Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106682-9190
1066829190
KOMATSU
6212711310
6212711310
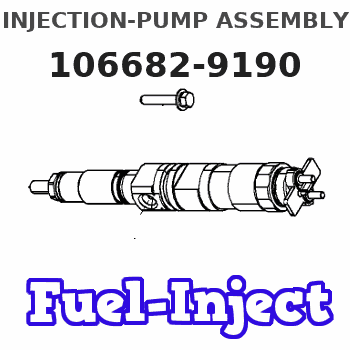
Rating:
Service parts 106682-9190 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6212-11-3202
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
24.5{250}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106682-9190
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106682-9190
1066829190
KOMATSU
6212711310
6212711310
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8130
Bosch type code
EFEP215A
Nozzle
105780-0050
Bosch type code
DN6TD119NP1T
Nozzle holder
105780-2090
Bosch type code
EFEP215
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Overflow valve
131424-7120
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3
2.95
3.05
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
14.4
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
352
349
355
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
49.3
49.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
370
370
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
7.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
410
410
410
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
22
20.5
23.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
16+0.2
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
335
315
355
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
12.4
Boost pressure
kPa
13.3
6.6
20
Boost pressure
mmHg
100
50
150
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
15.4
Boost pressure
kPa
44
41.3
46.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
280
320
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
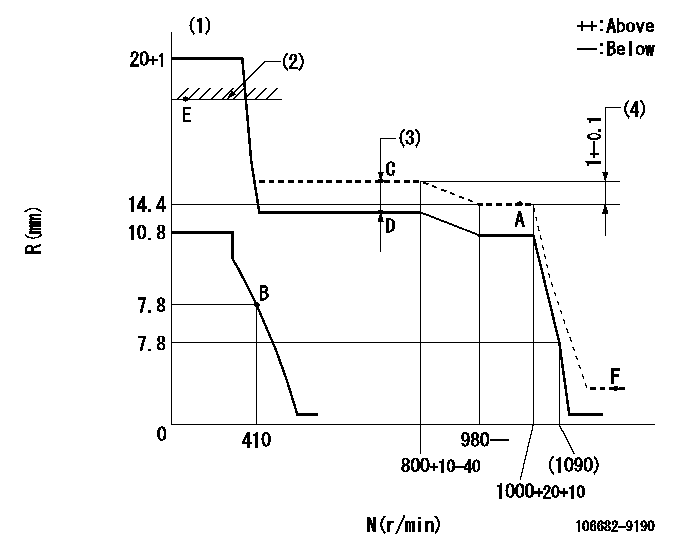
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Notch fixed: K
(2)RACK LIMIT: RAL
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(4)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=21 RAL=16+0.2mm BCL=3+-0.1mm N1=1000r/min N2=700r/min
----------
----------
K=21 RAL=16+0.2mm BCL=3+-0.1mm N1=1000r/min N2=700r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
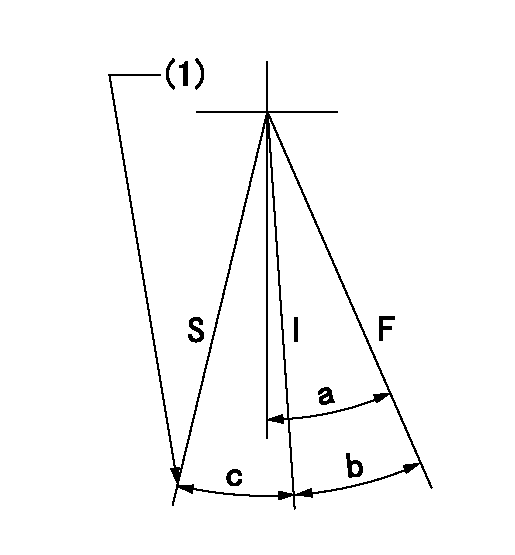
