Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 617 648
9400617648
ZEXEL
106682-9890
1066829890
KOMATSU
6162752240
6162752240
Rating:
Service parts 106682-9890 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
26.0(265)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106682-9890
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 617 648
9400617648
ZEXEL
106682-9890
1066829890
KOMATSU
6162752240
6162752240
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106682-9890
9 400 617 648
6162752240 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SA6D170 K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
SA6D170 K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8130
Bosch type code
EFEP215A
Nozzle
105780-0050
Bosch type code
DN6TD119NP1T
Nozzle holder
105780-2090
Bosch type code
EFEP215
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Overflow valve
131425-1620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
2.8
2.75
2.85
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.7
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
300
296
304
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
37.3
37.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
280
280
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
7.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
315
315
315
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15
10
20
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Rack position
11.7
Boost pressure
kPa
13.3
10.6
16
Boost pressure
mmHg
100
80
120
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Rack position
12.25
Boost pressure
kPa
24
17.3
30.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
180
130
230
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
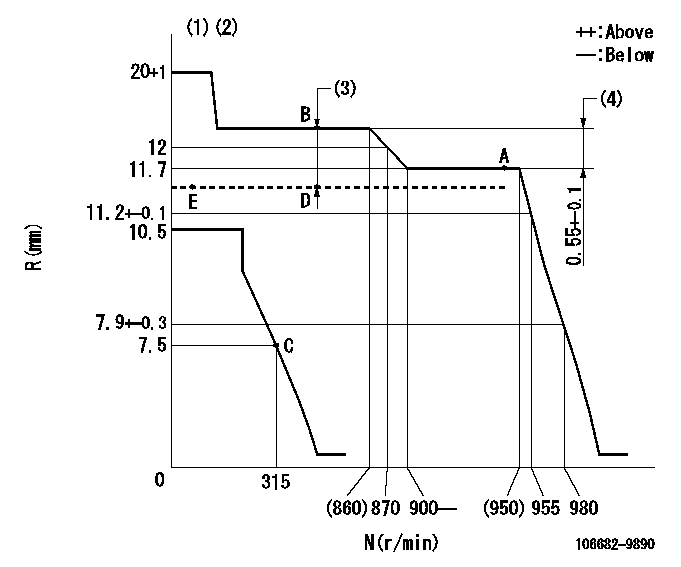
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(4)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=8 BCL=0.55+-0.1mm N1=900r/min N2=650r/min
----------
----------
K=8 BCL=0.55+-0.1mm N1=900r/min N2=650r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
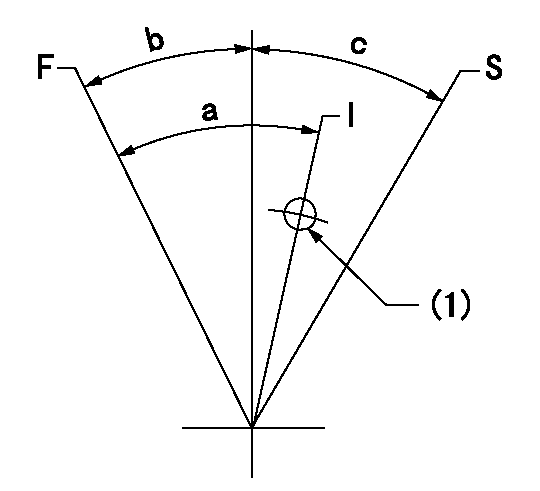
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
----------
aa=115mm
----------
a=26deg+-5deg b=4deg+-5deg c=27deg+-3deg
----------
aa=115mm
----------
a=26deg+-5deg b=4deg+-5deg c=27deg+-3deg
0000001501 LEVER
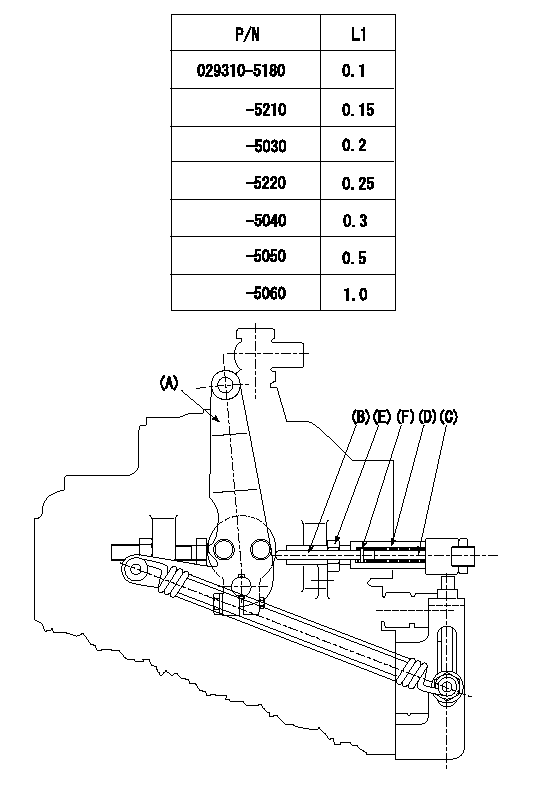
Speed lever adjustment
1. (1) For idling hold the speed lever (a) against the push rod (B).
(2)At this time, confirm that the spring (C) is not bent by the operating torque of the speed lever.
2. (1) To stop, bend the spring (C) using the speed lever.
(2)Position the rack at L2. (Adjustment is performed using the shim (F).)
(3)Set and fix using lock nut (E) so that it contacts the guide screw (D).
3. Confirm that the speed lever returns to the idling position when pulled in the stop direction and then released.
----------
L2=0.2~2mm
----------
----------
L2=0.2~2mm
----------
Timing setting
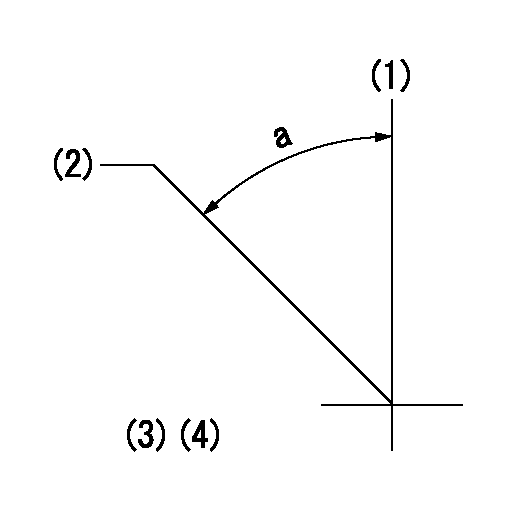
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
----------
----------
a=(40deg)
Information:
Operating Cost Information
