Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106672-3250
1066723250
HINO
220004982A
220004982a

Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106672-3250
1066723250
HINO
220004982A
220004982a
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve (drive side)
134424-1420
Overflow valve opening pressure (drive side)
kPa
162
147
177
Overflow valve opening pressure (drive side)
kgf/cm2
1.65
1.5
1.8
Overflow valve (governor side)
134424-1720
Overflow valve opening pressure (governor side)
kPa
162
147
177
Overflow valve opening pressure (governor side)
kgf/cm2
1.65
1.5
1.8
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
4.5
4.44
4.5
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
8.8
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
173
171
175
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
39.3
39.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
295
295
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
9.1
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
183.5
180.5
186.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-5
5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
39.3
39.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
295
295
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
8.8
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
171
165
177
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
39.3
39.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
295
295
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
8.4
Pump speed
r/min
1050
1050
1050
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
160.5
157.5
163.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-5
5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
39.3
39.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
295
295
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
7.4
Pump speed
r/min
1150
1150
1150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
137
132
142
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
39.3
39.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
295
295
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
F
Rack position
9.2+0.2
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
186
180
192
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
39.3
39.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
295
295
Rack limit
*
Injection quantity adjustment_07
Adjusting point
G
Rack position
6.4
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
86
84
88
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_08
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
4.6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
11
8
14
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Rack position
6.4
Boost pressure
kPa
9.3
9.3
11.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
70
70
85
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Rack position
8.8
Boost pressure
kPa
26
26
26
Boost pressure
mmHg
195
195
195
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment

N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Lever ratio: RT
(2)Target shim dimension: TH
(3)RACK LIMIT: RAL
(4)Set idle at delivery
(5)Damper spring setting: DL
----------
RT=0.8 TH=1.5mm RAL=9.2+0.2mm DL=3.6-0.2mm
----------
----------
RT=0.8 TH=1.5mm RAL=9.2+0.2mm DL=3.6-0.2mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=8deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=8deg+-5deg
0000000901

