Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
F 019 Z10 622
f019z10622
ZEXEL
106661-2180
1066612180

Rating:
Service parts 106661-2180 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7(180)/24.5(250)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
106661-2180
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
F 019 Z10 622
f019z10622
ZEXEL
106661-2180
1066612180
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-6920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
191
157
225
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.95
1.6
2.3
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.75
4.85
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
10.2
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
138.5
135.1
141.9
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
17.5
14.9
20.1
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(10.2)
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
138.5
137.5
139.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
27.3
27.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
205
205
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
137.5
134.5
140.5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
27.3
27.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
205
205
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
R2(R1-1.
6)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
101.5
98.5
104.5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
135
115
155
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R2(R1-1.
6)
Boost pressure
kPa
5.3
5.3
5.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
40
40
40
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R1(10.2)
Boost pressure
kPa
14
14
14
Boost pressure
mmHg
105
105
105
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
950--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
4
3.5
4.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
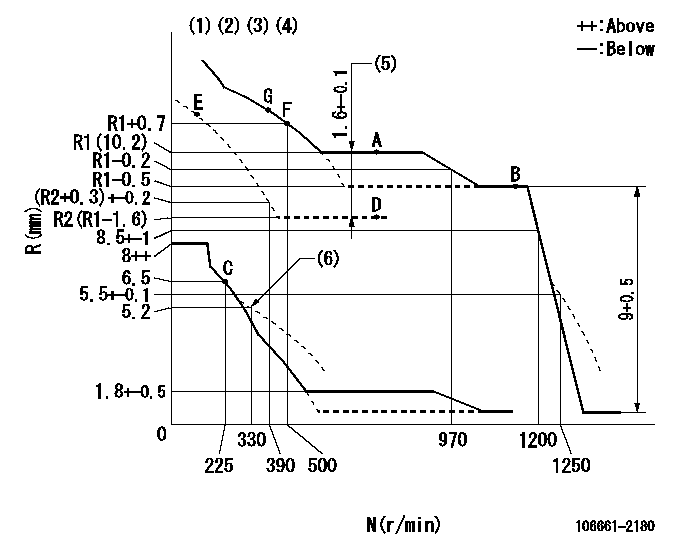
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Lever ratio: RT
(2)Target shim dimension: TH
(3)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(4)Boost compensator cancel stroke: BSL
(5)Boost compensator stroke
(6)Damper spring setting
----------
RT=1 TH=2.3mm BSL=1.6mm
----------
----------
RT=1 TH=2.3mm BSL=1.6mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
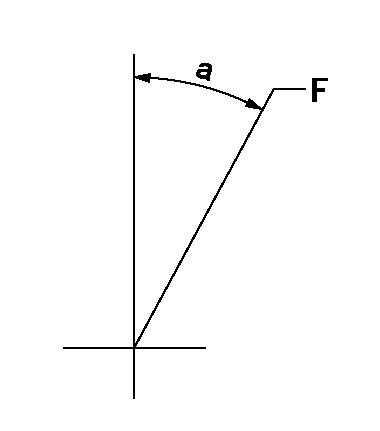
F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=15.5deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=15.5deg+-5deg
0000000901
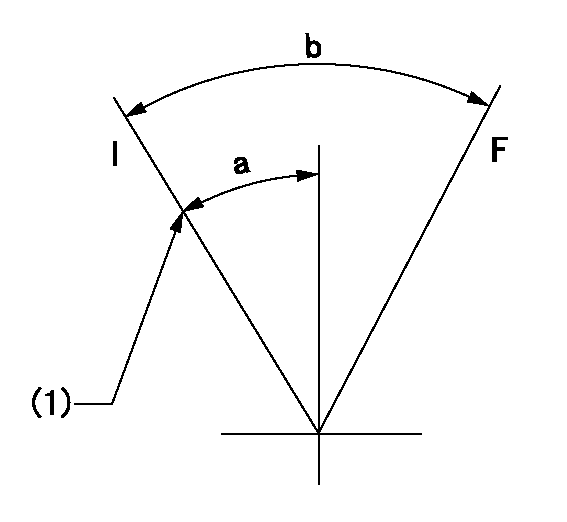
F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=24deg+-5deg b=31deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=24deg+-5deg b=31deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
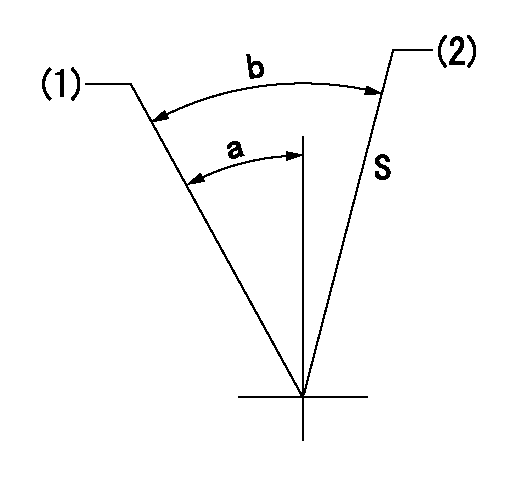
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Free (at shipping)
(2)Rack position = aa
----------
aa=3.4-0.5mm
----------
a=25.5deg+-5deg b=38.5deg+7deg-5deg
----------
aa=3.4-0.5mm
----------
a=25.5deg+-5deg b=38.5deg+7deg-5deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=325r/min Ra=6.2+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=325r/min Ra=6.2+-0.1mm
----------
Timing setting
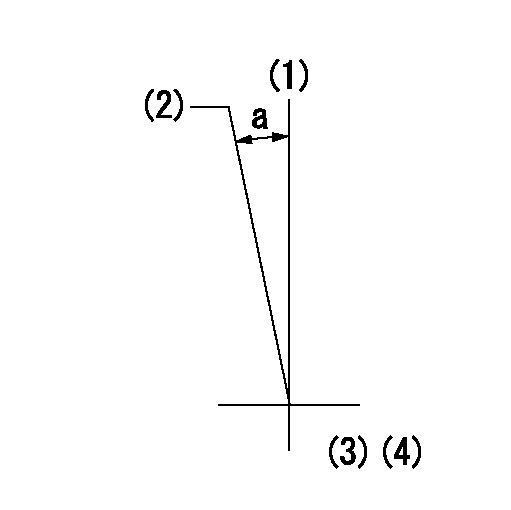
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=13deg
----------
a=(7deg)
----------
aa=13deg
----------
a=(7deg)
Information:
The electrical system is a combination of two separate electric circuits: The charging circuit and the starting circuit. Each circuit is dependent on some of the same components. The battery (batteries), on-off start switch, circuit breaker, ammeter, cables and wires from the battery are common in each of the circuits.
The ignition switch must be ON to allow the electrical system to function. Some charging circuit components will be damaged if the engine is operated with the ignition switch OFF.
