Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 612 314
9400612314
ZEXEL
106682-1050
1066821050
Rating:
Service parts 106682-1050 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
1-15300-392-2
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7{180}/22.1{225}
14.
NOZZLE
Include in #1:
106682-1050
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 612 314
9400612314
ZEXEL
106682-1050
1066821050
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8130
Bosch type code
EFEP215A
Nozzle
105780-0050
Bosch type code
DN6TD119NP1T
Nozzle holder
105780-2090
Bosch type code
EFEP215
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Overflow valve
134424-4320
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
RED4 control unit part number
407915-0
590
RED4 rack sensor specifications
mm
19
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.27
3.33
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Rack position
(13.3)
PWM
%
63.1
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
376
373
379
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Rack position
(6.7)
PWM
%
26+-2.8
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15.5
12.3
18.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-13
13
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Test data Ex:
Speed control lever angle
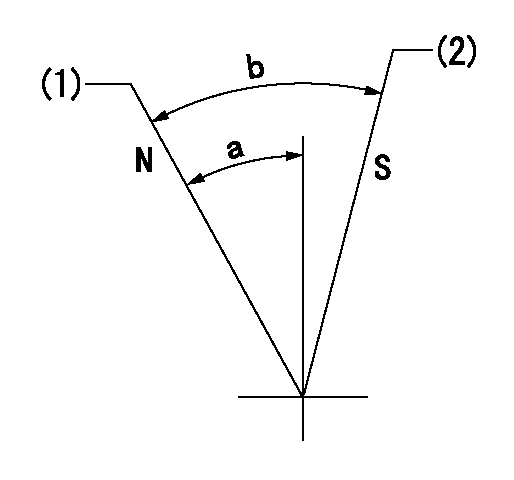
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Rack position bb
----------
aa=20mm bb=1mm
----------
a=27deg+-5deg b=37deg+-5deg
----------
aa=20mm bb=1mm
----------
a=27deg+-5deg b=37deg+-5deg
0000000901

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Positions of coupling's threaded installation holes at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(100deg)
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(100deg)
Stop lever angle

(PWM) Pulse width modulation (%)
(R) Rack position (mm)
Rack sensor output characteristics
1. Rack limit adjustment
(1)Measure the rack position R2 for PWM a2%.
(2)Confirm that it is within the range R2 = 15+-1 mm.
(3)Measure the rack position R1 at PWM a %.
(4)Confirm that it is within the range R2 - R1 = 10+-0.1 mm.
2. Check the limp home operation.
(1)Move the switch box's limp home switch to the limp home side.
(2)Confirm rack position L1 (mm ) and L2 (mm) for PWM in the above table.
3. Check the pull down operation.
(1)Confirm that the rack position is 19 mm at PWM B%.
(2)In the conditions described in the above table, move the switch box's pull down switch to the pull down side and confirm that the rack position momentarily becomes 1 mm or less.
----------
a1=16.25% a2=72.5% L1=1--mm L2=19++mm A=5 % B=95%
----------
----------
a1=16.25% a2=72.5% L1=1--mm L2=19++mm A=5 % B=95%
----------
Information:
Primary Engine Test For Low Power 1. The customer must be asked many questions to determine whether his complaint is valid, or whether his diagnosis of an actual problem is correct.Some of the questions that must be asked are as follows:a. Does poor performance occur when the vehicle is operated at steady speed on a level road surface, or when vehicle is pulled up a grade? A positive response to either or both of the above conditions would indicate a low power (steady state) problem. Begin with Low Power Diagnosis.b. Does the poor performance always occur under the same conditions or is the problem intermittent (happens only occasionally)? This is a very important line of questioning to pursue. Any constant performance problem can normally be identified and the problem corrected. If an intermittent problem exists, the mechanic must be aware that the condition is only occasional, and must run certain tests several times in an attempt to force the malfunction condition. If the condition is not duplicated, the diagnosis that no problem exists will be incorrect, and the vehicle operator will again be confronted with the problem somewhere out on the road.c. Was the engine running rough or misfiring when the poor performance was noticed? A positive response to this question will indicate the need to isolate the bad cylinder(s) and correct the problem. See section Cylinder Misfire.2. Check the crankcase oil level and the coolant level of the radiator. Remove the boost air line from the AFRC (air-fuel ratio control) during the Primary Engine Test. This will prevent the AFRC from becoming pnuematically activated during the checks. If activated, the AFRC could give an indication of a problem when there is none.3. A slightly lower rpm (15 rpm below low limit) should be expected for the engine in vehicle than the rpm shown in the RACK SETTING INFORMATION. This is caused by the parasitic loads of the engine accessories involved.4. With the engine running, the throttle must have enough travel for the governor control lever to break over (go past the normal governor stop for high idle position) a small amount when the throttle pedal is fully depressed. If full travel is not available, disconnect throttle linkage from governor lever. With throttle linkage disconnected, full travel of governor lever will indicate linkage problems, and the linkage will have to be adjusted. Limited travel of the governor lever will indicte a problem within the governor.5. Only a mechanic with the correct training should change the high idle setting. The procedure is given in the Service Manual under the subject GOVERNOR ADJUSTMENTS.6. If high idle rpm can not be made correct with the high idle adjustment screw, there is a problem inside the governor. Disassemble the governor and check for damaged parts or wrong parts installed in the governor. Some common problems are worn bushings, worn spring seat, or a broken or wrong governor spring.7. Before 8S4627 Circuit Tester is installed, be sure to test the light for correct