The term "Life Cycle Costs" can be defined as the sum of the individual costs experienced by an engine from the day of purchase until the day of retirement. In other words, the total Owning and Operating Costs.Owning Costs are fixed costs such as initial purchase price, interest on borrowed money, depreciation and taxes.Operating Costs are a combination of fixed and variable costs such as fuel, oil, operator expenses, road taxes, tires, chassis maintenance and repair, permits, licenses, engine maintenance and repair and downtime.The difference between revenues generated and Life Cycle Costs (total Owning and Operating Costs) is profit.Caterpillar and your Caterpillar dealer cannot guarantee that you will make a profit. However, Caterpillar and your Caterpillar dealer can provide you with a variety of services that can help you reduce the costs that impact your profits.An Engine Operating Cost Analysis is a service provided by your dealer that was developed by Caterpillar to help you reduce the Life Cycle Cost of your engine.More specifically, an Engine Operating Cost Analysis is a computerized program that examines existent and expectant oil, fuel, maintenance, minor repair, overhaul and downtime costs for the period of time you expect to own the engine. It also calculates the operating cost per mile (km), hour or day.This useful tool provides your dealer with the specific information needed to develop a customized Maintenance Management program for your operation which will minimize your engine's operating costs.Before a cost analysis can be performed, your dealer needs to gather as much information as possible about your operation. He will need to know the length of time you plan to keep your engine/vehicle, your average cost of fuel and oil as well as a variety of other ownership and cost related facts and figures.Once this information is obtained, your dealer will enter the data into an established computerized program to produce an Engine Operating Cost Analysis printout reflecting your current and projected operating costs per mile (km), hour or day.The typical printout of the Engine Operating Cost Analysis program has up to four engine scenarios which can be run at one time. The printout is divided into three major areas: * General Information* Engine Operating Information* Operating Cost SummaryGeneral Information
The General Information section contains basic user data such as name, business, location, ownership, usage per year, etc., information.Engine Operating Information
The Engine Operating Information section is divided into eight subsections that address fuel consumption, oil consumption, preventive maintenance, component repairs such as water pumps, turbochargers, air compressors, etc., before failure repairs, after failure repairs, user's revenue rate per hour and lastly, miscellaneous costs such as operator wages, insurance premiums, etc.Current and expected cost information reflected in the Engine Operating Information section is based on the data provided by you. These are the costs that affect your engine's operating cost.Operating Cost Summary
The Operating Cost Summary section is exactly what it implies, a summary. Here the total dollar expense and percentage of the total operating expense is calculated for each of