F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Set point I
(2)At delivery
----------
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=45deg+-3deg c=47deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=45deg+-3deg c=47deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
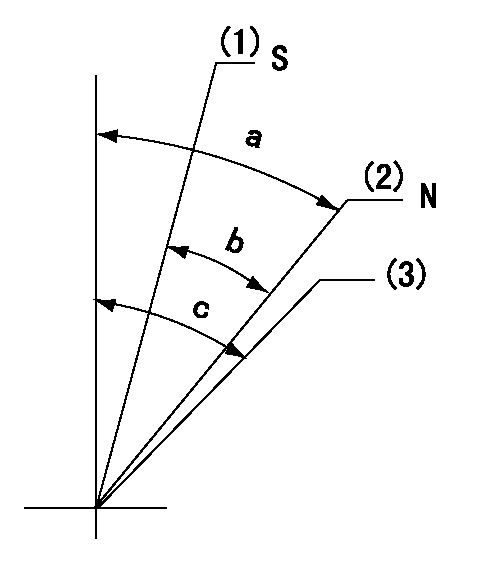
N:Engine manufacturer's normal use
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa, stopper bolt setting
(2)Rack position bb
(3)Free (at delivery)
----------
aa=2.5-0.5mm bb=12mm
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=30deg+-5deg c=(50deg)
----------
aa=2.5-0.5mm bb=12mm
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=30deg+-5deg c=(50deg)
0000001501 RACK SENSOR
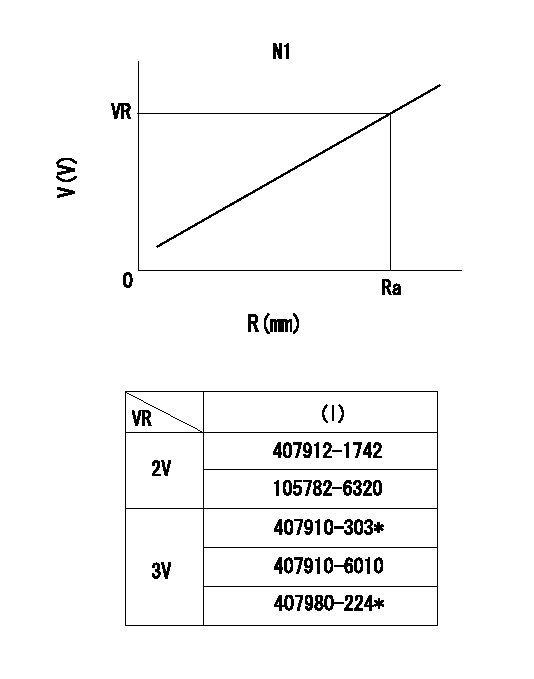
R:Rack position (mm)
V:Voltage (V)
After installing the rack sensor, confirm the output value (VR).
----------
N1=650r/min Ra=8.8mm VR=1.7+-0.1V
----------
----------
N1=650r/min Ra=8.8mm VR=1.7+-0.1V
----------
Timing setting
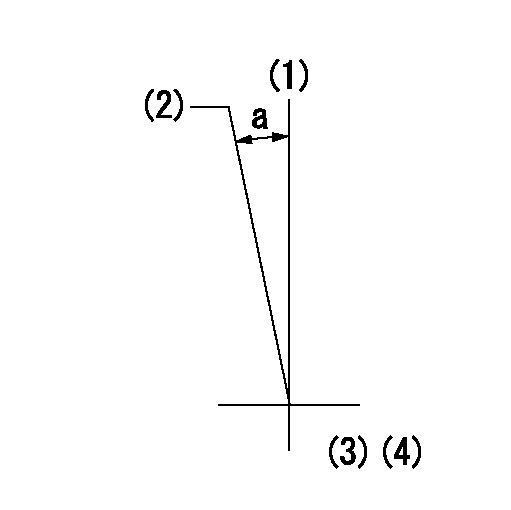
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
General Information
Learn principles of operation of engines from "Basic Engine" in Fundamentals of Service Manual 30 - ENGINES.Design Characteristics
The 3-164D, 3-179D, 4-219D, 4-239D, 4-276D, 6-329D, 6-359D, and 6-414D engines have:1. Internal combustion2. Four strokes per cycle3. In-line type cylinder block4. Diesel fueling5. Valves in cylinder head6. Natural aspiration7. Liquid coolant8. Pressure lubricationThe 4-239T, 4-276T, 6-359T, and 6-414T engines have:1. Internal combustion2. Four strokes per cycle3. In-line type cylinder block4. Diesel fueling5. Valves in cylinder head6. Turbocharger7. Liquid coolant8. Pressure lubricationFront Reference
Fig. 1-Water PumpThe water pump (Fig. 1) end is the "front" of the engine.Direction of Crankshaft Rotation
Fig. 2-Crankshaft RotationThe crankshaft turns clockwise when viewed from the water pump end.Firing Order
Fig. 3-Cylinder Arrangement3-164 and 3-179 EngineFiring order is: 1-2-3
Fig. 4-Cylinder Arrangement4-219, 4-239, and 4-276 EnginesFiring order is: 1-3-4-2
Fig. 5-Cylinder Arrangement6-329, 6-359, and 6-414 EnginesFiring order is: 1-5-3-6-2-4
Learn principles of operation of engines from "Basic Engine" in Fundamentals of Service Manual 30 - ENGINES.Design Characteristics
The 3-164D, 3-179D, 4-219D, 4-239D, 4-276D, 6-329D, 6-359D, and 6-414D engines have:1. Internal combustion2. Four strokes per cycle3. In-line type cylinder block4. Diesel fueling5. Valves in cylinder head6. Natural aspiration7. Liquid coolant8. Pressure lubricationThe 4-239T, 4-276T, 6-359T, and 6-414T engines have:1. Internal combustion2. Four strokes per cycle3. In-line type cylinder block4. Diesel fueling5. Valves in cylinder head6. Turbocharger7. Liquid coolant8. Pressure lubricationFront Reference
Fig. 1-Water PumpThe water pump (Fig. 1) end is the "front" of the engine.Direction of Crankshaft Rotation
Fig. 2-Crankshaft RotationThe crankshaft turns clockwise when viewed from the water pump end.Firing Order
Fig. 3-Cylinder Arrangement3-164 and 3-179 EngineFiring order is: 1-2-3
Fig. 4-Cylinder Arrangement4-219, 4-239, and 4-276 EnginesFiring order is: 1-3-4-2
Fig. 5-Cylinder Arrangement6-329, 6-359, and 6-414 EnginesFiring order is: 1-5-3-6-2-4