Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 225
9400611225
ZEXEL
106675-4541
1066754541
Rating:
Service parts 106675-4541 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6152-12-3100
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
27.5{280}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106675-4541
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 225
9400611225
ZEXEL
106675-4541
1066754541
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131425-2120
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.8
3.75
3.85
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
8.5
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
139.5
137.5
141.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
46.7
46.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
350
350
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
5.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
11
9.5
12.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
125
115
135
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Rack position
R1-0.7
Boost pressure
kPa
18.7
16
21.4
Boost pressure
mmHg
140
120
160
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Rack position
R1(8.5)
Boost pressure
kPa
33.3
26.6
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
250
200
300
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
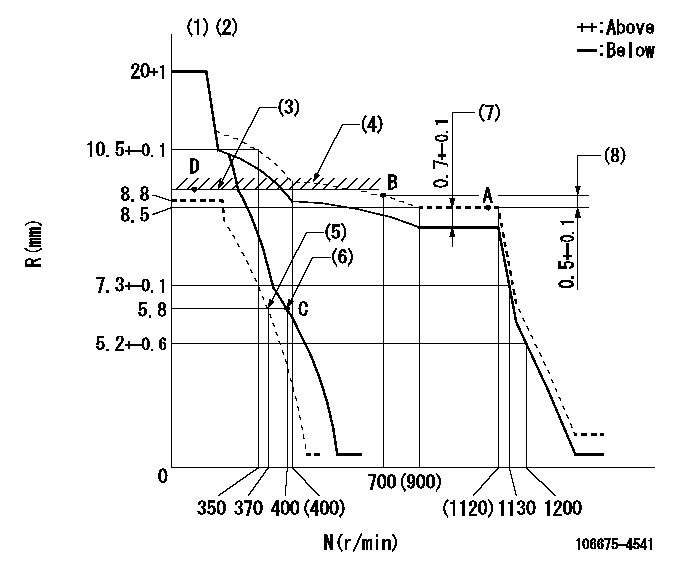
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)The torque control spring must does not have a set force.
(5)Set idle sub-spring
(6)Main spring setting
(7)Boost compensator stroke
(8)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=18 N1=1100r/min N2=700r/min
----------
----------
K=18 N1=1100r/min N2=700r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
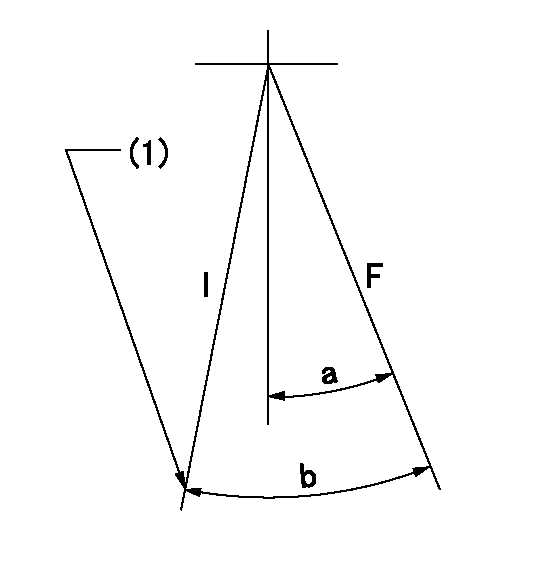
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=23deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=23deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa, speed = bb (stamp at delivery)
(2)Normal
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min
----------
a=33deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min
----------
a=33deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
Timing setting
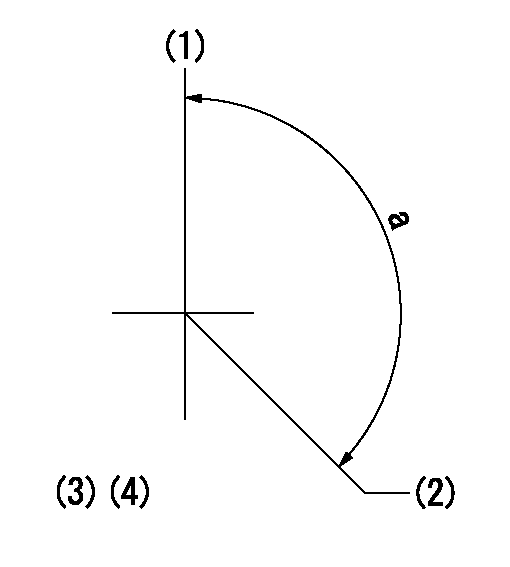
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(150deg)
----------
----------
a=(150deg)
Information:
Introduction
Procedure to prevent injector Plunger Spring failure due to inadequate fuel system priming.
The low-pressure fuel system must be primed after injector replacement or other repair to the low-pressure fuel system circuit which may allow air to enter the system.
Inadequate priming can result in air being present in the low-pressure fuel system and inside the injectors.
Attempting to start the engine without adequate priming may result in an early hour failure of the injector plunger spring.
Follow the procedure below to prevent injector failure due to inadequate priming.
DO NOT START THE ENGINE WITHOUT PRIMING THE FUEL SYSTEM
Illustration 1 g03735591
Damaged plunger spring due to improper fuel system primingFuel System Priming Procedure:
Disconnect the injector harness at the valve cover.
Use the hand primer to fill the fuel system. Pump until the hand primer becomes too hard to depress by hand.
Crank the engine 3 times for 15 seconds each. Reapply the hand primer after each cranking cycle.
Once the hand primer remains hard to depress after the 15 second crank, reconnect the injector harness and start the engine.
Clear any related fault codes (ET) that were logged while cranking the engine with the injector harness disconnected.
Illustration 2 g03736011
Procedure to prevent injector Plunger Spring failure due to inadequate fuel system priming.
The low-pressure fuel system must be primed after injector replacement or other repair to the low-pressure fuel system circuit which may allow air to enter the system.
Inadequate priming can result in air being present in the low-pressure fuel system and inside the injectors.
Attempting to start the engine without adequate priming may result in an early hour failure of the injector plunger spring.
Follow the procedure below to prevent injector failure due to inadequate priming.
DO NOT START THE ENGINE WITHOUT PRIMING THE FUEL SYSTEM
Illustration 1 g03735591
Damaged plunger spring due to improper fuel system primingFuel System Priming Procedure:
Disconnect the injector harness at the valve cover.
Use the hand primer to fill the fuel system. Pump until the hand primer becomes too hard to depress by hand.
Crank the engine 3 times for 15 seconds each. Reapply the hand primer after each cranking cycle.
Once the hand primer remains hard to depress after the 15 second crank, reconnect the injector harness and start the engine.
Clear any related fault codes (ET) that were logged while cranking the engine with the injector harness disconnected.
Illustration 2 g03736011

