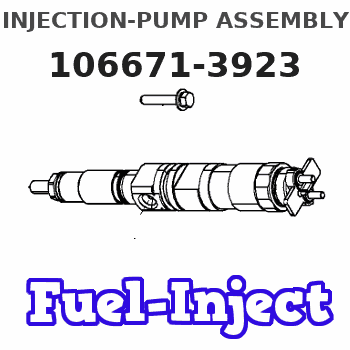
Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106671-3923
1066713923
HINO
220004921A
220004921a
Rating:
Service parts 106671-3923 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
23600-1221
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106671-3923
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106671-3923
1066713923
HINO
220004921A
220004921a
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
134424-0920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
162
147
177
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.65
1.5
1.8
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.24
3.3
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.1+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
119.5
116.5
122.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
10.5+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
129.5
127.5
131.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
11+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
1150
1150
1150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
143
140
146
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
6.6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15
12
18
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
F
Rack position
11.6+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
126.3
119.3
133.3
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
750--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
700
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
1.4
0.9
1.9
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1150
Advance angle
deg.
4
3.5
4.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
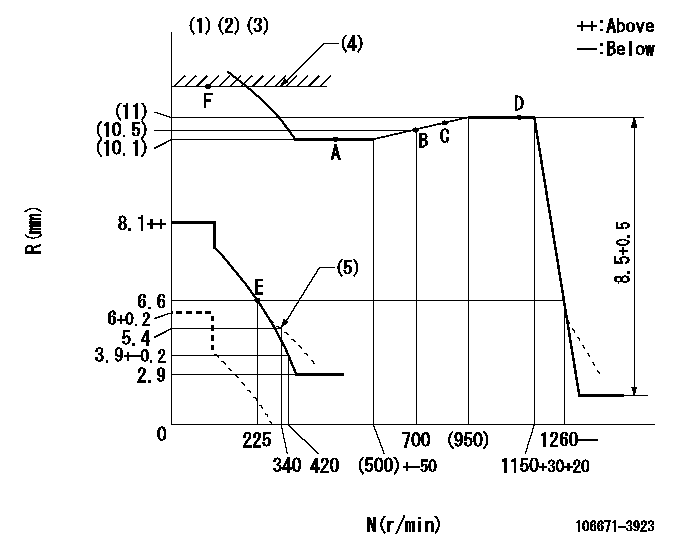
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Lever ratio: RT
(2)Target shim dimension: TH
(3)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(4)RACK LIMIT
(5)Damper spring setting
----------
RT=1 TH=2.6mm
----------
----------
RT=1 TH=2.6mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=3deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=3deg+-5deg
0000000901
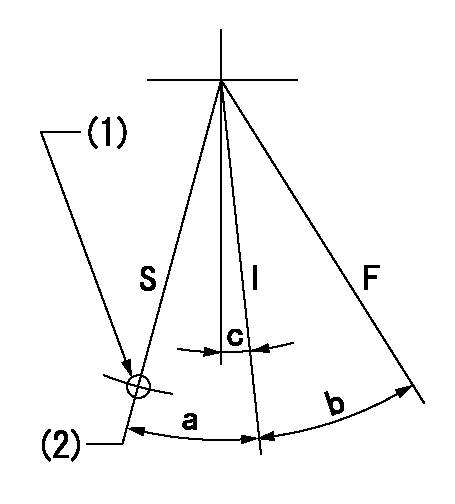
F:Full load
I:Idle
S:Stop
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Rack position = bb (speed = cc)
----------
aa=75mm bb=6+0.2mm cc=0r/min
----------
a=13deg+-3deg b=(28deg)+-3deg c=1deg+-5deg
----------
aa=75mm bb=6+0.2mm cc=0r/min
----------
a=13deg+-3deg b=(28deg)+-3deg c=1deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
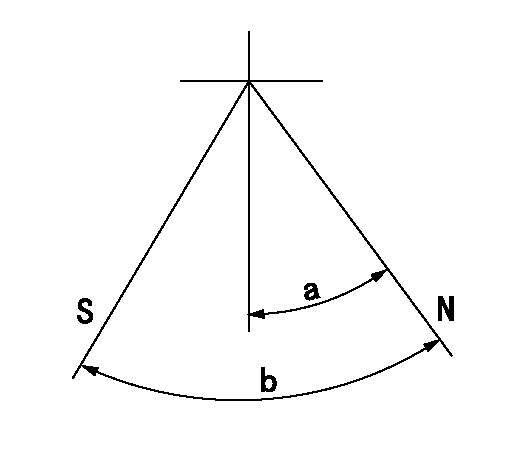
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=64deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=64deg+-5deg
0000001501 GOVERNOR TORQUE CONTROL

Dr:Torque control stroke
(A): Without torque control spring capsule
1. Adjustment procedures
(1)Procedure is the same as that for the RFD (former type), except that the positive torque control stroke must be determined at the full lever setting.
