Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 283
9400611283
ZEXEL
106682-9901
1066829901
MITSUBISHI-HEAV
35A6500370
35a6500370
Rating:
Service parts 106682-9901 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
35A61-00010
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106682-9901
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 283
9400611283
ZEXEL
106682-9901
1066829901
MITSUBISHI-HEAV
35A6500370
35a6500370
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8130
Bosch type code
EFEP215A
Nozzle
105780-0050
Bosch type code
DN6TD119NP1T
Nozzle holder
105780-2090
Bosch type code
EFEP215
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Overflow valve
131424-3420
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
2.8
2.75
2.85
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
15
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
479
470
488
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
93.3
93.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
700
700
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
7.6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
25.5
22.5
28.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Rack position
R1-4
Boost pressure
kPa
40
37.3
42.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
280
320
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Rack position
R1(15)
Boost pressure
kPa
80
73.3
86.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
600
550
650
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
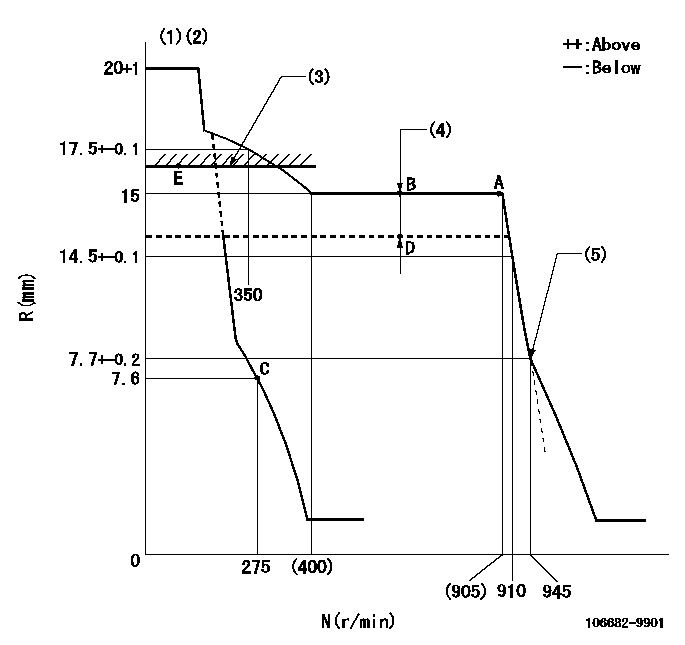
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)At excess fuel lever operation (at boost pressure 0): L1
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(5)Idle sub spring setting: L2.
----------
K=9 L1=15.5+0.2mm BCL=4+-0.1mm L2=7.7-0.5mm
----------
----------
K=9 L1=15.5+0.2mm BCL=4+-0.1mm L2=7.7-0.5mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
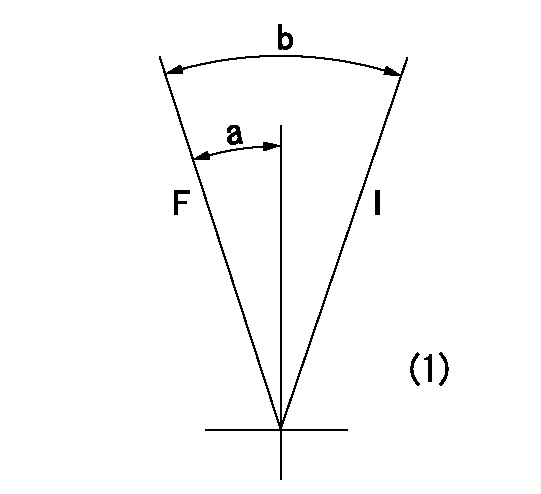
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)At the center of the lever key groove
----------
----------
a=16deg+-5deg b=35deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=16deg+-5deg b=35deg+-5deg
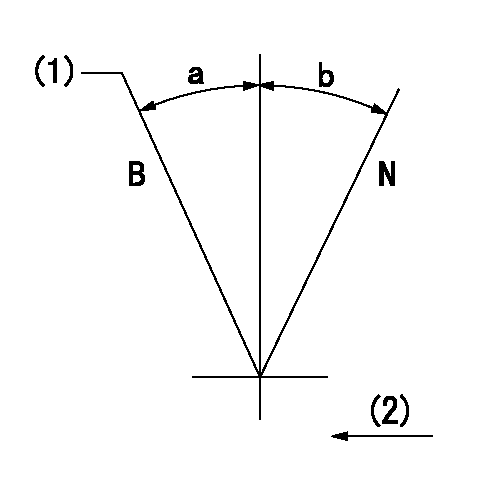
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=23deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=23deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
0000001101
N:Normal
B:When boosted
(1)Rack position = aa (point E) at boost pressure = 0.
