Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 610 874
9400610874
ZEXEL
106671-6080
1066716080
ISUZU
1156031121
1156031121

Rating:
Service parts 106671-6080 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
1-15300-332-0
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7{180}/22.1{225}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106671-6080
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 610 874
9400610874
ZEXEL
106671-6080
1066716080
ISUZU
1156031121
1156031121
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-1920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.5
4.47
4.53
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.5
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
149
147
151
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
6.4+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
290
290
290
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10.5
7.3
13.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-13
13
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.5)
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
149
147
151
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
28.7
28.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
215
215
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.3
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
153.5
147.5
159.5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
28.7
28.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
215
215
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R2-1.5
Boost pressure
kPa
8.7
7.4
10
Boost pressure
mmHg
65
55
75
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R2(R1-1.
3)
Boost pressure
kPa
15.3
15.3
15.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
115
115
115
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
850--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
800
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
875
Advance angle
deg.
1.5
1
2
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
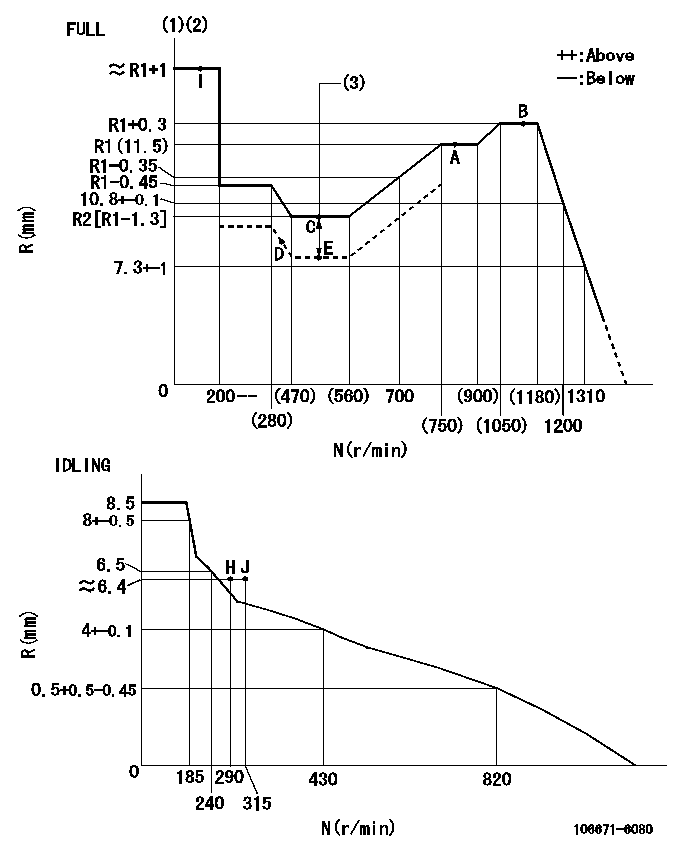
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=AD53 BCL=1.5+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=AD53 BCL=1.5+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
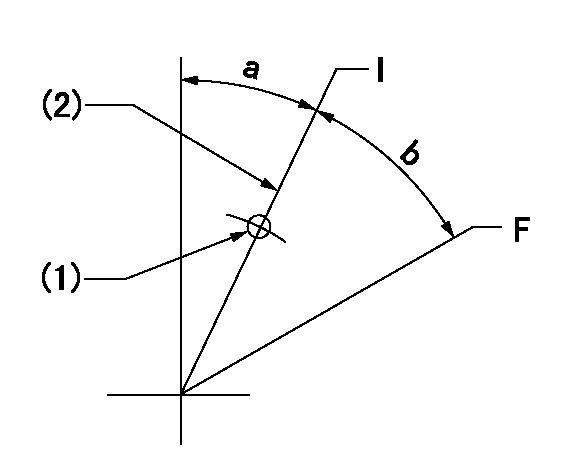
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=27deg+-5deg b=29.5deg+-3deg
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=27deg+-5deg b=29.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
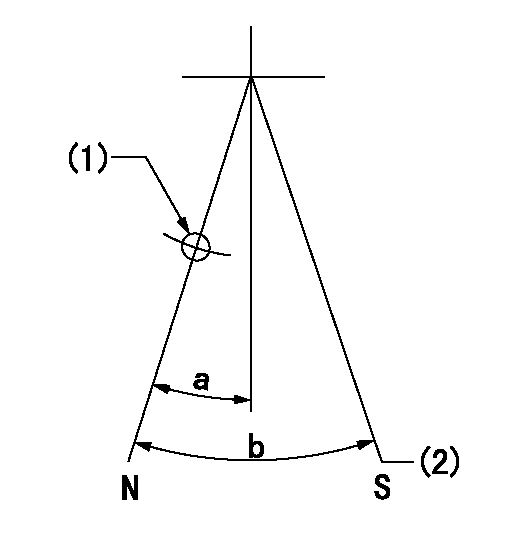
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
(2)Set the stopper bolt so that speed = bb and rack position = cc. (Confirm non-injection.)
