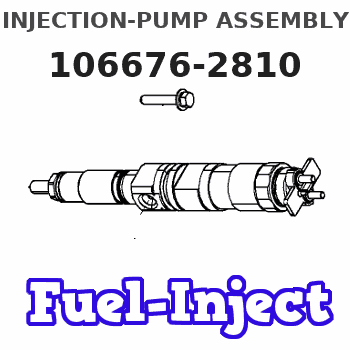
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 617 465
9400617465
ZEXEL
106676-2810
1066762810
MITSUBISHI
ME441574
me441574
Rating:
Service parts 106676-2810 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME441575
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106676-2810
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 617 465
9400617465
ZEXEL
106676-2810
1066762810
MITSUBISHI
ME441574
me441574
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106676-2810
9 400 617 465
ME441574 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D24TL K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
6D24TL K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-4420
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.9
3.85
3.95
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
13.8
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
161
158
164
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
34.7
34.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
260
260
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
16
13.4
18.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Rack position
10.65
Boost pressure
kPa
5.3
4
6.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
40
30
50
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Rack position
12.25
Boost pressure
kPa
21.3
21.3
21.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
160
160
160
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
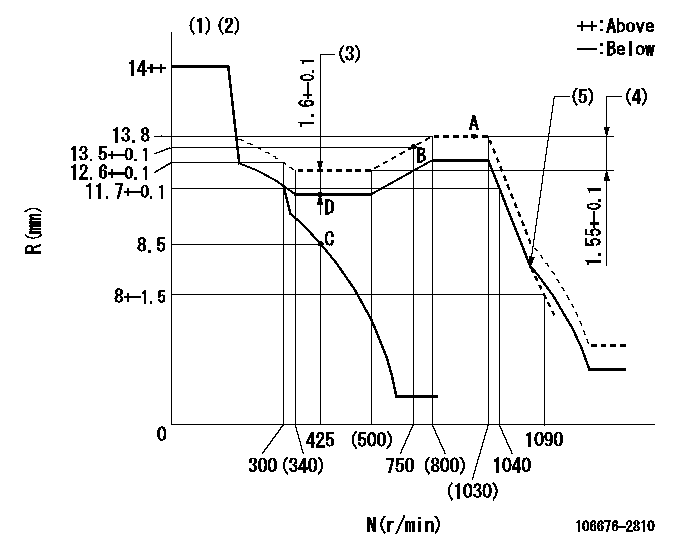
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Notch fixed: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Boost compensator stroke
(4)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
(5)Idle sub spring setting: L1.
----------
K=9 N1=1000r/min N2=400r/min L1=9-0.2mm
----------
----------
K=9 N1=1000r/min N2=400r/min L1=9-0.2mm
----------
Timer adjustment
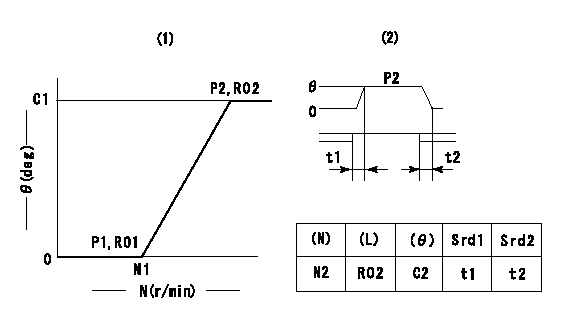
(1)Adjusting range
(2)Step response time
(N): Speed of the pump
(L): Load
(theta) Advance angle
(Srd1) Step response time 1
(Srd2) Step response time 2
1. Adjusting conditions for the variable timer
(1)Adjust the clearance between the pickup and the protrusion to L.
----------
L=1.5-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(10deg) t1=2.5--sec. t2=2.5--sec.
----------
N1=750++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=10+-0.3deg R01=0/4 load R02=4/4 load
----------
L=1.5-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(10deg) t1=2.5--sec. t2=2.5--sec.
----------
N1=750++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=10+-0.3deg R01=0/4 load R02=4/4 load
Speed control lever angle
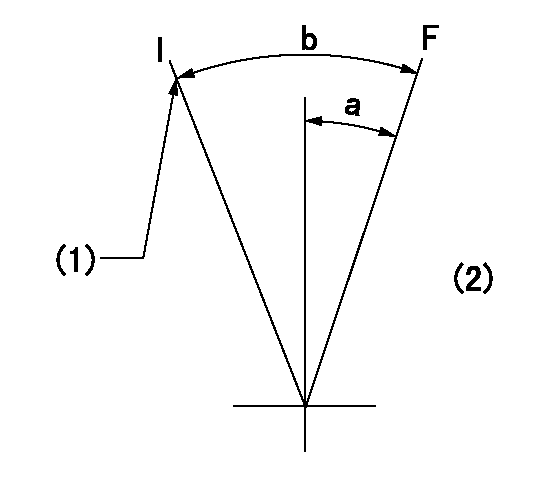
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
(2)Base lever only
----------
----------
a=(3deg)+-5deg b=(17deg)+-5deg
----------
----------
a=(3deg)+-5deg b=(17deg)+-5deg
Stop lever angle
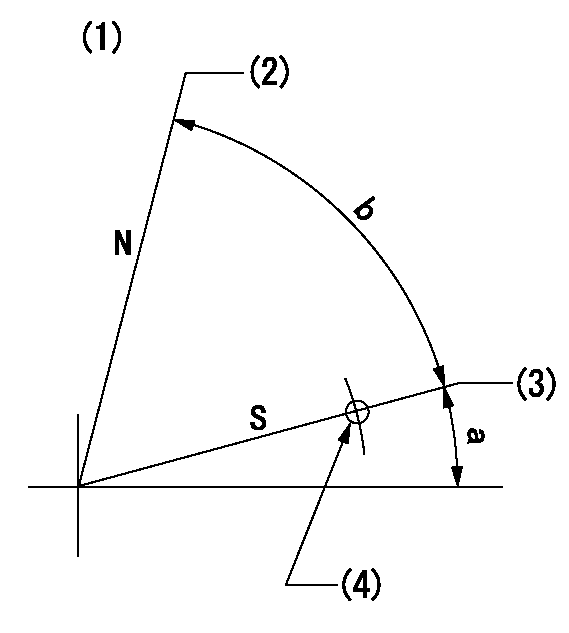
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)No return spring
(2)Set the outer screw where it contacts the inside (seal at delivery)
(3)Rack position = aa, speed = bb (stamp at delivery)
(4)Use the hole above R = cc
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min cc=17mm
----------
a=14deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min cc=17mm
----------
a=14deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
0000001501 RACK SENSOR
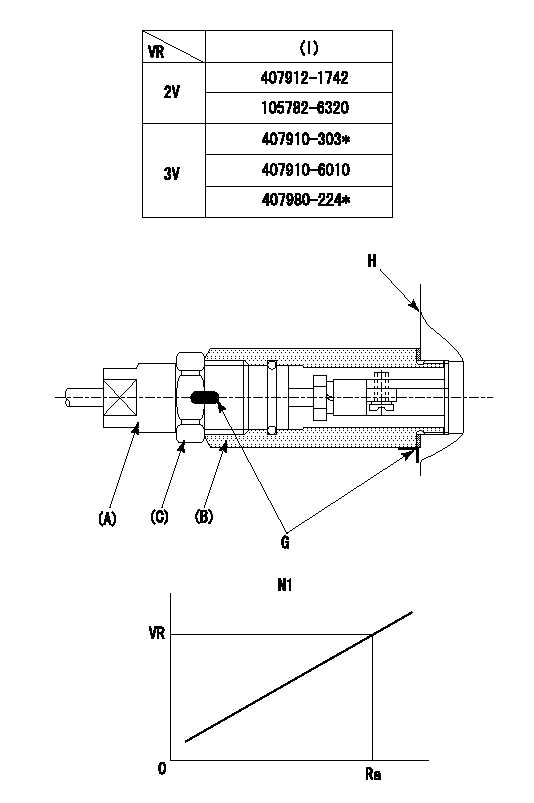
(VR) measurement voltage
(I) Part number of the control unit
(G) Apply red paint.
(H): End surface of the pump
1. Rack sensor adjustment (-0620)
(1)Fix the speed control lever at the full position
(2)Set the speed to N1 r/min.
(If the boost compensator is provided, apply boost pressure.)
(3)Adjust the bobbin (A) so that the rack sensor's output voltage is VR+-0.01.
(4)At that time, rack position must be Ra.
(5)Apply G at two places.
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the nut (F)
Connecting part between the joint (B) and the end surface of the pump (H)
----------
N1=1000r/min Ra=13.8mm
----------
----------
N1=1000r/min Ra=13.8mm
----------
0000001601 TAMPER PROOF

Tamperproofing-equipped boost compensator cover installation procedure
(A) After adjusting the boost compensator, tighten the bolts to remove the heads.
(1)Before adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten the screw to the specified torque.
(Tightening torque T = T1 maximum)
(2)After adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten to the specified torque to break off the bolt heads.
(Tightening torque T = T2)
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
0000001701 SPEED SENSOR
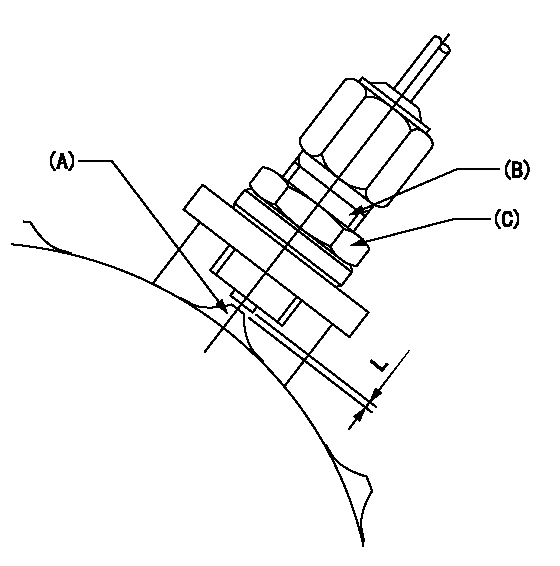
(A) Flyweight projection
(B) Pickup sensor
(c) Lock nut
Speed sensor installation
(1)Install the speed sensor so that the clearance between the sensor and the flyweight projection is L.
(This gap is the gap when the pickup sensor is returned 1.5 turns from where it contacts the flyweight tooth.)
----------
L=1.3~1.5mm
----------
----------
L=1.3~1.5mm
----------
Timing setting
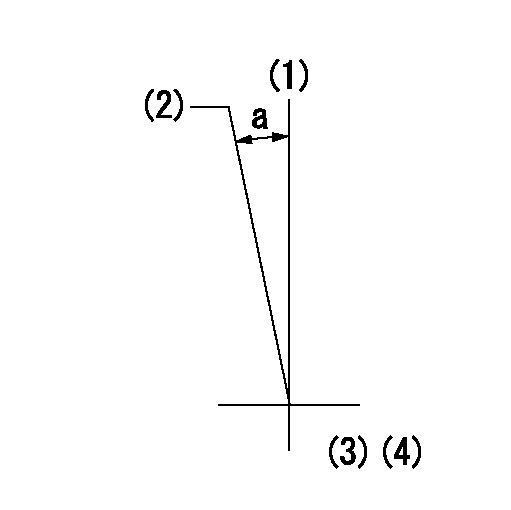
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=5deg
----------
a=(2deg)
----------
aa=5deg
----------
a=(2deg)
Information:
Cut apart used filters to see contaminants. Use a 6V790S FilterCutter
to cut the filter housing.
Maintenance for Engines Using Heavy Fuel
Engines operating on heavy fuel must be carefully monitored and maintained.Service intervals must be strictly observed. Operators must be trained toperform a thorough service inspection.
"As Needed" Periodic Activities
Test fuel as it is delivered. Identify contaminant levels immediately and notify appropriate operations personnel.
Before storage, test for compatibility between fuel in the tanks and the fuel being purchased. Keep the fuel in separate tanks if possible.
Use regular S.O.S oil analysis to determine if there are wear particles in the oil, and maintain the proper TBN level.
Request infrared analysis on used oils to determine the effects of burning heavy fuel on the crankcase oil.
Daily Activities
Maintain and monitor fuel treatment equipment.
Record engine temperatures to assure adequate jacket water temperature, aftercooler temperature, and air intake temperature.
If equipped with a turbocharger water wash attachment, wash the turbocharger exhaust turbine. It is necessary to remove deposits from the turbine side of the turbocharger. (A washer attachment which does this is available on 3600 Family Engines.)
Check exhaust thermocouples and record exhaust temperatures. Be alert for worn exhaust valves.
Measure valve stem projection when new; use a stationary point such asthe valve cover gasket surface for a reference point. Record the measurementsfor each valve for later follow-up measurements. If valve stem projection movesmore than 1.25 mm (.050 in.) consider disassembly to find the reason. Anotherway to observe valve face wear is to measure and record changes on valve lashover a period of time.
Monitor fuel and oil filter differentials every shift. Check for filter plugging.
Drain settling and fuel tank bottoms daily. Take note if there is excessive water or sediment.
Every 1000 Hours
Check one cylinder head for exhaust valve seating and carbon build-up. Check the fuel injectors for adequate nozzle spray pattern. Make sure the valve rotators are operating.
Clean the turbocharger (exhaust turbine) (3500 and 3600 Family Engines without washers).
Operating the Engine at Low Load
If you're expecting to operate your engine at part load for extendedperiods, switch to No.2 diesel fuel or marine diesel oil. (Make sure the fuelinjectors are not run without fuel during the switch.)
The following chart shows the relationship between engine load and length oftime. It will guide you on what type of fuel to burn in light load applications.
Chart with time and numbers.
Other Heavy Fuel Tips
Here are some things to keep in mind when using heavy fuels.
Cut apart used filters to see contaminants. As contamination levels increase, the quality of diesel fuel is generally decreasing.
As fuel quality decreases, it becomes even more important to have good fuel treatment systems. The treatment system can sometimes compensate for poor fuel quality. ..but there is less margin for error with a system that is not working correctly.
Often, diesel engines cannot operate on fuel that is straight from the fuel tank (bunkered).
Viscosity does not relate to quality. Do not use fuel thickness
Have questions with 106676-2810?
Group cross 106676-2810 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
106676-2810
9 400 617 465
ME441574
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D24TL
6D24TL
