Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106671-4320
1066714320

Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106671-4320
1066714320
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.7
4.65
4.75
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.3
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
145
143
147
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
46.7
46.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
350
350
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
11.2
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
161
158
164
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
46.7
46.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
350
350
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
5.2+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
250
250
250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
14.5
13
16
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
8.2
Boost pressure
kPa
14.7
12.7
16.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
110
95
125
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
10.3
Boost pressure
kPa
33.3
33.3
33.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
250
250
250
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
750--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
700
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
3
2.5
3.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
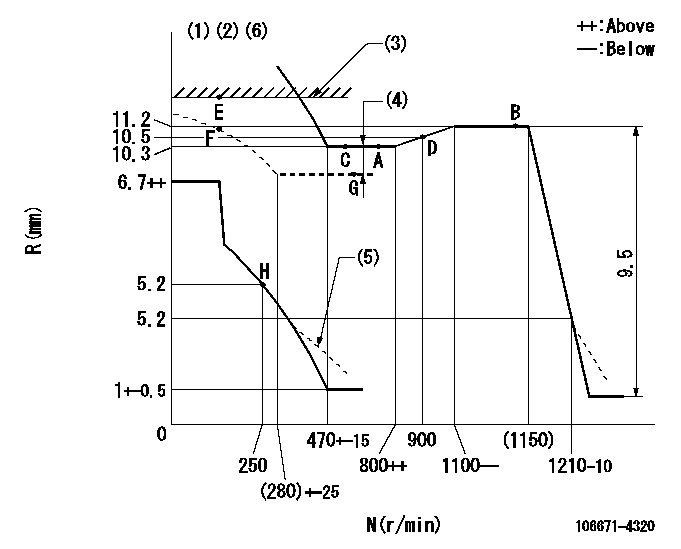
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Lever ratio: RT
(2)Target shim dimension: TH
(3)RACK LIMIT: RAL
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(5)Damper spring setting: DL
(6)Microswitch adjustment unnecessary.
----------
RT=1 TH=3mm RAL=11.9+-0.1mm BCL=2.1+-0.1mm DL=4.9-0.2mm
----------
----------
RT=1 TH=3mm RAL=11.9+-0.1mm BCL=2.1+-0.1mm DL=4.9-0.2mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
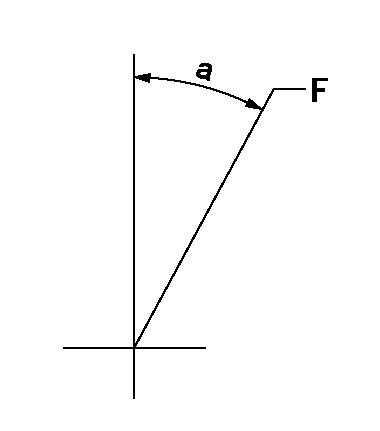
F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=7deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=7deg+-5deg
0000000901
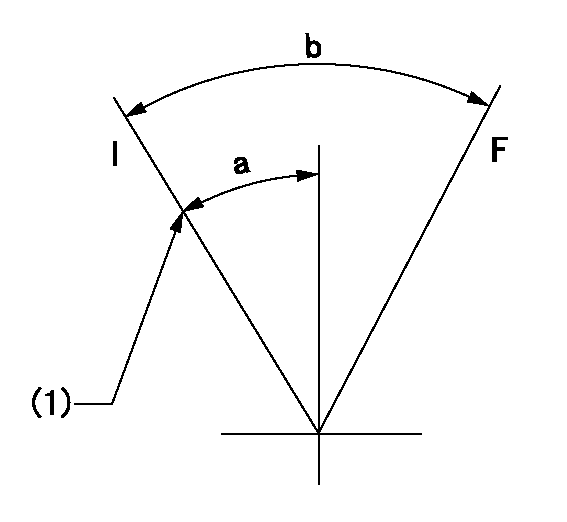
F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=34deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=34deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=73deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=73deg+-5deg
Timing setting
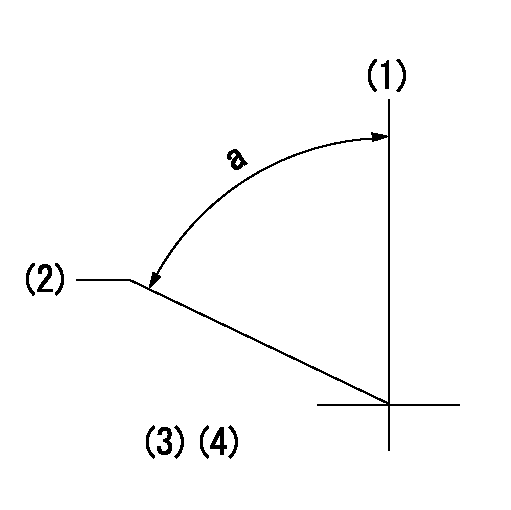
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position for the No. 6 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(70deg)
----------
----------
a=(70deg)
Information:
Caterpillar Diesel Engines can operate effectively in cold weather. However, engine operation in cold weather is dependent on the type of fuel used and how well the fuel moves through fuel related components. The purpose of this section is to explain some of the problems and steps that can be taken to minimize fuel problems during cold weather operation [below 5°C (40°F)].Fuel and the Effect from Cold Weather
The two types of diesel fuel available for your engine are typically grades No. 1 and No.2. No.2 diesel fuel is the most commonly used fuel. No. 1 diesel fuel, or a blend of No. 1 and No.2, is best suited for cold weather operation.Quantities of No. 1 diesel fuel are limited, and generally only available during the winter months in the colder climates. During cold weather operation, if No. 1 fuel is unavailable, it may be necessary to use No.2 diesel fuel.There are three major differences between No. 1 and No.2 diesel fuel. No. 1 diesel fuel has:* a lower cloud point* a lower pour point* a lower BTU (kJ) (heat content) rating per unit volume of fuel than the average No.2 diesel fuel.When using No. 1 diesel fuel, you may notice a drop in power and fuel efficiency. You should not experience any other operating effects.The cloud point is the temperature at which a cloud or haze of wax crystals begins to form in the fuel and cause fuel filters to plug. The pour point is the temperature which diesel fuel begins to