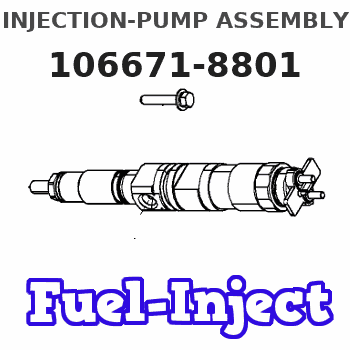
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 610 894
9400610894
ZEXEL
106671-8801
1066718801
HINO
220009111A
220009111a
Rating:
Service parts 106671-8801 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
23600-2412E
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
16.7{170}/23.5{240}
14.
NOZZLE
Include in #1:
106671-8801
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 610 894
9400610894
ZEXEL
106671-8801
1066718801
HINO
220009111A
220009111a
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-4420
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
162
147
177
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.65
1.5
1.8
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
3.9
3.84
3.9
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.9
Pump speed
r/min
550
550
550
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
189.5
187.5
191.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
53.3
53.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
400
400
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
9.45
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
169.5
166.5
172.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-5
5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
53.3
53.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
400
400
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
3.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
250
250
250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10.5
7.5
13.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
200
195
205
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
53.3
53.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
400
400
Rack limit
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
110
110
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
550
550
550
Rack position
(7.8)
Boost pressure
kPa
13.3
13.3
15.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
100
100
115
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
550
550
550
Rack position
9.9
Boost pressure
kPa
40
40
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
300
300
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
700--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
650
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1000
Advance angle
deg.
4
3.7
4.3
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
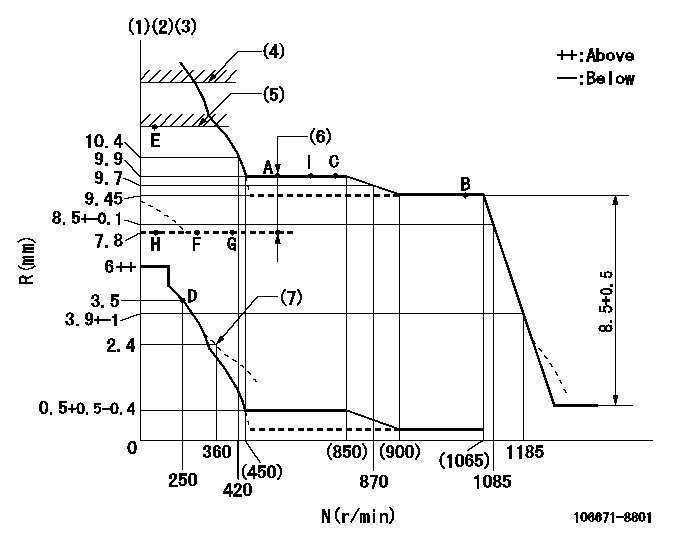
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Lever ratio: RT
(2)Target shim dimension: TH
(3)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(4)Stop lever setting: R1
(5)RACK LIMIT
(6)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(7)Damper spring setting
----------
RT=1 TH=2.3mm R1=(12.1)+0.5mm BCL=(2.1)mm
----------
----------
RT=1 TH=2.3mm R1=(12.1)+0.5mm BCL=(2.1)mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=12.5deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=12.5deg+-5deg
0000000901
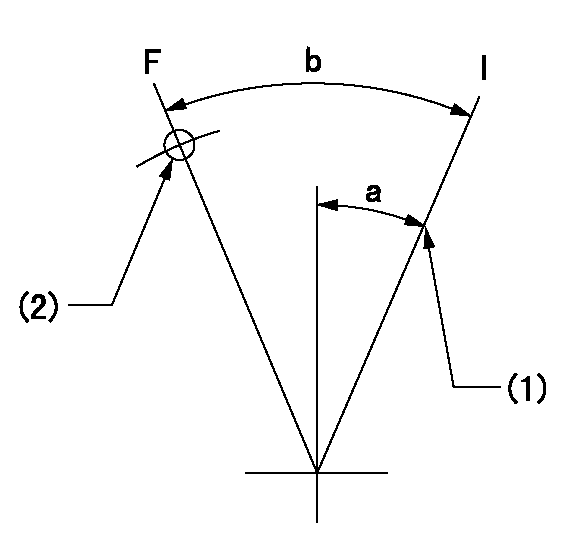
F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
(2)Use the hole at R = aa
----------
aa=50mm
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=34.5deg+-3deg
----------
aa=50mm
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=34.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
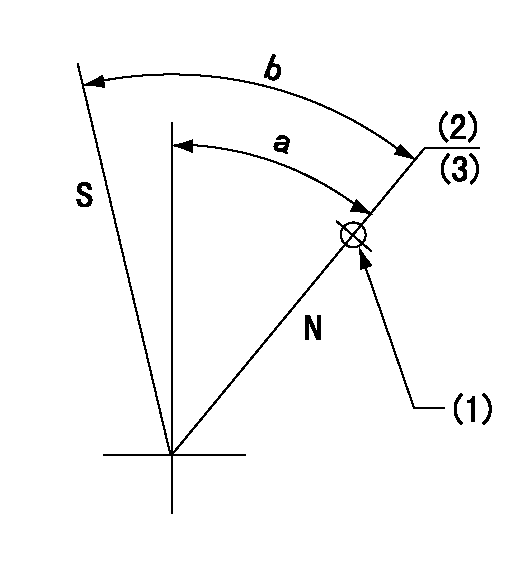
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Set the rack position at bb before adjusting the governor
(3)Set the stopper screw. (After setting, apply red paint.)
