Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106671-6670
1066716670
ISUZU
1156034710
1156034710
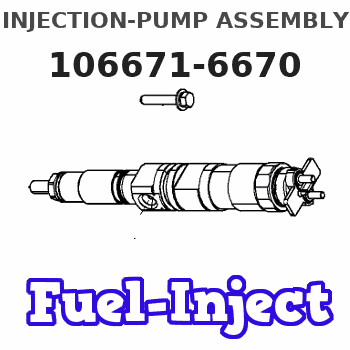
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106671-6670
1066716670
ISUZU
1156034710
1156034710
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-3920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4
3.97
4.03
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.5
Pump speed
r/min
1450
1450
1450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
127.5
125.5
129.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
116
116
Boost pressure
mmHg
870
870
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
7.2+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
19
15.8
22.2
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-13
13
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
7.8
Boost pressure
kPa
46.7
44
49.4
Boost pressure
mmHg
350
330
370
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
9.95
Boost pressure
kPa
103
103
103
Boost pressure
mmHg
770
770
770
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1250--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1300
Advance angle
deg.
1
0.5
1.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
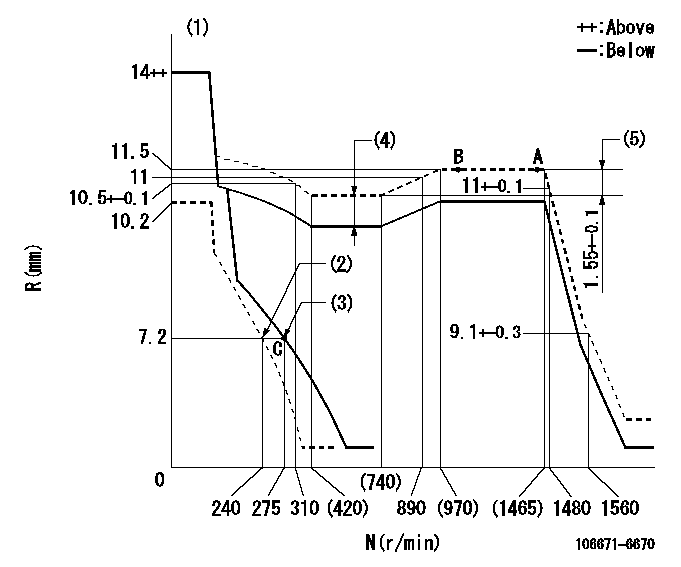
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Set idle sub-spring
(3)Main spring setting
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(5)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=13 BCL=2.15+-0.1mm N1=1450r/min N2=600r/min
----------
----------
K=13 BCL=2.15+-0.1mm N1=1450r/min N2=600r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
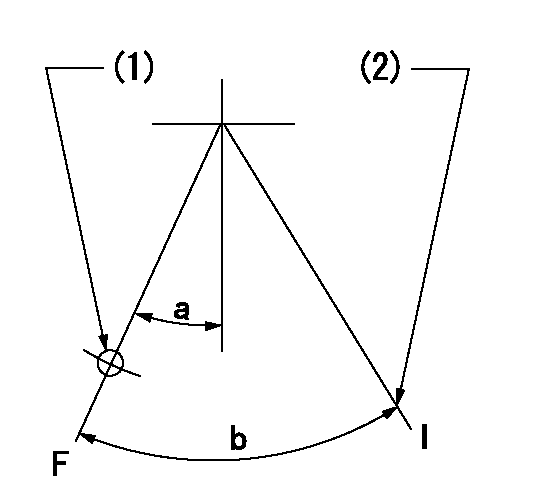
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=70mm
----------
a=(23deg)+-5deg b=(34deg)+-5deg
----------
aa=70mm
----------
a=(23deg)+-5deg b=(34deg)+-5deg
Stop lever angle
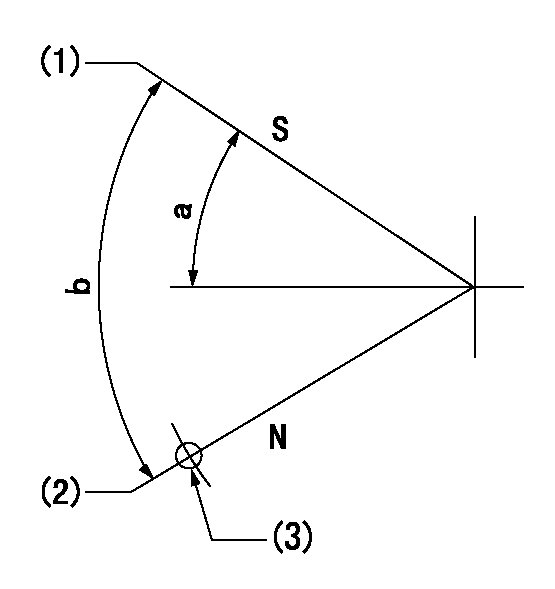
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa, speed = bb (stamp at delivery)
(2)Normal
(3)Use the hole above R = cc
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min cc=33mm
----------
a=25.5deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min cc=33mm
----------
a=25.5deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
Timing setting
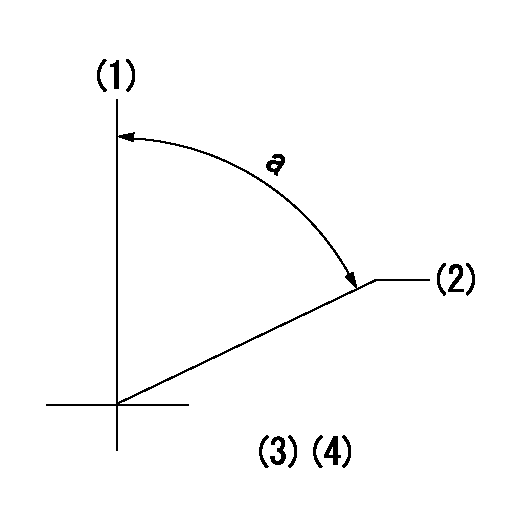
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Positions of coupling's threaded installation holes at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=17deg
----------
a=(50deg)
----------
aa=17deg
----------
a=(50deg)
Information:
Test Procedure
System Operation
The SLC 5/04 diagnostic indicators are located on the front of the following components: Power Supply, CPU and I/O Modules.The diagnostic indicators help trace the source of the fault. Faults can be found in the following components: Input devices, Output devices, Wiring and The controller.The thermocouple module has five LED indicators. Four of the LED indicators are "Channel Status" indicators. The "Channel Status" indicators are numbered according to the channel. One of the LED indicators is a "Module Status" indicator. You can recover from the "Channel Status" errors.Diagnostics are displayed on the "Module Status" LED indicator. Operating errors are displayed on the "Module Status" LED indicator. Problems may be detected during powerup or problems may be detected during operation. When an error occurs the module will not communicate with the processor. The channel is disabled and the data is cleared.