2. Procedures for adjustment
(1)Remove the torque control spring capsule.
(2)Operate the pump at approximately N1. (End of idling spring operation < N1.)
(3)Tilt the lever to the full side.
(4)Set so that R = RF.
(5)Increase the speed by pushing in the screw (attached to the bracket on the rear of the tension lever) through the adjusting window.
(6)Adjust so that the torque control stroke Dr1 can be obtained.
(7)Align N2 and N3 with the torque control spring capsule.
3. Final confirmation
(1)After final confirmation, temporarily set the load lever to N = N1, R = idling position.
(2)From this condition, increase speed to N = N4.
(3)Confirm that positive torque control stroke is Dr2.
----------
N1=500r/min N2=(600)+-50r/min N3=(950)r/min N4=1000r/min RF=(10.1)mm Dr1=0.9mm Dr2=0+0.3mm
----------
----------
N1=500r/min N2=(600)+-50r/min N3=(950)r/min N4=1000r/min RF=(10.1)mm Dr1=0.9mm Dr2=0+0.3mm
----------
0000001601 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=300r/min Ra=6.7+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=300r/min Ra=6.7+-0.1mm
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
3406 Electronic Truck Engine
Oil Filter (1), Oil Level Gage (2), Water Pump (3), Alternator Bracket (4), Turbocharger (5), Crankcase Breather (6), Damper (7), Water Temperature Sensor (8) and Thermostat Housing (9).
Fuel Filter and Priming Pump (10), Electronic Governor (11), Electronic ECM (12), Oil Filler (13), Compressor (14), Grounding Stud (15) and Lift Eye (16).Engine Information
The Caterpillar 3406 Diesel Truck engine is direct fuel injected, turbocharged and an air-to-air aftercooler arrangement (ATAAC). The cooling system consists of a gear driven centrifugal pump, with one thermostat which regulates the engine coolant water temperature, an oil cooler and an OEM radiator incorporating a shunt system.The engine lubricating oil, which is both cooled and filtered, is supplied by a gear-type pump. Bypass valves provide unrestricted flow of lubrication oil to the engine parts when oil viscosity is high, or if either the oil cooler or the oil filter elements should become plugged.Engine efficiency, efficiency of emission controls and engine performance depend on adherence to proper operation and maintenance recommendations, and the use of recommended fuels and lubrication oils.Electronic Engine Control (if equipped)
The programmable electronic engine control is designed to provide electronic governing, automatic air-fuel ratio control, torque rise shaping, injection timing control and system diagnostics with the capability for future expansion.Other benefits such as improved cold starting capability, tamper diagnostics, cruise control, vehicle speed limiting, low and high gears engine rpm limiting (progressive shift engine speed control), PTO governor, ATA data link (SAE J1587) and an Engine Monitoring Package.The fuel system is mechanically actuated and electronically controlled combining the pumping, electronic fuel metering and injecting elements to produce higher injection pressures.High injection pressures help to reduce fuel consumption and particulate emissions.Individual injection pumps, one for each cylinder, meter and pump fuel under high pressure to an injection valve for each cylinder.A full range electronic governor controls the fuel injection pump output to maintain desired engine rpm. The governor functions like the Caterpillar mechanical governor in the mid-range, but includes additional features. These include programmable isochronous low idle and 20 to 200 rpm governor overrun.Automatic timing advance provides the best fuel injection timing over the full range of engine speed. The injection timing is varied as a function of engine operating conditions.This optimizes the engine's performance for starting, emissions, noise, fuel consumption and driveability.The Electronic Engine Control has built-in diagnostics to assure that all components are functioning and operating properly.In the event of a system component deviation from programmed limits, the operator will be alerted to the condition by a dashboard mounted CHECK ENGINE/DIAGNOSTIC lamp.A Caterpillar service tool or cruise control switches (if equipped) are needed to read the numerical code of the diagnostic flash code. There are three types of diagnostic codes; active (fault), logged and event. These codes are logged and stored in the system memory.Multi-Torque Rating (if equipped)
