Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 341
9400611341
ZEXEL
106682-1030
1066821030
ISUZU
1156033540
1156033540
Rating:
Service parts 106682-1030 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
1-15300-387-1
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
22.1{225}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106682-1030
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 341
9400611341
ZEXEL
106682-1030
1066821030
ISUZU
1156033540
1156033540
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106682-1030
9 400 611 341
1156033540 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6WG1-TMC K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
6WG1-TMC K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8130
Bosch type code
EFEP215A
Nozzle
105780-0050
Bosch type code
DN6TD119NP1T
Nozzle holder
105780-2090
Bosch type code
EFEP215
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-4-1000
Overflow valve
134424-4320
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
2.8
2.75
2.85
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.4
Pump speed
r/min
1050
1050
1050
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
441
437
445
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
147
147
Boost pressure
mmHg
1100
1100
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
4.4+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15.5
12.3
18.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
210
210
250
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Rack position
8.8
Boost pressure
kPa
69.3
66.6
72
Boost pressure
mmHg
520
500
540
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Rack position
(11.4)
Boost pressure
kPa
133
133
133
Boost pressure
mmHg
1000
1000
1000
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
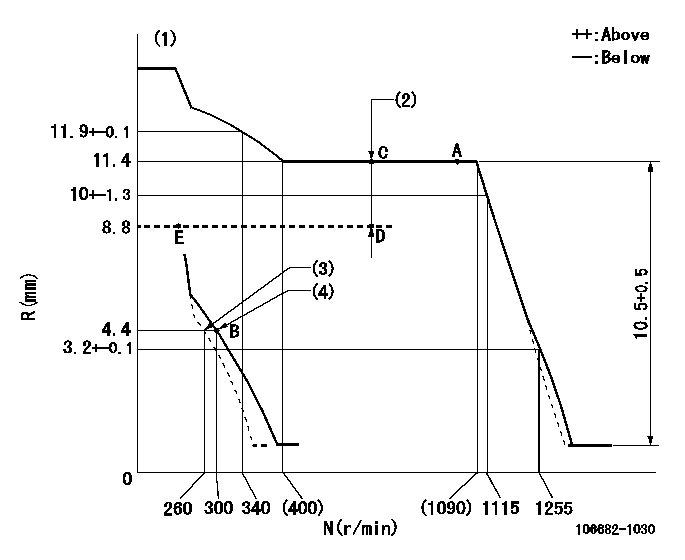
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(2)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(3)Main spring setting
(4)Set idle sub-spring
----------
BCL=(2.6)mm
----------
----------
BCL=(2.6)mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
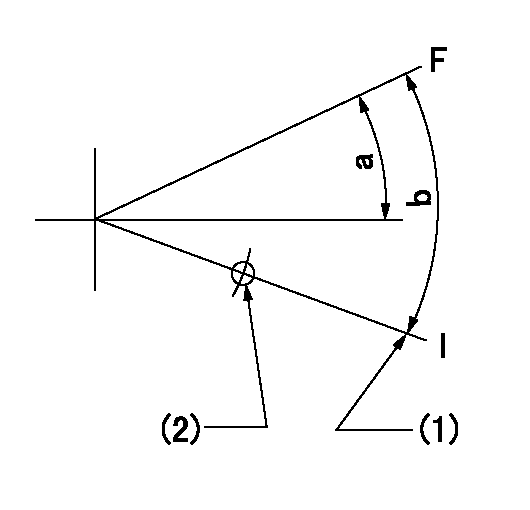
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
(2)Use the hole at R = aa
----------
aa=135mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=13.5deg+-5deg
----------
aa=135mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=13.5deg+-5deg
0000000901
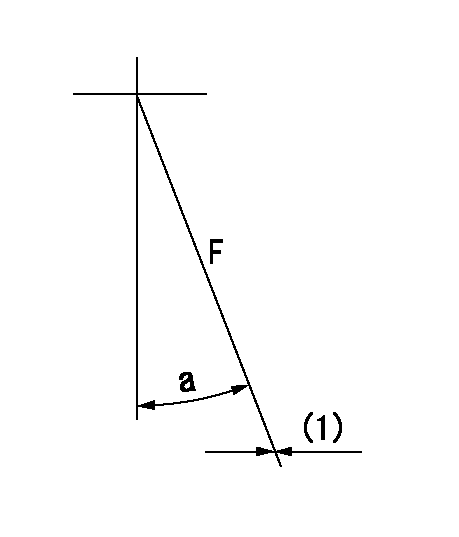
F:Full load
(1)Fix using the stopper bolt.
