Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 616 594
9400616594
ZEXEL
106661-2111
1066612111
MITSUBISHI
ME056852
me056852

Rating:
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 616 594
9400616594
ZEXEL
106661-2111
1066612111
MITSUBISHI
ME056852
me056852
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
106661-2111
9 400 616 594
ME056852 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D22T2 * K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
6D22T2 * K 14CA INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6P,6PD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
131424-6920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
191
157
225
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.95
1.6
2.3
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.8
4.75
4.85
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
10.6
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
149
145.3
152.7
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
11.5
9.8
13.2
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(10.6)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
149
148
150
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
29.3
29.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
220
220
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1-0.35
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
147.5
145.5
149.5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
29.3
29.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
220
220
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
R1+1.25
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
174
170
178
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
29.3
29.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
220
220
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
F
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
131
91
171
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
R2(R1-1.
7)
Boost pressure
kPa
6
6
6
Boost pressure
mmHg
45
45
45
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
R1-0.8
Boost pressure
kPa
10
8.7
11.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
75
65
85
Boost compensator adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
R1(10.6)
Boost pressure
kPa
16
16
16
Boost pressure
mmHg
120
120
120
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
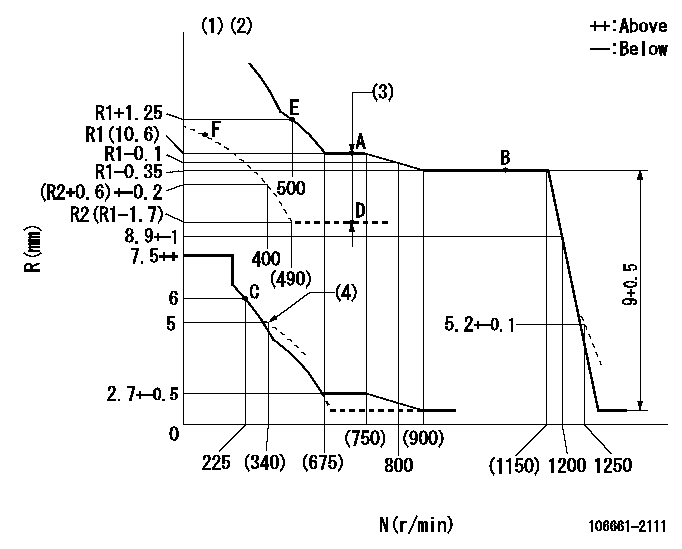
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(2)Boost compensator cancel stroke: BSL
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(4)Damper spring setting
----------
BSL=1.8mm BCL=1.7+-0.1mm
----------
----------
BSL=1.8mm BCL=1.7+-0.1mm
----------
Timer adjustment
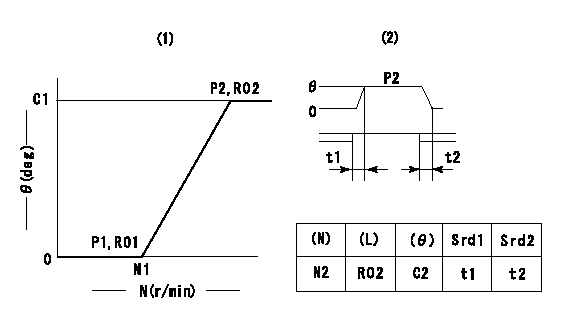
(1)Adjusting range
(2)Step response time
(N): Speed of the pump
(L): Load
(theta) Advance angle
(Srd1) Step response time 1
(Srd2) Step response time 2
1. Adjusting conditions for the variable timer
(1)Adjust the clearance between the pickup and the protrusion to L.
----------
L=1-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(8.8)deg t1=2.5--sec. t2=2.5--sec.
----------
N1=750++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=8.8+-0.3deg R01=0/4load R02=4/4load
----------
L=1-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(8.8)deg t1=2.5--sec. t2=2.5--sec.
