Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 616 915
9400616915
ZEXEL
106671-6610
1066716610
ISUZU
1156034360
1156034360
Rating:
Service parts 106671-6610 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7(180)/22.1(225)
14.
NOZZLE
Include in #1:
106671-6610
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 616 915
9400616915
ZEXEL
106671-6610
1066716610
ISUZU
1156034360
1156034360
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106671-6610
9 400 616 915
1156034360 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6SD1-T * K 14CA PE6P,6PD PE
6SD1-T * K 14CA PE6P,6PD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-4320
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.2
4.17
4.23
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.1
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
139.5
137.5
141.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
140
140
Boost pressure
mmHg
1050
1050
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
6.4+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
475
475
475
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
14.5
11.3
17.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-13
13
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R1-1.6
Boost pressure
kPa
56
53.3
58.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
420
400
440
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R1(11.1)
Boost pressure
kPa
127
120.3
133.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
950
900
1000
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
550--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
Advance angle
deg.
0
-0.5
0
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
650+-25
Advance angle
deg.
-2.5
-3
-2
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
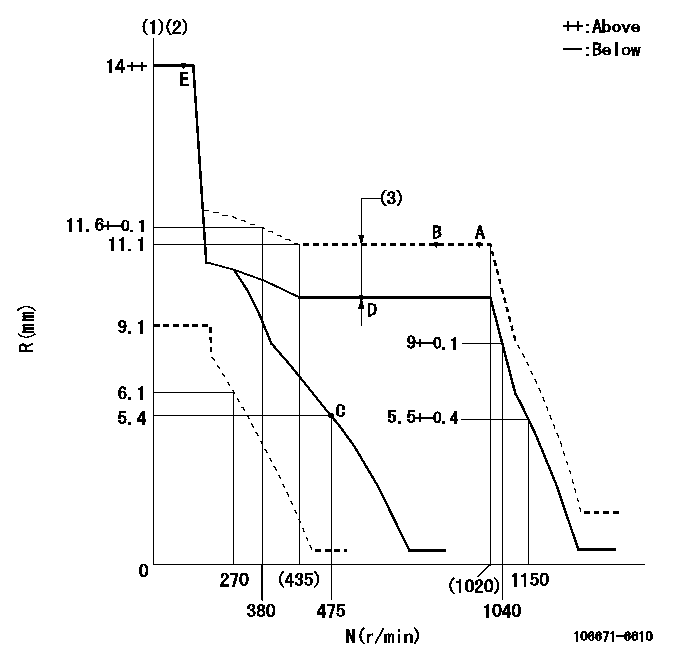
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
K=18 BCL=1.6+-0.1mm
----------
----------
K=18 BCL=1.6+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
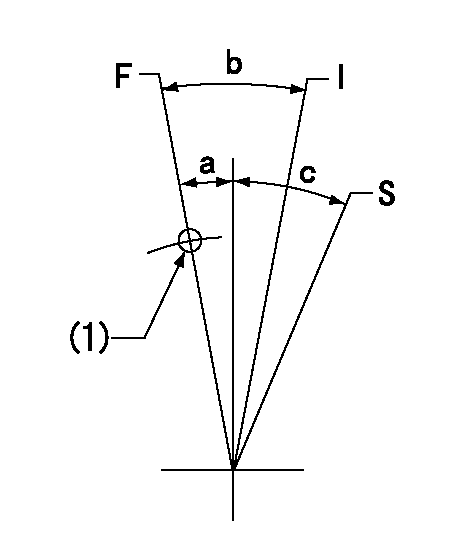
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
----------
aa=70mm
----------
a=(11deg)+-5deg b=(19deg)+-5deg c=35deg+-3deg
----------
aa=70mm
----------
a=(11deg)+-5deg b=(19deg)+-5deg c=35deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
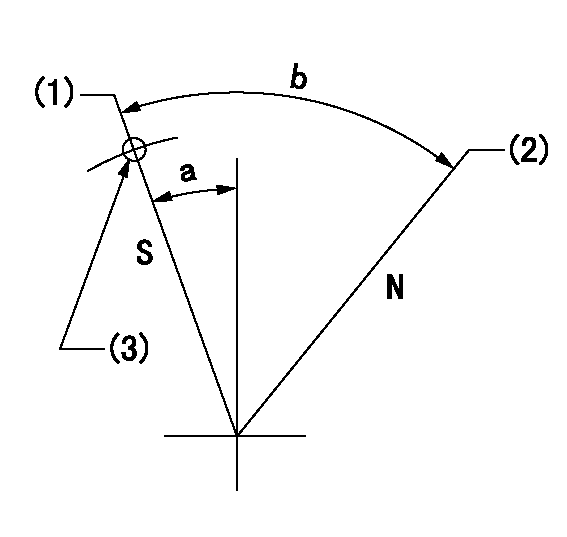
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa, speed = bb (stamp at delivery)
(2)Normal
(3)Use the hole above R = cc
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min cc=23mm
----------
a=15deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1-0.5mm bb=0r/min cc=23mm
----------
a=15deg+-5deg b=70deg+-5deg
0000001501 TAMPER PROOF

Tamperproofing-equipped boost compensator cover installation procedure
(A) After adjusting the boost compensator, tighten the bolts to remove the heads.
