In addition, a new troubleshooting checklist is included with all service repair for HUEI pumps and HEUI injectors. The checklist is a summary of the diagnostic procedure steps to be confirmed before a suspect component is replaced. The checklist must be completed and returned with the suspect components in order to aid engineering to determine the cause of failure.Following the instructions step-by-step is critical in order to diagnose the failed component correctly. Do not skip steps in the procedures. Skipping steps in the procedure will lead to incorrect diagnosis of the problem.