Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
106661-0840
1066610840
NISSAN-DIESEL
1671396563
1671396563
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
106661-0840
1066610840
NISSAN-DIESEL
1671396563
1671396563
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 8-3-600
Overflow valve
132424-0620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
3.2
3.15
3.25
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.2
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
154.5
152.5
156.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
40
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
300
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
5.7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
11
10
12
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
10.1
Boost pressure
kPa
6.7
4
6.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
50
30
50
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
10.6
Boost pressure
kPa
10.7
9.4
12
Boost pressure
mmHg
80
70
90
Boost compensator adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
11.2
Boost pressure
kPa
20.7
20.7
20.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
155
155
155
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
700+50
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
900+40-1
0
Advance angle
deg.
0.9
0.4
1.4
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1150+30-
20
Advance angle
deg.
3
2.5
3.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
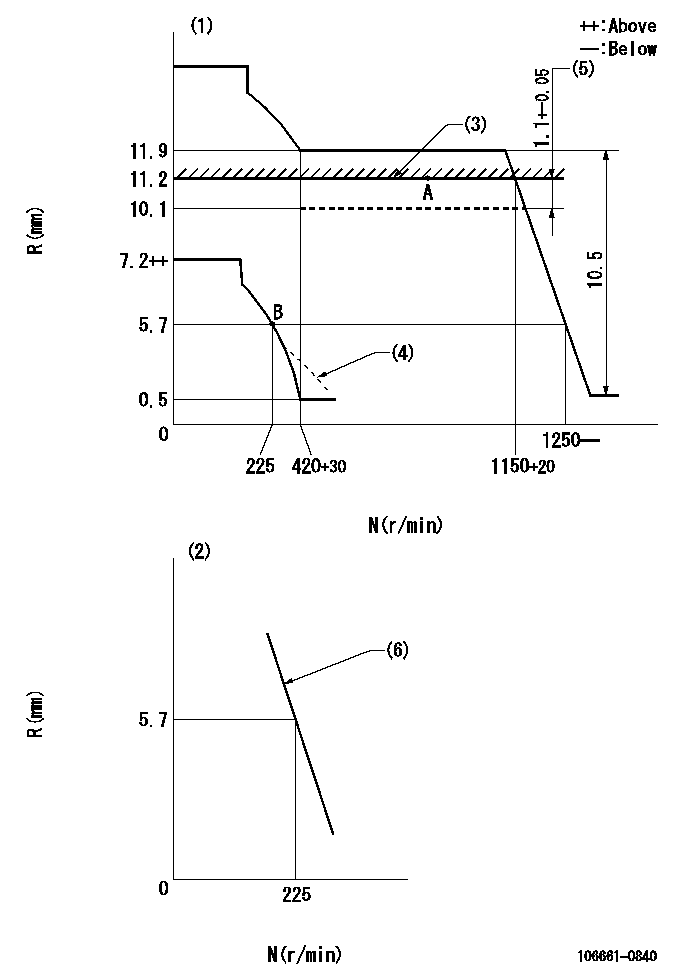
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Adjust with speed control lever at full position (minimum-maximum speed specification)
(2)Adjust with the load control lever in the full position (variable speed specification).
(3)Rack limit using stop lever
(4)Damper spring setting: DL
(5)Boost compensator stroke
(6)Main spring setting
----------
DL=4.7-0.2mm
----------
----------
DL=4.7-0.2mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
----------
----------
a=11deg+4deg-3deg b=22deg+4deg-4deg
----------
----------
a=11deg+4deg-3deg b=22deg+4deg-4deg
0000000901
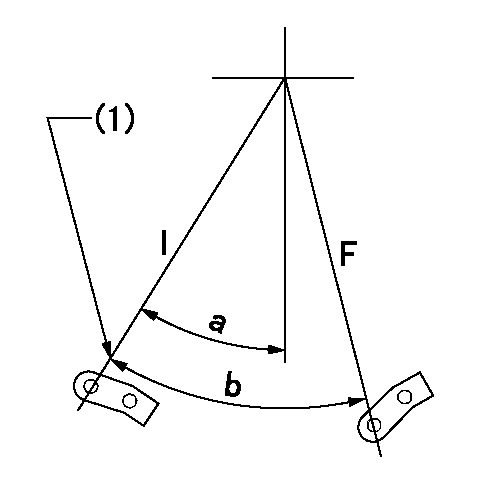
F:Full load
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=32.5deg+-5deg b=42deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=32.5deg+-5deg b=42deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
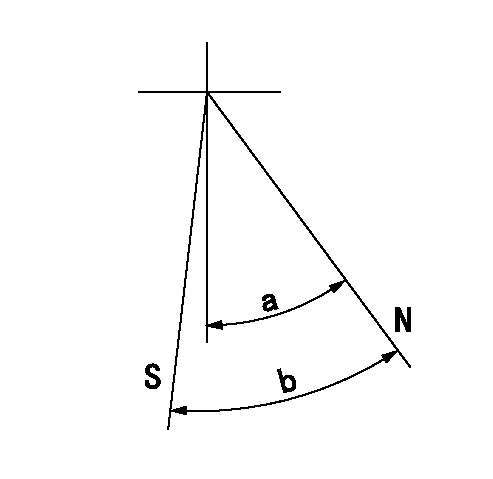
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=29.5deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=29.5deg+-3deg
Information:
Introduction
The problem that is identified below does not have a known permanent solution. Until a permanent solution is known, use the solution that is identified below.Problem
The DOC/DPF can become plugged if an NRS cooler failure occurs and coolant passes out the exhaust. Solution
If an engine has an NRS cooler failure, the DPF and DOC will need inspected for calcium deposits. In some cases calcium has partially filled the DPF and caused frequent regeneration issues, and erratic high soot loading readings.
Illustration 1 g03374496
Example of calcium deposits on DPF face
Illustration 2 g03374497
Example of calcium deposits on DPF faceThe calcium deposits will be a white and black powdery mixture on the face of the DPF and the DOC. Refer to Illustrations 1 and 2 for examples of a DPF with calcium plugging on the DPF face.Refer to Reuse And Salvage Guidelines, SEBF9223, "Inspection of Diesel Particulate Filters and Diesel Oxidation Catalysts for Tier 4 Machine and Industrial Engines" for further assistance.
The problem that is identified below does not have a known permanent solution. Until a permanent solution is known, use the solution that is identified below.Problem
The DOC/DPF can become plugged if an NRS cooler failure occurs and coolant passes out the exhaust. Solution
If an engine has an NRS cooler failure, the DPF and DOC will need inspected for calcium deposits. In some cases calcium has partially filled the DPF and caused frequent regeneration issues, and erratic high soot loading readings.
Illustration 1 g03374496
Example of calcium deposits on DPF face
Illustration 2 g03374497
Example of calcium deposits on DPF faceThe calcium deposits will be a white and black powdery mixture on the face of the DPF and the DOC. Refer to Illustrations 1 and 2 for examples of a DPF with calcium plugging on the DPF face.Refer to Reuse And Salvage Guidelines, SEBF9223, "Inspection of Diesel Particulate Filters and Diesel Oxidation Catalysts for Tier 4 Machine and Industrial Engines" for further assistance.