(1)Before adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten the screw to the specified torque.
(Tightening torque T = T1 maximum)
(2)After adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten to the specified torque to break off the bolt heads.
(Tightening torque T = T2 maximum)
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
Timing setting
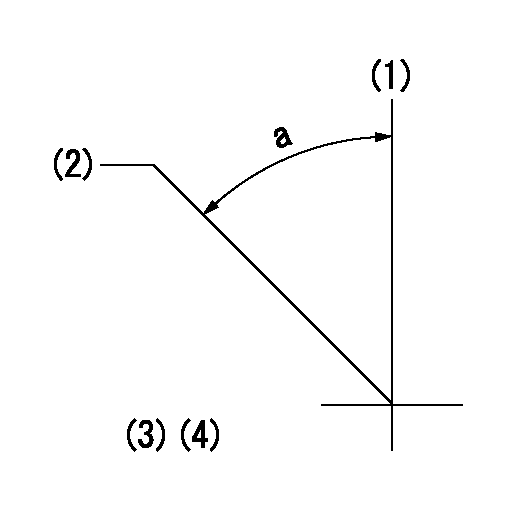
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Positions of coupling's threaded installation holes at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=11deg
----------
a=(50deg)
----------
aa=11deg
----------
a=(50deg)
Information:
Accidental engine starting can cause injury or death to personnel working on the equipment.To avoid accidental engine starting, disconnect the battery cable from the negative (−) battery terminal. Completely tape all metal surfaces of the disconnected battery cable end in order to prevent contact with other metal surfaces which could activate the engine electrical system.Place a Do Not Operate tag at the Start/Stop switch location to inform personnel that the equipment is being worked on.
2301A Electric Governor Control
The 2301A Electric Governor Control activates all of the components that are in the electric protection system. The components are activated in the same manner when the nonelectric governor is used. One difference exists in the main circuit. The fuel shutoff solenoid (FSOS) (line 43) is not used.When the electric governor control is used, the engine must run in a normal condition in order for the electric circuit to operate in the manner that is described below.
Current flows from the terminals (TS-28) (line 43) and (TS-31) (line 44), which are located on the terminal strip in the junction box.
Current from terminals (TS-28) (line 43) and (TS-31) (line 44) flows through the preregulator (PR) (line 48) or the fuse (F4) to the electric governor control.
When the engine flywheel is rotating, the current also flows through the electric governor actuator (EGA) (line 52). When a fault in the system causes the current to energize the slave relay (SR1), the following events occur in the electric circuit in order to stop the engine.
The slave relay (SR1) opens across the contacts (SR1-30) and (SR1-87a) (line 45). The relay closes across the contacts (SR1-30) and (SR1-87) (line 43).
When the circuit opens across contacts (SR1-30) and (SR1-87a), the current is stopped to the electric governor control.
Current to the electric governor actuator (EGA) is also stopped.
The mechanical spring load in the electric governor actuator (EGA) will now move the fuel control rod in order to stop fuel flow to the engine. Note: With the exception of the differences that are described in this section of the manual, all of the fault circuits in the electric protection system are identical for the 2301A Electric Governor Control and for the nonelectric governor control.
Illustration 5 g00292615
Junction Box Wiring for ETR protection system with OP, WT, and OS that does not require
Have questions with 106671-6610?
Group cross 106671-6610 ZEXEL
Isuzu
106671-6610
9 400 616 915
1156034360
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6SD1-T
6SD1-T