Multi-torque ratings provide for additional torque as engine load increases. This feature provides higher torque levels and better driveability while in the top gears ONLY. The engine electronics are able to determine when
Oil Filter (1), Oil Level Gage (2), Water Pump (3), Alternator Bracket (4), Turbocharger (5), Crankcase Breather (6), Damper (7), Water Temperature Sensor (8) and Thermostat Housing (9).
Fuel Filter and Priming Pump (10), Electronic Governor (11), Electronic ECM (12), Oil Filler (13), Compressor (14), Grounding Stud (15) and Lift Eye (16).Engine Information
The Caterpillar 3406 Diesel Truck engine is direct fuel injected, turbocharged and an air-to-air aftercooler arrangement (ATAAC). The cooling system consists of a gear driven centrifugal pump, with one thermostat which regulates the engine coolant water temperature, an oil cooler and an OEM radiator incorporating a shunt system.The engine lubricating oil, which is both cooled and filtered, is supplied by a gear-type pump. Bypass valves provide unrestricted flow of lubrication oil to the engine parts when oil viscosity is high, or if either the oil cooler or the oil filter elements should become plugged.Engine efficiency, efficiency of emission controls and engine performance depend on adherence to proper operation and maintenance recommendations, and the use of recommended fuels and lubrication oils.Electronic Engine Control (if equipped)
The programmable electronic engine control is designed to provide electronic governing, automatic air-fuel ratio control, torque rise shaping, injection timing control and system diagnostics with the capability for future expansion.Other benefits such as improved cold starting capability, tamper diagnostics, cruise control, vehicle speed limiting, low and high gears engine rpm limiting (progressive shift engine speed control), PTO governor, ATA data link (SAE J1587) and an Engine Monitoring Package.The fuel system is mechanically actuated and electronically controlled combining the pumping, electronic fuel metering and injecting elements to produce higher injection pressures.High injection pressures help to reduce fuel consumption and particulate emissions.Individual injection pumps, one for each cylinder, meter and pump fuel under high pressure to an injection valve for each cylinder.A full range electronic governor controls the fuel injection pump output to maintain desired engine rpm. The governor functions like the Caterpillar mechanical governor in the mid-range, but includes additional features. These include programmable isochronous low idle and 20 to 200 rpm governor overrun.Automatic timing advance provides the best fuel injection timing over the full range of engine speed. The injection timing is varied as a function of engine operating conditions.This optimizes the engine's performance for starting, emissions, noise, fuel consumption and driveability.The Electronic Engine Control has built-in diagnostics to assure that all components are functioning and operating properly.In the event of a system component deviation from programmed limits, the operator will be alerted to the condition by a dashboard mounted CHECK ENGINE/DIAGNOSTIC lamp.A Caterpillar service tool or cruise control switches (if equipped) are needed to read the numerical code of the diagnostic flash code. There are three types of diagnostic codes; active (fault), logged and event. These codes are logged and stored in the system memory.Multi-Torque Rating (if equipped)
Multi-torque ratings provide for additional torque as engine load increases. This feature provides higher torque levels and better driveability while in the top gears ONLY. The engine electronics are able to determine when