thicken and be more resistant to flow through fuel pumps and lines.Be aware of these fuel values when purchasing your diesel fuel. Anticipate the average outside (ambient) temperature for the area your engine will be operating. Engines fueled in one climate may not operate satisfactorily if moved to another because of problems that result from cold weather.Before troubleshooting for low power or poor performance in winter months, check the type of fuel being used.When No.2 diesel fuel is used: starting aids, engine oil pan heaters, engine coolant heaters, fuel heaters, and fuel line insulation also provide a means of minimizing starting and fuel problems in cold weather.Fuel Related Components in Cold Weather
Fuel Tanks
Condensation can form in partially filled fuel tanks. Top off fuel tanks before leaving overnight.Fuel tanks should contain some provision for draining water and sediment from the bottom of the tanks. Some fuel tanks use supply pipes that allow water and sediment to settle below the end of the fuel supply pipe.Some fuel tanks use supply lines that take fuel directly from the bottom of the tank. If equipped with this system, regular maintenance of the fuel system filter(s) is important.Check the fuel level in the day tank daily by observing the sight gauge. Drain the water and sediment from any fuel storage tank weekly, at the oil change period, and before the fuel tank is refilled. This will help prevent water and/or sediment from being pumped from the fuel storage tank into the
The two types of diesel fuel available for your engine are typically grades No. 1 and No.2. No.2 diesel fuel is the most commonly used fuel. No. 1 diesel fuel, or a blend of No. 1 and No.2, is best suited for cold weather operation.Quantities of No. 1 diesel fuel are limited, and generally only available during the winter months in the colder climates. During cold weather operation, if No. 1 fuel is unavailable, it may be necessary to use No.2 diesel fuel.There are three major differences between No. 1 and No.2 diesel fuel. No. 1 diesel fuel has:* a lower cloud point* a lower pour point* a lower BTU (kJ) (heat content) rating per unit volume of fuel than the average No.2 diesel fuel.When using No. 1 diesel fuel, you may notice a drop in power and fuel efficiency. You should not experience any other operating effects.The cloud point is the temperature at which a cloud or haze of wax crystals begins to form in the fuel and cause fuel filters to plug. The pour point is the temperature which diesel fuel begins to thicken and be more resistant to flow through fuel pumps and lines.Be aware of these fuel values when purchasing your diesel fuel. Anticipate the average outside (ambient) temperature for the area your engine will be operating. Engines fueled in one climate may not operate satisfactorily if moved to another because of problems that result from cold weather.Before troubleshooting for low power or poor performance in winter months, check the type of fuel being used.When No.2 diesel fuel is used: starting aids, engine oil pan heaters, engine coolant heaters, fuel heaters, and fuel line insulation also provide a means of minimizing starting and fuel problems in cold weather.Fuel Related Components in Cold Weather
Fuel Tanks
Condensation can form in partially filled fuel tanks. Top off fuel tanks before leaving overnight.Fuel tanks should contain some provision for draining water and sediment from the bottom of the tanks. Some fuel tanks use supply pipes that allow water and sediment to settle below the end of the fuel supply pipe.Some fuel tanks use supply lines that take fuel directly from the bottom of the tank. If equipped with this system, regular maintenance of the fuel system filter(s) is important.Check the fuel level in the day tank daily by observing the sight gauge. Drain the water and sediment from any fuel storage tank weekly, at the oil change period, and before the fuel tank is refilled. This will help prevent water and/or sediment from being pumped from the fuel storage tank into the