The charging circuit is in operation when the diesel engine is operating. The electricity producing (charging) unit is an alternator. A regulator in the circuit senses the state of charge in the battery and regulates the alternator output to keep the batter fully charged.The alternator has four main components: end frame assembly (brush end), rotor assembly, stator and shell assembly, and end frame assembly (drive end).A separate regulator senses the charge condition of the battery as well as electrical system power demand and controls the alternator output accordingly by limiting the field current.
ALTERNATOR
Never operate the alternator without the battery in the circuit. Making or breaking an alternator connection with a heavy load on the circuit will sometimes result in regulator damage.
The starting motor is a device used to rotate the flywheel of an engine fast enough to start the engine.
ALTERNATOR REGULATOR
ELECTRIC STARTING MOTORThe starting motor includes a solenoid. The solenoid engages the pinion with the ring gear on the engine flywheel, when the solenoid is energized. The pinion always engages before the electric contacts in the solenoid causes the circuit between the battery and the starting motor to close. An overrunning clutch protects the starting motor from being overspeeded. Releasing the start-switch disengages the pinion and flywheel ring gear.A solenoid is a magnetic switch that uses low current to close a high current circuit. The solenoid is an electro-magnet with a movable core. There are contacts on the end of the core. The contacts are held apart by a spring pushing the core away from the magnetic center of the coil. Low current energizes the coil and forms a magnetic field. The magnetic field pulls the core to the center of the coil, closing the contacts and completing the starting circuit.
SOLENOID
The ignition switch must be ON to allow the electrical system to function. Some charging circuit components will be damaged if the engine is operated with the ignition switch OFF.
The charging circuit is in operation when the diesel engine is operating. The electricity producing (charging) unit is an alternator. A regulator in the circuit senses the state of charge in the battery and regulates the alternator output to keep the batter fully charged.The alternator has four main components: end frame assembly (brush end), rotor assembly, stator and shell assembly, and end frame assembly (drive end).A separate regulator senses the charge condition of the battery as well as electrical system power demand and controls the alternator output accordingly by limiting the field current.
ALTERNATOR
Never operate the alternator without the battery in the circuit. Making or breaking an alternator connection with a heavy load on the circuit will sometimes result in regulator damage.
The starting motor is a device used to rotate the flywheel of an engine fast enough to start the engine.
ALTERNATOR REGULATOR
ELECTRIC STARTING MOTORThe starting motor includes a solenoid. The solenoid engages the pinion with the ring gear on the engine flywheel, when the solenoid is energized. The pinion always engages before the electric contacts in the solenoid causes the circuit between the battery and the starting motor to close. An overrunning clutch protects the starting motor from being overspeeded. Releasing the start-switch disengages the pinion and flywheel ring gear.A solenoid is a magnetic switch that uses low current to close a high current circuit. The solenoid is an electro-magnet with a movable core. There are contacts on the end of the core. The contacts are held apart by a spring pushing the core away from the magnetic center of the coil. Low current energizes the coil and forms a magnetic field. The magnetic field pulls the core to the center of the coil, closing the contacts and completing the starting circuit.
SOLENOID