----------
N1=750++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=8.8+-0.3deg R01=0/4load R02=4/4load
Speed control lever angle
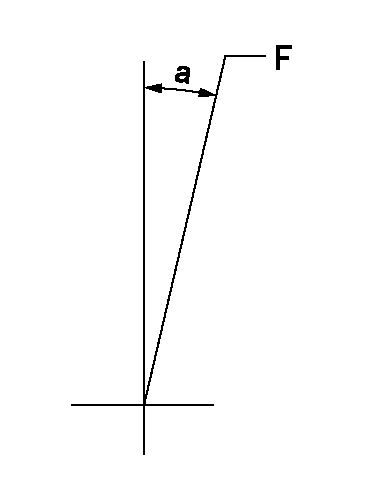
F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=14.5deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=14.5deg+-5deg
0000000901
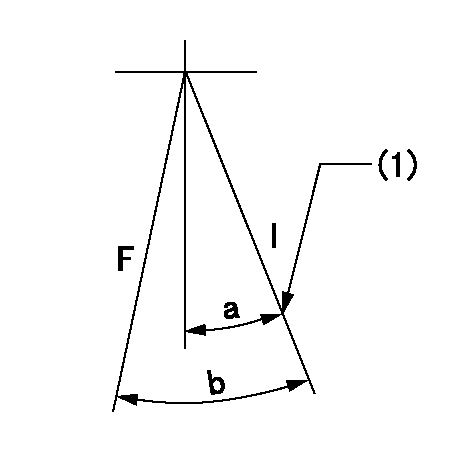
F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=28deg+-5deg b=29.5deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=28deg+-5deg b=29.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
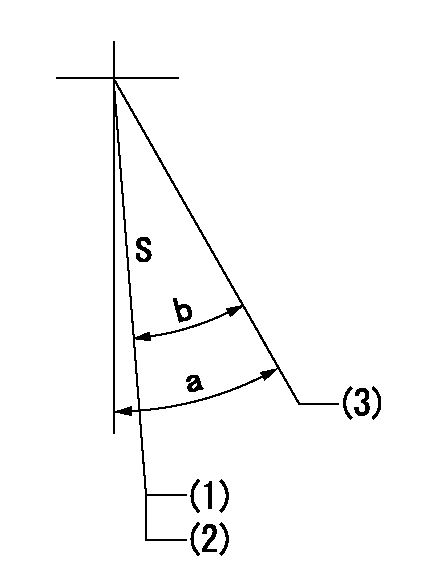
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
(3)Free (at shipping)
----------
aa=3.8-0.5mm
----------
a=38deg+-5deg b=37.5deg+7deg-5deg
----------
aa=3.8-0.5mm
----------
a=38deg+-5deg b=37.5deg+7deg-5deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=325r/min Ra=5.7+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=325r/min Ra=5.7+-0.1mm
----------
0000001601 RACK SENSOR

V1:Supply voltage
V2f:Full side output voltage
V2i:Idle side output voltage
(A) Black
(B) Yellow
(C) Red
(D) Trimmer
(E): Shaft
(F) Nut
(G) Load lever
1. Load sensor adjustment
(1)Connect as shown in the above diagram and apply supply voltage V1.
(2)Hold the load lever (G) against the full side.
(3)Turn the shaft so that the voltage between (A) and (B) is V2.
(4)Hold the load lever (G) against the idle side.
(5)Adjust (D) so that the voltage between (A) and (B) is V2i.
(6)Repeat the above adjustments.
(7)Tighten the nut (F) at the point satisfying the standards.
(8)Hold the load lever against the full side stopper and the idle side stopper.
(9)At this time, confirm that the full side output voltage is V2f and the idle side output voltage is V2i.
----------
V1=5+-0.02V V2f=0.15+0.03V V2i=2.35-0.03V
----------
----------
V1=5+-0.02V V2f=0.15+0.03V V2i=2.35-0.03V
----------
0000001701 LEVER
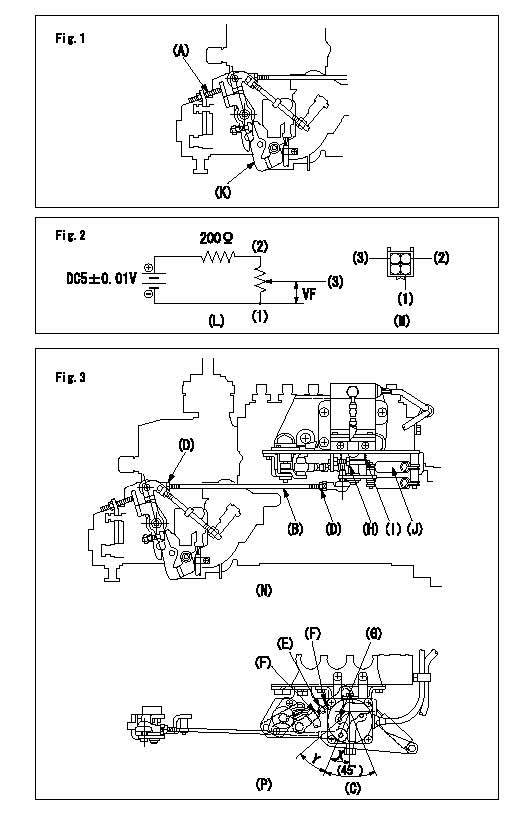
(A) Stopper bolt
(B) Link
(C) S/M lever
(d) Nut
(E) Ring
(F) Nut
(G) S/M lever pin
(H) Stopper bolt
(I) Torsion spring
(J) Return spring
(K) Accelerator lever
(L) Output measurement circuit
(M) Potentiometer terminal
(N) Viewed from front.