----------
----------
a=15deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=15deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
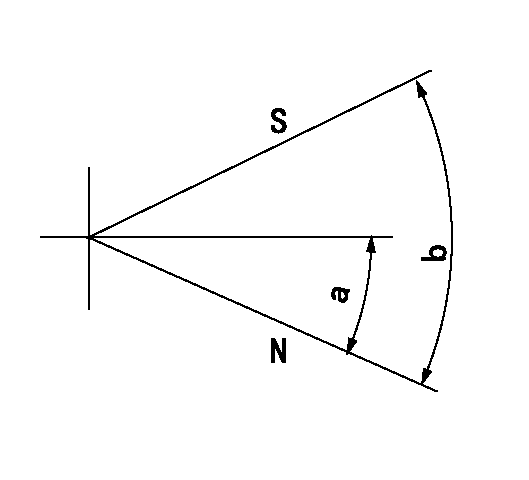
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=27deg+-5deg b=71deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=27deg+-5deg b=71deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of coupling's threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(30deg)
----------
----------
a=(30deg)
Information:
AUTOMATIC CONTROL
1. Pressure reducing valve. 2. Manual control valve. 3. BrakeSaver control lever. 4. Air pressure gauge. 5. Oil temperature gauge. 6. BrakeSaver control valve. 7. Double check valve. 8. Solenoid valve. 9. Key switch. 10. Mode selector switch. 11. Accelerator switch. 12. Clutch switch.Because the solenoid valve sends full air pressure to the BrakeSaver control valve, there is no modulation in the AUTOMATIC-MANUAL position.When the mode selector switch (10) is in the AUTOMATIC-MANUAL position and the accelerator pedal is released (pedal up), the BrakeSaver is operating at its maximum capacity. When the clutch is released (pedal down) the BrakeSaver goes off. When the clutch is engaged again (pedal up), the BrakeSaver comes back on. A light pressure on the accelerator pedal turns the BrakeSaver off and lets the vehicle run freely. More pressure on the accelerator pedal sends fuel to the engine.When the BrakeSaver is turned off, the pressure air goes out of the system through a passage in the manual control valve (2) or in the solenoid valve (8). This lets the pressure air out of the BrakeSaver control valve (6) and removes the braking force from the BrakeSaver.The manual control valve (2) can be operated with the mode selector switch (10) in the AUTOMATIC-MANUAL position. During normal operation, the solenoid valve will send full air pressure to the BrakeSaver control valve and remove the effect of the manual control valve. If there is a failure in the electrical system when the mode selector switch is in the AUTOMATIC-MANUAL position, the manual control valve will have an effect.Jake Brake
The JAKE BRAKE permits the operator to control the speed of the vehicle on grades, curves, or anytime when speed reduction is necessary, but long applications of the service brakes are not desired. In downhill operation, or any slow down condition, the engine crankshaft is turned by the rear wheels (through the differential, driveshaft, transmission and clutch). To reduce the speed of the vehicle, an application of a braking force can be made to the pistons of the engine.The JAKE BRAKE, when activated, does this through the conversion of the engine from a source of power to an air compressor that absorbs (takes) power. This conversion is made possible by a master to slave piston arrangement, where movement of the rocker arm for the exhaust valves of one cylinder is transferred hydraulically to open the exhaust valves of another cylinder near the top of its normal compression stroke cycle. The compressed cylinder charge is now released into the exhaust manifold.The release of the compressed air pressure to the atmosphere prevents the return of energy to the engine piston on the expansion (power) stroke. The result is an energy loss, since the work done by the compression of the cylinder charge is not returned by the the expansion process. This energy loss is taken from the rear wheels, which provides the braking action for the vehicle.Jake Brake Components
JAKE BRAKE INSTALLED
1. Rear housing. 2. Front housing. 3. Stud. 4. Support
Have questions with 106682-1030?
Group cross 106682-1030 ZEXEL
Isuzu
106682-1030
9 400 611 341
1156033540
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6WG1-TMC
6WG1-TMC