Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 616 936
9400616936
ZEXEL
106671-7421
1066717421
MITSUBISHI
ME056612
me056612

Rating:
Service parts 106671-7421 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME056329
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7(180)/21.6(220)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106671-7421
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 616 936
9400616936
ZEXEL
106671-7421
1066717421
MITSUBISHI
ME056612
me056612
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106671-7421
9 400 616 936
ME056612 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D22 * K
6D22 * K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-4620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.75
4.85
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
8.1
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
109
106.3
111.7
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
F
Rack position
5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
16.5
14
19
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(8.1)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
109
108
110
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
5.7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
16.5
14
19
Fixing the rack
*
Remarks
(check)
(check)
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
150
110
190
Fixing the lever
*
Remarks
After startup boost setting
After startup boost setting
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
950
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1050
Advance angle
deg.
2.2
1.7
2.7
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1150
Advance angle
deg.
5.5
5
6
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
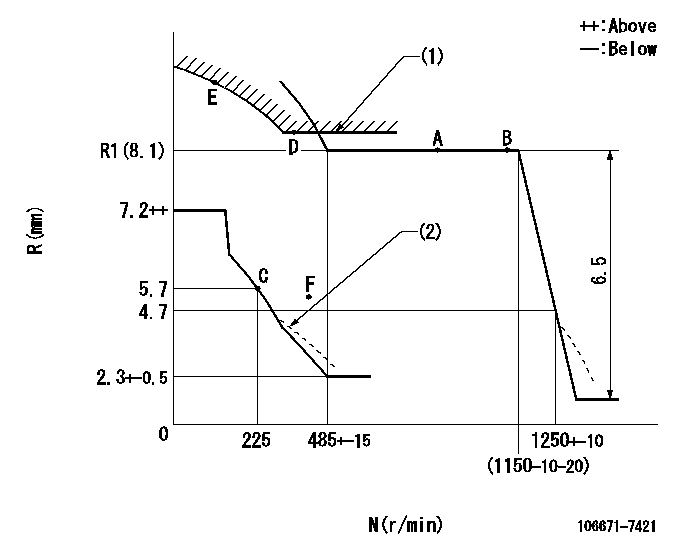
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Excess fuel setting for starting: SXL
(2)Damper spring setting: DL
----------
SXL=R1+1+0.8mm DL=4.5-0.2mm
----------
----------
SXL=R1+1+0.8mm DL=4.5-0.2mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
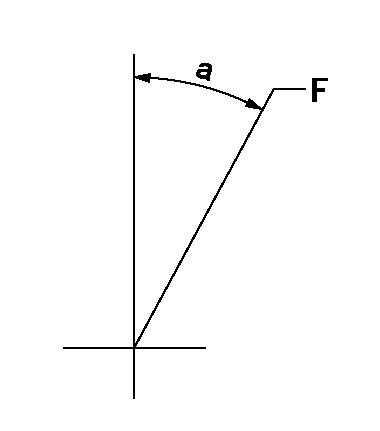
F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=27deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=27deg+-5deg
0000000901
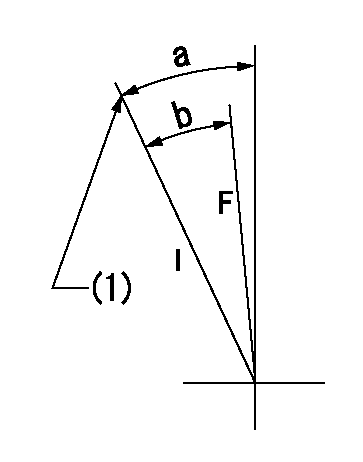
F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=24deg+-5deg b=21.5deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=24deg+-5deg b=21.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Set the stopper bolt at rack position = bb
(3)Free (at shipping)
----------
aa=16.6mm bb=4.1-0.5mm
----------
a=35deg+-5deg b=61.5deg+7deg-5deg c=(6deg)
----------
aa=16.6mm bb=4.1-0.5mm
----------
a=35deg+-5deg b=61.5deg+7deg-5deg c=(6deg)
Timing setting
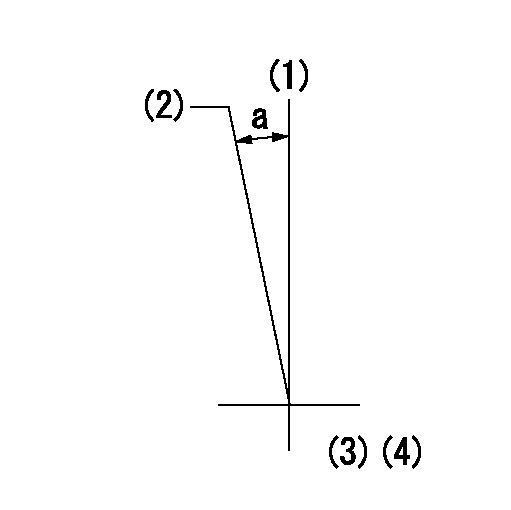
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(7deg)
----------
----------
a=(7deg)
Information:
Preferred Fuel Grades
The two main types of diesel fuel that are available for your truck engine are typically low sulfur No. 1 diesel fuel and low sulfur No. 2 diesel fuel. Although No. 2 diesel fuels are the most commonly used fuel, No. 1 diesel fuels or a blend of No. 1 diesel fuel and No. 2 diesel fuel is best suited for cold weather operation.There are three major differences between No. 1 diesel fuel and No. 2 diesel fuel.