(P) Viewed from top.
(1)Black
(2)Blue-red
(3)Blue-yellow
Accelerator lever angle, potentiometer and stopper bolt adjustment
1. Accelerator lever angle adjustment (see Fig. 1)
(1)Hold the load lever against the idle side stopper bolt and fix it in the idling position.
(2)Screw in the accelerator lever stopper bolt (A) and back off the stopper bolt (A) from the position where the accelerator lever contacts the load lever and fix the nut.
Tightening torque: 4.9~7 N.m (0.5~0.7 kgf.m)
2. Potentiometer adjustment (See fig 2 and fig 3)
Apply DC5+-0.01V to between the potentiometer terminals (2) ~ (1) and measure the output voltage VF between (3) ~ (1).
(1)Hold the load lever against the idle side stopper bolt and fix it in the idling position.
(2)Adjust the S/M lever (C)'s lever angle using the link (B) so that X = 22.5+-3 deg , then fix nut (D).
Tightening torque: 3.4~4.9 N.m (0.35~0.5 kgf.m)
(3)Hold the load lever against the full side stopper bolt and fix it in the full position.
(4)Adjust the potentiometer output voltage using the link (E) so that VF = 0.25+-0.1V, the temporarily fix nut (F).
(5)Move the load lever several times between the idle side and the full side. Confirm that it moves smoothly and that output voltage VF = 0.05~0.5V. Then fix nut (F).
Tightening torque: 3.4~4.9 N.m (0.35~0.5 kgf.m)
3. Step motor's idle side stopper bolt adjustment (See fig 3)
(1)After completing accelerator lever angle and potentiometer adjustment, position the load lever against the idle stopper bolt and fix in the idling position.
(2)Screw in stopper bolt (H) until the S/M lever pin (G) contacts the lever (C).
(3)Return the stopper bolt (H) 10 deg+2 deg (approx. 5.7 turns) from the position in (2) above and fix using the nut.
(Reference: lever angle Y = 39.5deg+2deg
Tightening torque: 4.9~7 N.m (0.5~0.7 kgf.m)
4. Final confirmation
Confirm that the load lever is returned to the idling position through the torsion spring (I) and one return spring (J). (Remove 1 return spring.)
----------
----------
----------
----------
Timing setting
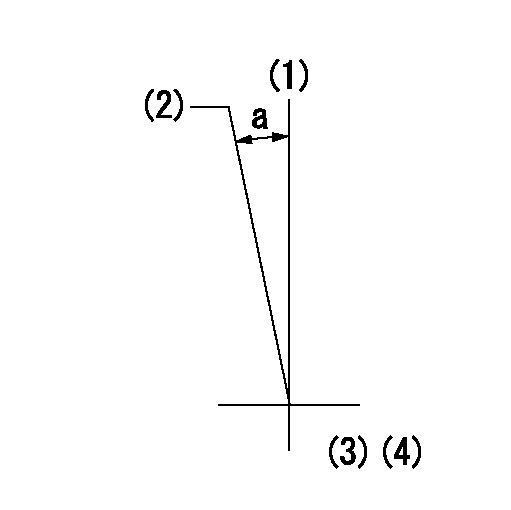
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=9deg
----------
a=(7deg)
----------
aa=9deg
----------
a=(7deg)
Information:
General Instructions
These instructions are a review of many items which a serviceman encounters in servicing and maintaining a truck engine.PROBLEM ANALYZING: In analyzing a system malfunction, use this systematic procedure to locate and correct the problem.1. Determine problem.2. List possible causes.3. Devise checks.4. Conduct checks in logical order to determine cause.5. Consider remaining service life against cost of parts and labor.6. Make necessary repair.7. Recheck.SAFETY: Your safety and that of others is always the number one consideration when servicing or maintaining trucks and truck engines. Safety is a matter of thoroughly understanding the job to be done and the application of good common sense. It is not just a matter of "do's" and "don'ts".CLEANLINESS: The most important single item in assuring long engine life is to keep dirt out of vital working parts. Precautions have been taken to safeguard against this. Enclosed compartments, seals and filters have been provided to keep the supply of air, fuel, coolant and lubricants clean. It is important that these safeguards be maintained.Whenever fuel, lubricating oil, coolant lines or air lines are disconnected, clean the point of disconnection as well as the adjacent area. As soon as the disconnection is made, cap, plug or tape the line or opening to prevent entry of foreign material. The same recommendations for cleaning and covering apply when access covers or inspection plates are removed.Clean and inspect all parts. Be sure all passages and holes are open. Cover all parts to keep them clean. Be sure parts are clean when they are installed. Leave new parts in their containers until ready for assembly.REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION: Use a hoist to remove heavy components. Engine removal should be accomplished by using an adjustable lifting beam. All supporting members (chains and cables) should be parallel to each other and as near perpendicular as possible to the top of the object being lifted. When it is necessary to remove a component on an angle, remember that the capacity of an eyebolt