Illustration 1 g00563580
Diagram of the LED indicators
Illustration 2 g00563584
Diagram of the thermocouple module
Illustration 3 g00563586
Schematic of the thermocouple moduleFunctional Test
The "Module Status" LED is on. The module is operating normally. Stop.
The "Channel Status" LED is on. The module is operating normally. Stop.
The "Module Status" LED is off. The module is in a fault condition. Proceed to 6.
The "Channel Status" LED is off. The channel is not enabled. This is normal if the sensor is not wired.
The "Channel Status" LED is blinking. The module is in a fault condition. Proceed to 10.
Check the electrical connectors and check the wiring.
Bodily contact with electrical potential can cause bodily injury or death.To avoid the possibility of injury or death, ensure that the main power supply has been disconnected before performing any maintenance or removing any modules.
Disconnect the power supply.
Check the electrical connectors and check the wiring for damage or bad connections.
Verify that all modules are properly seated.
Verify the status of the LED on the SLC 5/04.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
All of the components are fully installed. All of the components are free of corrosion. All of the components are free of damage. All of the modules are properly seated. Proceed to 7.
The components are not fully installed. The components are not free of corrosion. The components are damaged. All of the modules are not properly seated. Repair the component. Verify that the repair resolves the problem. STOP.
Check the LED indicator on the module.
Connect the power supply.
Cycle the power to the module.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
No errors are displayed on the LED indicators. Stop.
Errors are displayed on the LED indicators. Proceed to 8.
Check the module for a fault.
Bodily contact with electrical potential can cause bodily injury or death.To avoid the possibility of injury or death, ensure that the main power supply has been disconnected before performing any maintenance or removing any modules.
To avoid potential damage to the processor, handle all modules by the ends of the carrier or edges of the plastic housing. Skin oil or dirt can corrode metallic surfaces, inhibiting electrical contact.
Disconnect the power supply.
Remove the module from the chassis.Reference: Maintenance
System Operation
The SLC 5/04 diagnostic indicators are located on the front of the following components: Power Supply, CPU and I/O Modules.The diagnostic indicators help trace the source of the fault. Faults can be found in the following components: Input devices, Output devices, Wiring and The controller.The thermocouple module has five LED indicators. Four of the LED indicators are "Channel Status" indicators. The "Channel Status" indicators are numbered according to the channel. One of the LED indicators is a "Module Status" indicator. You can recover from the "Channel Status" errors.Diagnostics are displayed on the "Module Status" LED indicator. Operating errors are displayed on the "Module Status" LED indicator. Problems may be detected during powerup or problems may be detected during operation. When an error occurs the module will not communicate with the processor. The channel is disabled and the data is cleared.
Illustration 1 g00563580
Diagram of the LED indicators
Illustration 2 g00563584
Diagram of the thermocouple module
Illustration 3 g00563586
Schematic of the thermocouple moduleFunctional Test
The "Module Status" LED is on. The module is operating normally. Stop.
The "Channel Status" LED is on. The module is operating normally. Stop.
The "Module Status" LED is off. The module is in a fault condition. Proceed to 6.
The "Channel Status" LED is off. The channel is not enabled. This is normal if the sensor is not wired.
The "Channel Status" LED is blinking. The module is in a fault condition. Proceed to 10.
Check the electrical connectors and check the wiring.
Bodily contact with electrical potential can cause bodily injury or death.To avoid the possibility of injury or death, ensure that the main power supply has been disconnected before performing any maintenance or removing any modules.
Disconnect the power supply.
Check the electrical connectors and check the wiring for damage or bad connections.
Verify that all modules are properly seated.
Verify the status of the LED on the SLC 5/04.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
All of the components are fully installed. All of the components are free of corrosion. All of the components are free of damage. All of the modules are properly seated. Proceed to 7.
The components are not fully installed. The components are not free of corrosion. The components are damaged. All of the modules are not properly seated. Repair the component. Verify that the repair resolves the problem. STOP.
Check the LED indicator on the module.
Connect the power supply.
Cycle the power to the module.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
No errors are displayed on the LED indicators. Stop.
Errors are displayed on the LED indicators. Proceed to 8.
Check the module for a fault.
Bodily contact with electrical potential can cause bodily injury or death.To avoid the possibility of injury or death, ensure that the main power supply has been disconnected before performing any maintenance or removing any modules.
To avoid potential damage to the processor, handle all modules by the ends of the carrier or edges of the plastic housing. Skin oil or dirt can corrode metallic surfaces, inhibiting electrical contact.
Disconnect the power supply.
Remove the module from the chassis.Reference: Maintenance