No. 1 diesel fuel has a lower cloud point. The fuel cloud point is the temperature when a haze appears in the fuel. When the temperature falls below the melting point of the paraffins a haze results. Paraffins are a wax that naturally occurs in petroleum products. The wax can alter the fuel characteristics in cold weather. Solid wax can fill the fuel filters. The solidified wax will stop the flow of fuel. The cloud point must not exceed the lowest expected ambient temperature or other precautions must be taken. Installing a fuel heater is the most practical way to address problems with the cloud point.
No. 1 diesel fuel has a lower pour point. The pour point of the fuel is the temperature that is 3 °C (5 °F) above the temperature that is required for fuel to flow. Fuel stops flowing below the pour point. A fuel's pour point should be at least 6°C (10°F) below the lowest ambient temperature that is required for engine start-up and for engine operation.
No. 1 diesel fuel has a lower rating for kJ or Btu per unit volume of fuel than the average No. 2 diesel fuel.
Table 1
Fuel Recommendations for Ambient Temperatures
Fuel Type Temperature Range(1)
No. 2 Above 0 °C (32 °F)
No. 1 −30 °C (−22 °F) to 0 °C (32 °F)
(1) Contact your Caterpillar dealer for information regarding the acceptable fuels and/or the acceptable blends, if there is potential for colder operating temperatures.No. 2 diesel fuel may be blended with No. 1 diesel fuel or blended with kerosene in the following proportions in order to achieve the capability to flow at lower temperatures.
Table 2
Modification of No. 2 Fuel
Ambient Temperature No. 2 Diesel Fuel (%)(1) No. 1 Diesel Fuel(1)
Above −10 °C (14 °F) 90 10
−10 °C (14 °F) to −20 °C (−4 °F) 70 30
Temperatures below −20 °C (−4 °F) 50 50
(1) Never blend the fuel with gasoline under any circumstances.No. 1 diesel fuel does not have the same energy per unit volume as No. 2 diesel fuel. No. 1 diesel fuel has less energy per unit volume. A reduction in power and fuel efficiency may be noticed with No. 1 diesel fuel or a blend of No. 1 diesel fuel and No. 2 diesel fuel but other operating effects should not be experienced.Check the type of fuel or the fuel blend that is being used before troubleshooting for poor performance during the winter. Be aware of these values when you purchase diesel fuel. Anticipate the average outside temperature for the area for operation
The two main types of diesel fuel that are available for your truck engine are typically low sulfur No. 1 diesel fuel and low sulfur No. 2 diesel fuel. Although No. 2 diesel fuels are the most commonly used fuel, No. 1 diesel fuels or a blend of No. 1 diesel fuel and No. 2 diesel fuel is best suited for cold weather operation.There are three major differences between No. 1 diesel fuel and No. 2 diesel fuel.
No. 1 diesel fuel has a lower cloud point. The fuel cloud point is the temperature when a haze appears in the fuel. When the temperature falls below the melting point of the paraffins a haze results. Paraffins are a wax that naturally occurs in petroleum products. The wax can alter the fuel characteristics in cold weather. Solid wax can fill the fuel filters. The solidified wax will stop the flow of fuel. The cloud point must not exceed the lowest expected ambient temperature or other precautions must be taken. Installing a fuel heater is the most practical way to address problems with the cloud point.
No. 1 diesel fuel has a lower pour point. The pour point of the fuel is the temperature that is 3 °C (5 °F) above the temperature that is required for fuel to flow. Fuel stops flowing below the pour point. A fuel's pour point should be at least 6°C (10°F) below the lowest ambient temperature that is required for engine start-up and for engine operation.
No. 1 diesel fuel has a lower rating for kJ or Btu per unit volume of fuel than the average No. 2 diesel fuel.
Table 1
Fuel Recommendations for Ambient Temperatures
Fuel Type Temperature Range(1)
No. 2 Above 0 °C (32 °F)
No. 1 −30 °C (−22 °F) to 0 °C (32 °F)
(1) Contact your Caterpillar dealer for information regarding the acceptable fuels and/or the acceptable blends, if there is potential for colder operating temperatures.No. 2 diesel fuel may be blended with No. 1 diesel fuel or blended with kerosene in the following proportions in order to achieve the capability to flow at lower temperatures.
Table 2
Modification of No. 2 Fuel
Ambient Temperature No. 2 Diesel Fuel (%)(1) No. 1 Diesel Fuel(1)
Above −10 °C (14 °F) 90 10
−10 °C (14 °F) to −20 °C (−4 °F) 70 30
Temperatures below −20 °C (−4 °F) 50 50
(1) Never blend the fuel with gasoline under any circumstances.No. 1 diesel fuel does not have the same energy per unit volume as No. 2 diesel fuel. No. 1 diesel fuel has less energy per unit volume. A reduction in power and fuel efficiency may be noticed with No. 1 diesel fuel or a blend of No. 1 diesel fuel and No. 2 diesel fuel but other operating effects should not be experienced.Check the type of fuel or the fuel blend that is being used before troubleshooting for poor performance during the winter. Be aware of these values when you purchase diesel fuel. Anticipate the average outside temperature for the area for operation
Have questions with 106671-7421?
Group cross 106671-7421 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
106671-7421
9 400 616 936
ME056612
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D22
6D22