diminishes as the angle between the supporting members and the object becomes less than 90°. Eyebolts and brackets should never be bent and should only have stress in tension.Some removals require the use of lifting fixtures to obtain proper balance and to provide safe handling.If a part resists removal, check to be certain all nuts and bolts have been removed and that an adjacent part is not interfering.DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY: When servicing or repairing the engine, complete each step in turn. Do not partially assemble one part and start assembling some other part. Make all adjustments as recommended. Always check the job after it is completed to see nothing has been overlooked.BOLTS AND BOLT TORQUE: Use bolts of the correct length. A bolt which is too long may "bottom" before the head is tight against the part it is to hold and cause failure. The threads in the assembly can also become damaged when a "long" bolt is used.If a bolt is too short, there may not be enough threads
These instructions are a review of many items which a serviceman encounters in servicing and maintaining a truck engine.PROBLEM ANALYZING: In analyzing a system malfunction, use this systematic procedure to locate and correct the problem.1. Determine problem.2. List possible causes.3. Devise checks.4. Conduct checks in logical order to determine cause.5. Consider remaining service life against cost of parts and labor.6. Make necessary repair.7. Recheck.SAFETY: Your safety and that of others is always the number one consideration when servicing or maintaining trucks and truck engines. Safety is a matter of thoroughly understanding the job to be done and the application of good common sense. It is not just a matter of "do's" and "don'ts".CLEANLINESS: The most important single item in assuring long engine life is to keep dirt out of vital working parts. Precautions have been taken to safeguard against this. Enclosed compartments, seals and filters have been provided to keep the supply of air, fuel, coolant and lubricants clean. It is important that these safeguards be maintained.Whenever fuel, lubricating oil, coolant lines or air lines are disconnected, clean the point of disconnection as well as the adjacent area. As soon as the disconnection is made, cap, plug or tape the line or opening to prevent entry of foreign material. The same recommendations for cleaning and covering apply when access covers or inspection plates are removed.Clean and inspect all parts. Be sure all passages and holes are open. Cover all parts to keep them clean. Be sure parts are clean when they are installed. Leave new parts in their containers until ready for assembly.REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION: Use a hoist to remove heavy components. Engine removal should be accomplished by using an adjustable lifting beam. All supporting members (chains and cables) should be parallel to each other and as near perpendicular as possible to the top of the object being lifted. When it is necessary to remove a component on an angle, remember that the capacity of an eyebolt diminishes as the angle between the supporting members and the object becomes less than 90°. Eyebolts and brackets should never be bent and should only have stress in tension.Some removals require the use of lifting fixtures to obtain proper balance and to provide safe handling.If a part resists removal, check to be certain all nuts and bolts have been removed and that an adjacent part is not interfering.DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY: When servicing or repairing the engine, complete each step in turn. Do not partially assemble one part and start assembling some other part. Make all adjustments as recommended. Always check the job after it is completed to see nothing has been overlooked.BOLTS AND BOLT TORQUE: Use bolts of the correct length. A bolt which is too long may "bottom" before the head is tight against the part it is to hold and cause failure. The threads in the assembly can also become damaged when a "long" bolt is used.If a bolt is too short, there may not be enough threads
Have questions with 106661-2111?
Group cross 106661-2111 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
106661-2111
9 400 616 594
ME056852
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D22T2
6D22T2