(2)Drive side
----------
aa=15.5+0.2mm
----------
a=15deg+-5deg b=(15deg)
----------
aa=15.5+0.2mm
----------
a=15deg+-5deg b=(15deg)
Timing setting
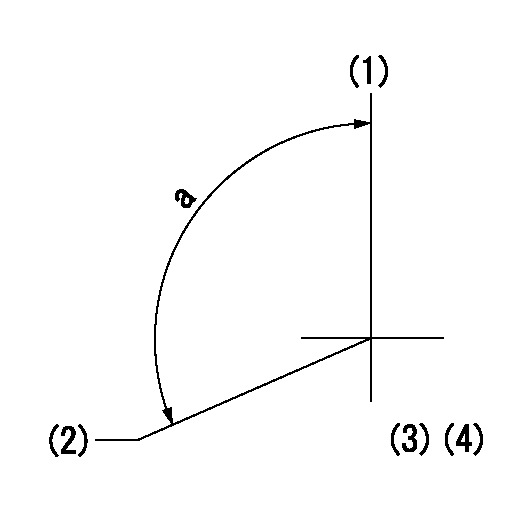
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(110deg)
----------
----------
a=(110deg)
Information:
Engine Lifting
When it is necessary to remove a component on an angle, remember that the capacity of an eyebolt is less as the angle between the supporting members and the object becomes less than 90°. Eyebolts and brackets should never be bent and should only be loaded in tension.
Use a hoist to remove heavy components. Lift the engine by using an adjustable lifting beam. All supporting members (chains and cables) should be parallel to each other, and as near perpendicular as possible to the top of the object being lifted.Some removals require the use of lifting fixtures to obtain proper balance and to provide safe handling. To remove the engine, use the two lifting eyes on the engine.Lifting eyes are designed for the arrangement as sold. Alterations to lifting eyes and/or arrangement weight make the lifting devices obsolete.If you make alterations, you are responsible for providing adequate lifting devices.Engine Storage
If the engine is not started for several weeks, the lubricating oil will drain from the cylinder walls and piston rings. Rust can form on the cylinder liner surface, which will increase engine wear and result in shorter engine life.To Prevent Excessive Engine Wear:
Be sure all lubrication recommendations mentioned in the Maintenance Management Schedule intervals chart are completed.If freezing temperatures can be expected, check the cooling system for adequate protection against freezing. A 50/50 solution of Caterpillar permanent-type antifreeze and approved water will give protection below -20°F (-29°C).If it will be impossible to start the engine every week, consult your Caterpillar dealer for instructions to prepare your engine for longer storage periods.If an engine remains out of service and its use is not immediately planned, special precautions should be taken. Refer to "Storage Procedures For Caterpillar Products," Form SEHS9031 for more detailed information on engine storage.
When it is necessary to remove a component on an angle, remember that the capacity of an eyebolt is less as the angle between the supporting members and the object becomes less than 90°. Eyebolts and brackets should never be bent and should only be loaded in tension.
Use a hoist to remove heavy components. Lift the engine by using an adjustable lifting beam. All supporting members (chains and cables) should be parallel to each other, and as near perpendicular as possible to the top of the object being lifted.Some removals require the use of lifting fixtures to obtain proper balance and to provide safe handling. To remove the engine, use the two lifting eyes on the engine.Lifting eyes are designed for the arrangement as sold. Alterations to lifting eyes and/or arrangement weight make the lifting devices obsolete.If you make alterations, you are responsible for providing adequate lifting devices.Engine Storage
If the engine is not started for several weeks, the lubricating oil will drain from the cylinder walls and piston rings. Rust can form on the cylinder liner surface, which will increase engine wear and result in shorter engine life.To Prevent Excessive Engine Wear:
Be sure all lubrication recommendations mentioned in the Maintenance Management Schedule intervals chart are completed.If freezing temperatures can be expected, check the cooling system for adequate protection against freezing. A 50/50 solution of Caterpillar permanent-type antifreeze and approved water will give protection below -20°F (-29°C).If it will be impossible to start the engine every week, consult your Caterpillar dealer for instructions to prepare your engine for longer storage periods.If an engine remains out of service and its use is not immediately planned, special precautions should be taken. Refer to "Storage Procedures For Caterpillar Products," Form SEHS9031 for more detailed information on engine storage.