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=30deg+-5deg b=24deg+-5deg c=21.5deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=30deg+-5deg b=24deg+-5deg c=21.5deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
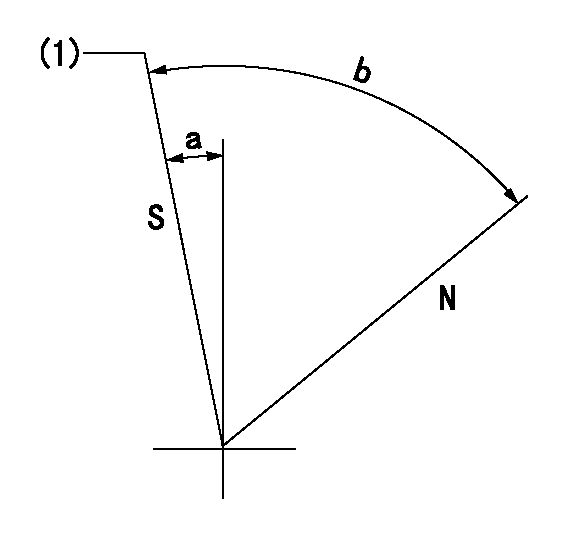
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Pump speed aa and rack position bb (to be sealed at delivery)
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.2mm
----------
a=29deg+-5deg b=(73deg)
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.2mm
----------
a=29deg+-5deg b=(73deg)
0000001501 LEVER
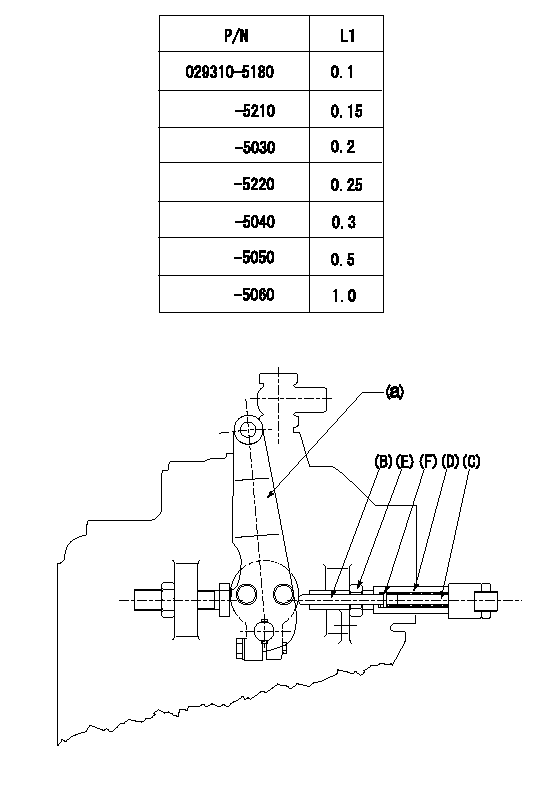
Speed lever adjustment
1. (1) For idling hold the speed lever (a) against the push rod (B).
(2)At this time, confirm that the spring (C) is not bent by the operating torque of the speed lever.
2. (1) To stop, bend the spring (C) using the speed lever.
(2)Set so that the rack position is L2.
(3)Set and fix using lock nut (E) so that it contacts the guide screw (D).
(4)Adjust rack position at this time using shim (F).
3. Confirm that the speed lever returns to the idling position when pulled in the stop direction and then released.
----------
L2=0.2~2mm
----------
----------
L2=0.2~2mm
----------
Timing setting
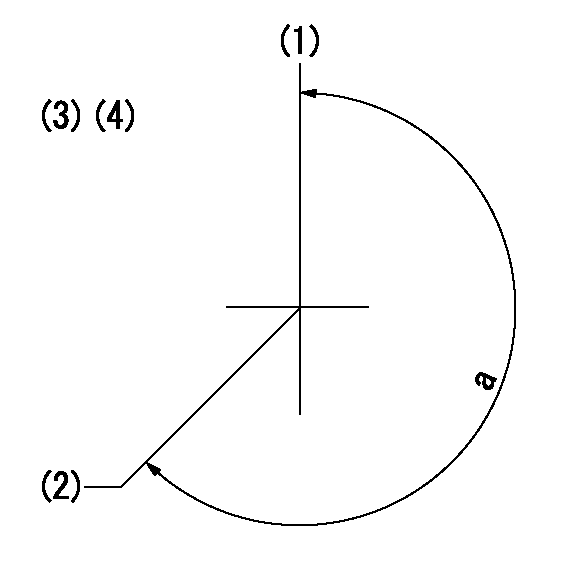
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(260deg)
----------
----------
a=(260deg)
Information:
Exhaust Smoke Can Be Seen While Starting
Possible Causes/Corrections Cold Outside TemperaturesIt may be necessary to use starting aids, or to heat engine oil or coolant at temperatures below -12°C (10°F). Air In Fuel SystemWith air in the fuel system, the engine will normally be difficult to start, run rough, and release a large amount of white smoke. If the engine will not start, loosen a fuel injection line nut at the through the head adapter and crank the engine until fuel comes out. Tighten the fuel line nut. Start the engine. If the engine still does not run smooth or releases a large amount of white smoke, loosen the fuel line nuts one at a time at the through the head adapters until the fuel that comes out is free of air. Tighten the fuel line nuts. If the air can not be removed in this way, put 35 kPa (5 psi) of air pressure to the fuel tank.
