Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
104748-1652
1047481652

Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
104748-1652
1047481652
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105000-2010
Bosch type code
NP-DN12SD12TT
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Opening pressure
MPa
14.7
14.7
15.19
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
150
150
155
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
31
30.5
31.5
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
29.5
28
31
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
31
30
32
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
2500
2500
2500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
26.8
25.3
28.3
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
2600
2600
2600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
26.7
25.1
28.3
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection timing adjustment_06
Pump speed
r/min
2700
2700
2700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
25.1
22.1
28.1
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2800
2800
2800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
20.8
19.8
21.8
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2900
2900
2900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
4
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
2800
2800
2800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
20.8
19.8
21.8
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
6.5
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
6
5
7
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
6
5
7
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
50
50
70
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Full
Full
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
50
50
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Magnet OFF at idling position
Magnet OFF at idling position
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Overflow quantity
cm3/min
370
240
500
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Pressure
kPa
363
343
383
Pressure
kgf/cm2
3.7
3.5
3.9
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Pressure
kPa
363
343
383
Pressure
kgf/cm2
3.7
3.5
3.9
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle_03
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Pressure
kPa
539
510
568
Pressure
kgf/cm2
5.5
5.2
5.8
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle_04
Pump speed
r/min
2300
2300
2300
Pressure
kPa
618
589
647
Pressure
kgf/cm2
6.3
6
6.6
Oil temperature
degC
52
50
54
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Timer stroke
mm
3.1
2.9
3.3
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_02
Pump speed
r/min
620
620
620
Timer stroke
mm
0.5
0.5
0.5
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Timer stroke
mm
3.1
2.9
3.3
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_04
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Timer stroke
mm
6.1
5.7
6.5
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_05
Pump speed
r/min
2300
2300
2300
Timer stroke
mm
7.4
7.1
7.8
Oil temperature
degC
52
50
54
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
0000001401
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18
17.5
18.5
Timer stroke TA
mm
2.3
2.3
2.3
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
0.8
0.6
1
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18
17
19
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
0.8
0.4
1.2
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9
9
9
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
2.2
2.2
2.2
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_04
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
7
6
8
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
2.2
1.6
2.8
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.8
5.7
5.9
MS dimension
mm
1.6
1.5
1.7
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
20
16
24
Control lever angle beta
deg.
40
39
41
Test data Ex:
0000001801 V-FICD ADJUSTMENT
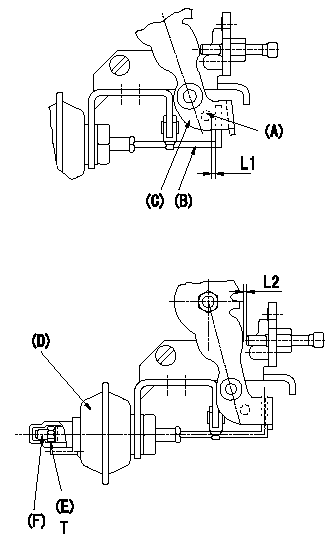
Adjustment of the V-FICD (perform with W-FICD released)
1. Adjust to obtain L1.
2. Confirm that L2 is obtained when negative pressure P1 (kPa) {P2 (mmHg)} is applied to the actuator.
Adjust the stroke using the actuator stroke adjusting screw (F).
(A): Pin
(B): Actuator shaft
(C): