Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
F 019 Z20 146
f019z20146
ZEXEL
106675-4890
1066754890
KOMATSU
6152721620
6152721620
Rating:
Service parts 106675-4890 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
27.5{280}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106675-4890
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
F 019 Z20 146
f019z20146
ZEXEL
106675-4890
1066754890
KOMATSU
6152721620
6152721620
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106675-4890
F 019 Z20 146
6152721620 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SAA6D125 K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
SAA6D125 K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131425-2120
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.2
4.15
4.25
Rack position
Point A or more. R=A
Point A or more. R=A
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.5
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
196.5
193.5
199.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
46.9
46.9
Boost pressure
mmHg
352
352
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
16.5
15
18
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
9.4
Boost pressure
kPa
6.7
5.4
8
Boost pressure
mmHg
50
40
60
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
10.1
Boost pressure
kPa
13.3
12
14.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
100
90
110
Boost compensator adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R1(12.3)
Boost pressure
kPa
33.6
33.6
33.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
252
252
252
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
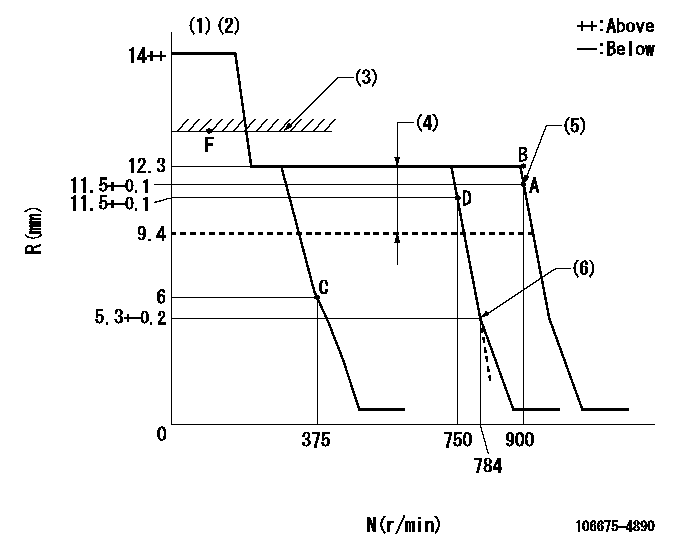
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)At excess fuel lever operation (at boost pressure 0): L1
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(5)Set at delivery
(6)Idle sub spring setting: L2.
----------
K=7 L1=13.5+0.2mm BCL=(2.9)mm L2=5.3-0.5mm
----------
----------
K=7 L1=13.5+0.2mm BCL=(2.9)mm L2=5.3-0.5mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
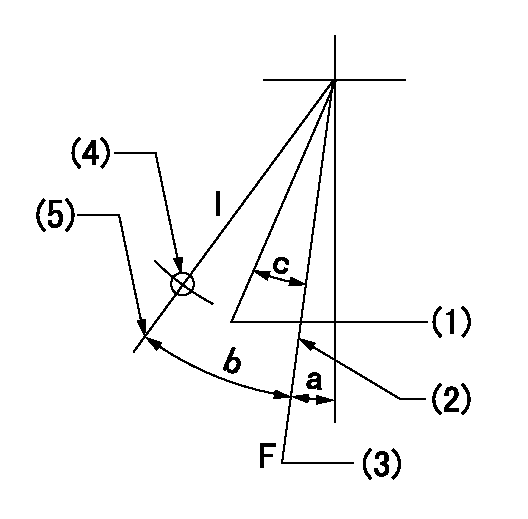
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)When pump speed set at aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
(3)Set the pump speed at bb.
(4)Use the hole above R = cc
(5)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=750r/min bb=900r/min cc=90mm
----------
a=5deg+-5deg b=21deg+-5deg c=6deg+-5deg
----------
aa=750r/min bb=900r/min cc=90mm
----------
a=5deg+-5deg b=21deg+-5deg c=6deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
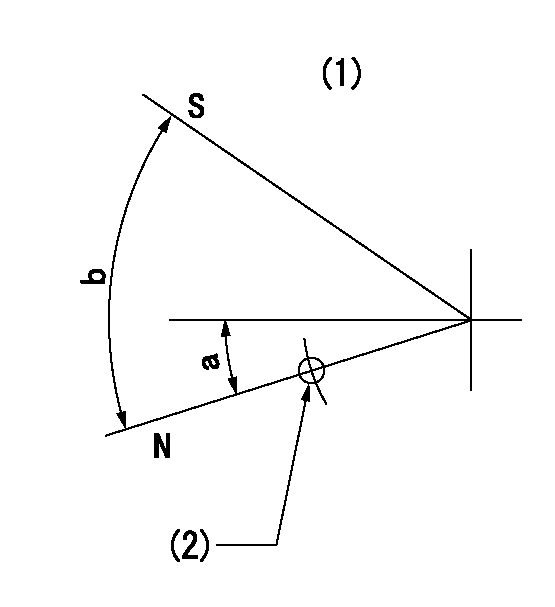
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)No return spring
(2)Use hole at R = aa (left hand side)
----------
aa=27mm
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
aa=27mm
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
0000001101
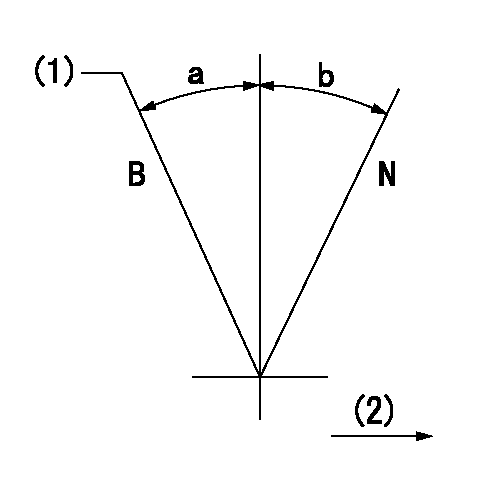
N:Normal
B:When boosted
(1)Rack position = aa at boost pressure 0.
(2)Drive side
----------
aa=13.5+0.2mm
----------
a=(11deg) b=(15deg)
----------
aa=13.5+0.2mm
----------
a=(11deg) b=(15deg)
Timing setting
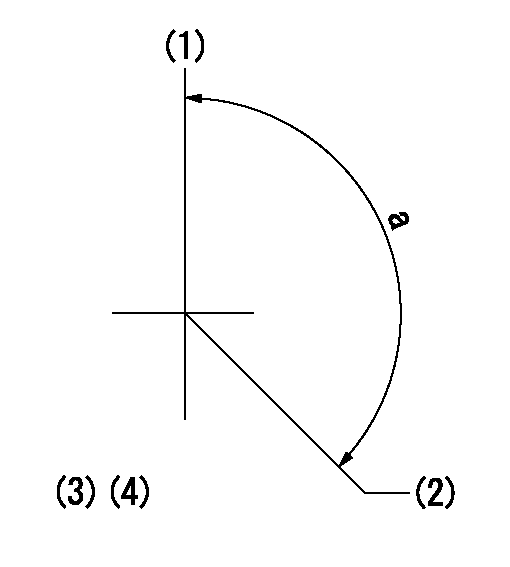
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)Rack position = at least aa
(4)-
----------
aa=11.5mm
----------
a=(140deg)
----------
aa=11.5mm
----------
a=(140deg)
Information:
Fuel Return Manifold Leaks and/or Leaks at Fuel Return Boots or Connectors ... Remove the valve cover(s). Make a visual inspection of the fuel return manifold, fuel return boots, and connectors. Boots and/or connectors with damage, or wrongly installed, will let fuel get into the oil. If you do not see leaks during the visual inspection, start the engine and visually inspect while the engine is running. Boots and/or connectors can cause leakage if the fuel return line has a restriction.Loose Fuel Injection Nozzle Nut(s) ... A loose fuel injection nozzle nut can cause fuel leakage. Tighten nozzle nut(s) to 30 5 lb. ft. (4,1 0,7 mkg).Defective Fuel Nozzle(s) ... Check fuel nozzle(s) for cracks in inlet fitting, inlet line, or nozzle body. If you do not see a crack, start the engine and visually inspect each nozzle for leaks. Cracks in the inlet fitting and nozzle body are nozzle defects. Cracks in the inlet line are caused by the nozzle not being tightened correctly.Defective Diaphragm in Fuel Transfer Pump ... A defective diaphragm will cause fuel leakage through the orifice in the fuel transfer pump housing. If you do not see leakage, make sure the orifice is open. Start the engine and again look for possible leakage. If the pump has leaks, install a new pump.Loose Fuel Injection Pump Retaining Bushing ... Loose retaining bushings will not hold the barrel of the injection pump correctly against the seat in the pump housing and fuel can get into the crankcase. A loose bushing can cause the engine to misfire or cause fuel leakage to the outside of the pump housing. Remove the fuel lines at the fuel injection pump and tighten each retaining bushing to 100 10 lb. ft. (13,8 1,4 mkg). To tighten the three rear retaining bushings the pump housing must be removed from the engine.Fuel Leaks Between Injection Pump Barrel(s) and Injection Pump Housing ... Dirt or foreign material under the barrel of the fuel injection pump will cause fuel leakage into the crankcase. Remove the housing of the fuel injection pump and the governor from the engine. Remove the plunger and barrel assemblies from the pump housing. Inspect the seat area of the barrel and housing. Be sure the seat is smooth and flat. Check the timing dimension and adjust as necessary. Install the fuel injection pumps. *Worn Fuel Injection Pumps ... It is possible for one or more of the plunger and barrel assemblies to be worn enough to cause fuel leakage between the plunger and barrel. Remove the housing of the fuel injection pump and the governor from the engine. Test the fuel injection pump on the test bench for fuel injection pumps. If a test bench is not available, install new plunger and barrel assemblies in place of those with damage.*Authorized dealers are equipped with the necessary tools and personnel familiar with disassembly and assembly procedures to perform these services.
Have questions with 106675-4890?
Group cross 106675-4890 ZEXEL
Komatsu
Komatsu
Komatsu
Niigata-Tekkou
Komatsu
Niigata-Tekkou
Komatsu
106675-4890
F 019 Z20 146
6152721620
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SAA6D125
SAA6D125