----------
aa=36mm bb=(12.1)+0.5mm
----------
a=35deg+-5deg b=39deg+-5deg
----------
aa=36mm bb=(12.1)+0.5mm
----------
a=35deg+-5deg b=39deg+-5deg
0000001501 ACS
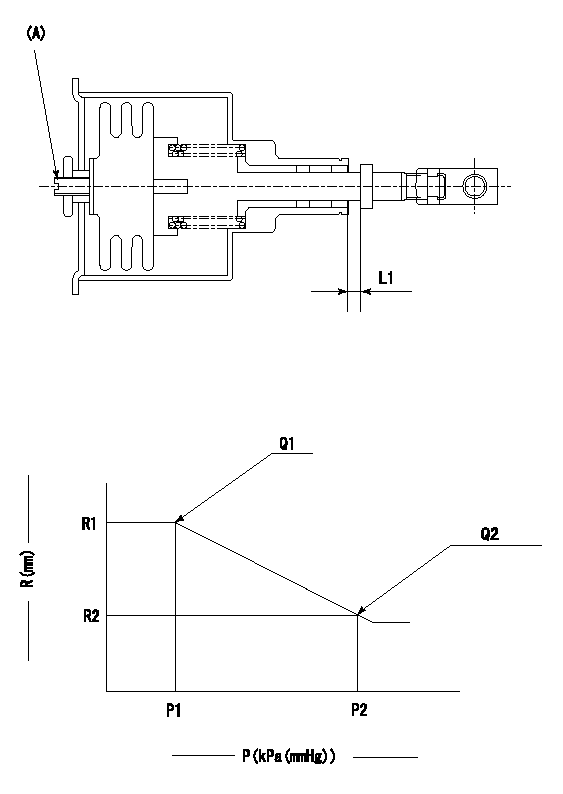
(A) Set screw
1. Aneroid compensator unit adjustment
Screw in (A) to obtain L1.
2. Adjustment following governor installation
(1)Set the speed of the pump to N1 r/min and fix the control lever at the full set position.
(2)Screw in the aneroid compensator to obtain the performance shown in the graph above.
----------
N1=1000r/min L1=(0.1~0.5)mm
----------
R1=9.45mm R2=- P1=52+-0.7kPa(390+-5mmHg) P2=- Q1=169.5+-3cm3/1000st Q2=-
----------
N1=1000r/min L1=(0.1~0.5)mm
----------
R1=9.45mm R2=- P1=52+-0.7kPa(390+-5mmHg) P2=- Q1=169.5+-3cm3/1000st Q2=-
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
Bulk storage
Follow all local regulations covering bulk storage tanks. Follow proper tank construction guidelines. Tank volume typically should be 110% of planned capacity. Appropriately vent indoor tanks. Plan for control of overflow of the tank. Heat tanks that dispense DEF in cold climates.Bulk tank breathers should be fitted with filtration to keep airborne debris from entering the tank. Desiccant breathers should not be used because water will be absorbed, which potentially can alter DEF concentration.Handling
Follow all local regulations covering transport and handling. DEF transport temperature is recommended to be −5° C (23° F) to 25° C (77° F). All transfer equipment and intermediate containers should be used exclusively for DEF. Containers should not be reused for any other fluids. Ensure that transfer equipment is made from DEF-compatible materials. Recommended material for hoses and other non-metallic transfer equipment include:
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Fluoroelastomer (FKM)
Ethylene Propylene Diane Ionomer (EPDM)The condition of hoses and other nonmetallic items that are used with DEF should be monitored for signs of degradation. DEF leaks are easily recognizable by white urea crystals that accumulate at the site of the leak. Solid urea can be corrosive to galvanized or unalloyed steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. Leaks should be repaired immediately to avoid damage to surrounding hardware.Cleanliness
Contaminants can degrade the quality and life of DEF. Filtering DEF is recommended when dispensed into the DEF tank. Filters should be compatible with DEF and should be used exclusively with DEF. Check with the filter supplier to confirm compatibility with DEF before using. Mesh-type filters using compatible metals, such as stainless steel, are recommended. Paper (cellulose) media and some synthetic filter media are not recommended because of degradation during use.Care should be taken when dispensing DEF. Spills should be cleaned immediately. Machine or engine surfaces should be wiped clean and rinsed with water. Caution should be used when dispensing DEF near an engine that has recently been running.Note: Spilling DEF onto hot components may cause the release of ammonia vapors. Do not breathe ammonia vapors. Do not clean up any spills with bleach.Stability
DEF fluid is stable when stored and handled properly. The quality of DEF rapidly degrades when stored at high temperatures. The ideal storage temperature for DEF is between −9° C (15.8° F) and 25° C (77° F). DEF that is stored above 35° C (95° F) for longer than 1 month must be tested before use. Testing should evaluate Urea Percentage, Alkalinity as NH3 and Biuret content.The length of storage of DEF is listed in the following table:
Table 3
Storage Temperature Expected DEF Life