Do not use more than 55 kPa (8 psi) of air pressure in the fuel tank or damage to the tank may result.
Check for leakage at the connections between the fuel tank and the fuel transfer pump. If leaks are found, tighten the connections or replace the lines. It there are no visual leaks, remove the fuel supply line from the tank and connect it to an outside fuel supply. If this corrects the problem, the suction line (standpipe) inside the fuel tank has a leak. Low Quality FuelRemove a small amount of fuel from the tank and check for water in the fuel. If there is water in the fuel, remove fuel from the tank until it is free of water and fill with a good quality fuel. For more information see Special Instruction, Form No. SEHS7067, Fuel Recommendations For Caterpillar Diesel Engines.Change the fuel filter and "prime" (remove the air and/or low quality fuel from the fuel system) the fuel system with the fuel priming pump. If there is no water in the fuel, prime and start the engine by using an outside source of fuel. If engine starts correctly using different fuel, remove all fuel from the tank and fill with good quality fuel. Prime the fuel system if necessary. Low Fuel PressureChange the primary and secondary fuel filters and check to make sure the fuel lines are not plugged or damaged. If the filters or lines are not the cause, a repair or replacement of the fuel transfer pump is needed. Fuel Injection Timing Not CorrectCheck and make necessary adjustments as in Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Valve Adjustment Not CorrectCheck and make necessary adjustments as in Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Intake valve lash is 0.38 mm (.015 in) and exhaust valve lash is 0.64 mm (.025 in). Defective Fuel Nozzle(s)Remove the fuel nozzles and test as in Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Low CompressionSee "Misfiring and Running Rough".Exhaust Smoke Cannot Be Seen While Starting
Possible Causes/Corrections
Possible Causes/Corrections Cold Outside TemperaturesIt may be necessary to use starting aids, or to heat engine oil or coolant at temperatures below -12°C (10°F). Air In Fuel SystemWith air in the fuel system, the engine will normally be difficult to start, run rough, and release a large amount of white smoke. If the engine will not start, loosen a fuel injection line nut at the through the head adapter and crank the engine until fuel comes out. Tighten the fuel line nut. Start the engine. If the engine still does not run smooth or releases a large amount of white smoke, loosen the fuel line nuts one at a time at the through the head adapters until the fuel that comes out is free of air. Tighten the fuel line nuts. If the air can not be removed in this way, put 35 kPa (5 psi) of air pressure to the fuel tank.
Do not use more than 55 kPa (8 psi) of air pressure in the fuel tank or damage to the tank may result.
Check for leakage at the connections between the fuel tank and the fuel transfer pump. If leaks are found, tighten the connections or replace the lines. It there are no visual leaks, remove the fuel supply line from the tank and connect it to an outside fuel supply. If this corrects the problem, the suction line (standpipe) inside the fuel tank has a leak. Low Quality FuelRemove a small amount of fuel from the tank and check for water in the fuel. If there is water in the fuel, remove fuel from the tank until it is free of water and fill with a good quality fuel. For more information see Special Instruction, Form No. SEHS7067, Fuel Recommendations For Caterpillar Diesel Engines.Change the fuel filter and "prime" (remove the air and/or low quality fuel from the fuel system) the fuel system with the fuel priming pump. If there is no water in the fuel, prime and start the engine by using an outside source of fuel. If engine starts correctly using different fuel, remove all fuel from the tank and fill with good quality fuel. Prime the fuel system if necessary. Low Fuel PressureChange the primary and secondary fuel filters and check to make sure the fuel lines are not plugged or damaged. If the filters or lines are not the cause, a repair or replacement of the fuel transfer pump is needed. Fuel Injection Timing Not CorrectCheck and make necessary adjustments as in Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Valve Adjustment Not CorrectCheck and make necessary adjustments as in Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Intake valve lash is 0.38 mm (.015 in) and exhaust valve lash is 0.64 mm (.025 in). Defective Fuel Nozzle(s)Remove the fuel nozzles and test as in Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Low CompressionSee "Misfiring and Running Rough".Exhaust Smoke Cannot Be Seen While Starting
Possible Causes/Corrections