Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106682-9360
1066829360
KOMATSU
6166711710
6166711710

Rating:
Service parts 106682-9360 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6162-14-3300
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
26.0{265}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106682-9360
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106682-9360
1066829360
KOMATSU
6166711710
6166711710
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8130
Bosch type code
EFEP215A
Nozzle
105780-0050
Bosch type code
DN6TD119NP1T
Nozzle holder
105780-2090
Bosch type code
EFEP215
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Overflow valve
131425-1620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
2.8
2.75
2.85
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
14.8
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
503
498
508
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Remarks
Standard point A's rack position same as row R
Standard point A's rack position same as row R
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12.5
11
14
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
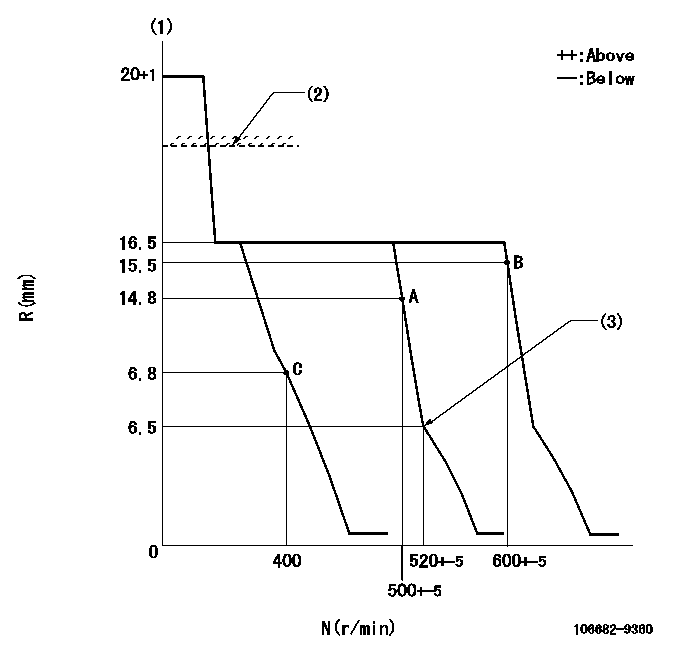
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)RACK LIMIT for 106684-4230; RAL
(3)Idle sub spring setting: L1.
----------
K=9 RAL=17+0.2mm L1=6.5-0.5mm
----------
----------
K=9 RAL=17+0.2mm L1=6.5-0.5mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
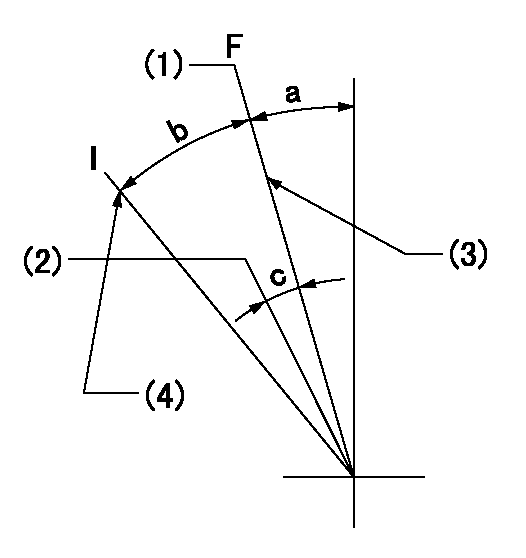
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Set the pump speed at aa. ( At delivery )
(2)Set the pump speed at bb.
(3)Stopper bolt setting
(4)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=600r/min bb=500r/min
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=15deg+-5deg c=7deg+-5deg
----------
aa=600r/min bb=500r/min
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=15deg+-5deg c=7deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=36.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=36.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of spline gear's aligning mark at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection (key position)
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=(20deg)
----------
a=(130deg)
----------
aa=(20deg)
----------
a=(130deg)
Information:
The troubleshooting chart provides a definite sequence to be followed for a logical procedure to determine the frequency and amplitude of vibration so that the source of the vibration can be located and corrected.1. The customer must be asked questions to determine whether his complaint is valid, or whether his diagnosis of the actual problem is correct.Some of the questions that must be asked are as follows: a. What components are vibrating?b. In what speed range does this vibration become excessive?c. Does clutch operation affect the vibration?d. What is the history of the problem?2. Run the engine through the idle speed range and note all vibrating components. Look for any loose or broken mounts, brackets, and fasteners. Repair and tighten any fixtures.3. Check idle speed range with clutch disengaged. If vibrations subside, there is a balance problem with the clutch disc. The clutch disc must be repaired or replaced.4. Further analysis requires the use of a vibration instrument. Any instrument which can accurately measure the displacement of the vibration (usually in mils-inch/1000) and the frequency (cycles per second) will be sufficient. A vibration instrument such as the IRD Mechanalysis Model 320 or an equivalent instrument can be used to analyze vibration.5. Measure vibration of cab components which have the objectionable vibration.Run engine slowly through the speed range and measure vibration with the instrument filter OUT. When peak amplitudes are found, run the engine at the speeds they occur and with the instrument filter IN, find the frequency of the vibration.If the frequency of vibration is 1/2 times of engine rpm (1/2 order), the vibration is caused by a cylinder misfiring. This must be corrected before further vibration analysis is made.If the frequency of vibration is 3 times engine rpm, no corrective action can be taken on the engine because this is the firing frequency of the 3406 engine. The problem is in the cab or chassis resonance.If frequency is some order other than 1/2 or 3rd, then further measurements must be made on the engine.6. Measurements taken on the engine must be made perpendicular to the crankshaft at the front and, rear of the engine in vertical and horizontal directions.7. Record all vibrations over 4.0 mils and the engine rpm at which it occurs (100 rpm intervals are sufficient) with instrument filter OUT. Note any sudden increase and decrease in amplitudes. These occur in resonant speed ranges.If no amplitudes exceed 4.0 mils, the engine is within Caterpillar Specifications.If amplitudes exceed 4.0 mils, the vibrations must be measured with the instrument filter IN to obtain the frequency of the vibrations.8. Run the engine at high idle. With the instrument filter IN, check the frequency range and record any amplitudes over 4.0 mils and the corresponding frequency. Analysis of vibrations for the possible causes is done by identifying the frequency of the vibration and where on the engine it is the greatest magnitude. Make reference to Special Instruction, Troubleshooting Engine Vibration In Vehicular Equipment, Form No. SEHS7914 for additional information