Below 25° C (77° F) 18 months
25° C (77° F) to 30° C (86° F) 12 months
30° C (86° F) to 35° C (95° F) 6 months
Above 35° C (95° F) test quality before use Refer to "ISO 22241" document series for more information about DEF quality control.Note: Dispose of all fluids according to applicable regulations and mandates.General Characteristics of DEF
For detailed information on the requirements and
Follow all local regulations covering bulk storage tanks. Follow proper tank construction guidelines. Tank volume typically should be 110% of planned capacity. Appropriately vent indoor tanks. Plan for control of overflow of the tank. Heat tanks that dispense DEF in cold climates.Bulk tank breathers should be fitted with filtration to keep airborne debris from entering the tank. Desiccant breathers should not be used because water will be absorbed, which potentially can alter DEF concentration.Handling
Follow all local regulations covering transport and handling. DEF transport temperature is recommended to be −5° C (23° F) to 25° C (77° F). All transfer equipment and intermediate containers should be used exclusively for DEF. Containers should not be reused for any other fluids. Ensure that transfer equipment is made from DEF-compatible materials. Recommended material for hoses and other non-metallic transfer equipment include:
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Fluoroelastomer (FKM)
Ethylene Propylene Diane Ionomer (EPDM)The condition of hoses and other nonmetallic items that are used with DEF should be monitored for signs of degradation. DEF leaks are easily recognizable by white urea crystals that accumulate at the site of the leak. Solid urea can be corrosive to galvanized or unalloyed steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. Leaks should be repaired immediately to avoid damage to surrounding hardware.Cleanliness
Contaminants can degrade the quality and life of DEF. Filtering DEF is recommended when dispensed into the DEF tank. Filters should be compatible with DEF and should be used exclusively with DEF. Check with the filter supplier to confirm compatibility with DEF before using. Mesh-type filters using compatible metals, such as stainless steel, are recommended. Paper (cellulose) media and some synthetic filter media are not recommended because of degradation during use.Care should be taken when dispensing DEF. Spills should be cleaned immediately. Machine or engine surfaces should be wiped clean and rinsed with water. Caution should be used when dispensing DEF near an engine that has recently been running.Note: Spilling DEF onto hot components may cause the release of ammonia vapors. Do not breathe ammonia vapors. Do not clean up any spills with bleach.Stability
DEF fluid is stable when stored and handled properly. The quality of DEF rapidly degrades when stored at high temperatures. The ideal storage temperature for DEF is between −9° C (15.8° F) and 25° C (77° F). DEF that is stored above 35° C (95° F) for longer than 1 month must be tested before use. Testing should evaluate Urea Percentage, Alkalinity as NH3 and Biuret content.The length of storage of DEF is listed in the following table:
Table 3
Storage Temperature Expected DEF Life
Below 25° C (77° F) 18 months
25° C (77° F) to 30° C (86° F) 12 months
30° C (86° F) to 35° C (95° F) 6 months
Above 35° C (95° F) test quality before use Refer to "ISO 22241" document series for more information about DEF quality control.Note: Dispose of all fluids according to applicable regulations and mandates.General Characteristics of DEF
For detailed information on the requirements and