The term "Life Cycle Costs" can be defined as the sum of the individual costs experienced by an engine from the day of purchase until the day of retirement. In other words, the total Owning and Operating Costs.Owning Costs are fixed costs such as initial purchase price, interest on borrowed money, depreciation and taxes.Operating Costs are a combination of fixed and variable costs such as fuel, oil, operator expenses, road taxes, tires, chassis maintenance and repair, permits, licenses, engine maintenance and repair and downtime.The difference between revenues generated and Life Cycle Costs (total Owning and Operating Costs) is profit.Caterpillar and your Caterpillar dealer cannot guarantee that you will make a profit. However, Caterpillar and your Caterpillar dealer can provide you with a variety of services that can help you reduce the costs that impact your profits.An Engine Operating Cost Analysis is a service provided by your dealer that was developed by Caterpillar to help you reduce the Life Cycle Cost of your engine.More specifically, an Engine Operating Cost Analysis is a computerized program that examines existent and expectant oil, fuel, maintenance, minor repair, overhaul and downtime costs for the period of time you expect to own the engine. It also calculates the operating cost per mile (km), hour or day.This useful tool provides your dealer with the specific information needed to develop a customized Maintenance Management program for your operation which will minimize your engine's operating costs.Before a cost analysis can be performed, your dealer needs to gather as much information as possible about your operation. He will need to know the length of time you plan to keep your engine/vehicle, your average cost of fuel and oil as well as a variety of other ownership and cost related facts and figures.Once this information is obtained, your dealer will enter the data into an established computerized program to produce an Engine Operating Cost Analysis printout reflecting your current and projected operating costs per mile (km), hour or day.The typical printout of the Engine Operating Cost Analysis program has up to four engine scenarios which can be run at one time. The printout is divided into three major areas: * General Information* Engine Operating Information* Operating Cost SummaryGeneral Information
The General Information section contains basic user data such as name, business, location, ownership, usage per year, etc., information.Engine Operating Information
The Engine Operating Information section is divided into eight subsections that address fuel consumption, oil consumption, preventive maintenance, component repairs such as water pumps, turbochargers, air compressors, etc., before failure repairs, after failure repairs, user's revenue rate per hour and lastly, miscellaneous costs such as operator wages, insurance premiums, etc.Current and expected cost information reflected in the Engine Operating Information section is based on the data provided by you. These are the costs that affect your engine's operating cost.Operating Cost Summary
The Operating Cost Summary section is exactly what it implies, a summary. Here the total dollar expense and percentage of the total operating expense is calculated for each of
Have questions with 106682-9890?
Group cross 106682-9890 ZEXEL
Komatsu
Komatsu
Mitsubishi-Heav
Komatsu
Komatsu
Komatsu
Komatsu
Komatsu
106682-9890
9 400 617 648
6162752240
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SA6D170
SA6D170