----------
aa=40mm bb=0r/min cc=1.5+-0.3mm
----------
a=22deg+-5deg b=41deg+-5deg
----------
aa=40mm bb=0r/min cc=1.5+-0.3mm
----------
a=22deg+-5deg b=41deg+-5deg
Timing setting
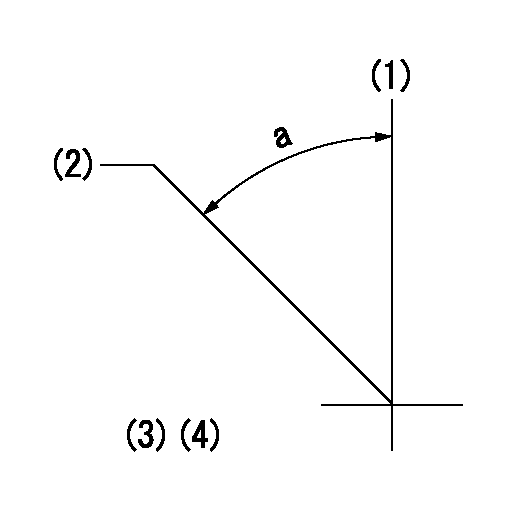
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(50deg)
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(50deg)
Information:
Personal injury can result from being struck by parts propelled by a released spring force.Make sure to wear all necessary protective equipment.Follow the recommended procedure and use all recommended tooling to release the spring force.
Care must be taken to ensure that fluids are contained during performance of inspection, maintenance, testing, adjusting and repair of the product. Be prepared to collect the fluid with suitable containers before opening any compartment or disassembling any component containing fluids.Dispose of all fluids according to local regulations and mandates.
If possible, take the fuel injection pump to a clean work area.
Clean the outside surfaces of the fuel injection pump.
Illustration 1 g03117860
Typical example
Place a suitable container under the fuel injection pump to collect any fuel from the fuel injection pump. Use a suitable tool to loosen the drain plug (1). If necessary, retain the fuel collected for analysis if required.
Illustration 2 g03117878
Typical example
Use a suitable pair of pliers to remove the throttle return spring (2).Note: Care should be taken when the spring is removed.
Illustration 3 g03117896
Typical example
Loosen self-locking nut (3). Do not remove the nut.
Illustration 4 g03117916
Typical example
Use a suitable pair of pliers to lift and disconnect throttle spring (4). Remove self-locking nut (3), washer, upper retainer, spring, lower retainer, spacer, lever, and dust cap.Note: Care should be taken when the spring is removed.
Illustration 5 g03117938
Typical example
Remove four screws (6) in the governor cover (7). Gently push the throttle shaft (5) down into the cover (7).
Illustration 6 g03117956
Typical example
To inspect the internal components of the fuel injection pump, gently lift and rotate the cover (7).Note: The cover is still connected internally, if resistance is felt, lower the cover and move the cover backwards. Attempt to lift the cover again.
Inspect the internal components of the fuel injection pump. Refer to steps 9a and 9b.
Illustration 7 g03117961
Typical example
If good quality fuel is being used, the components will be clean. Refer to illustration 7. Take photographs of the identification plate of the fuel injection pump and any evidence found. Attach the photographs to support the claim story.
Illustration 8 g03118119
Typical example
Illustration 9 g03118121
Typical example
If the injection pump has been run with excessive water in the fuel, there will be signs of rust and oxidization of the steel components. Refer to illustration 8. Fuel with dirt ingress will show a build-up of dirt on the components. Refer to illustration 9.Note: Issues with the fuel injection pump that are due to dirt and water void Caterpillar warranty. Advise the customer on the correct fuel, maintenance, and fuel storage procedures. Refer to the relevant Operation and Maintenance Manual for more information.If the fuel injection pump shows signs that contaminated fuel is the root cause of the problem, the evidence can be shown to the customer immediately.After the fuel injection pump has been inspected, the fuel injection pump must not be used in service.Rebuild the fuel injection pump. Refer to steps 1 to 6
Lower the cover (7) back into position. Ensure the throttle shaft (5), has been returned to the original position.
Install the four screws (6) to the cover (7). Tighten the
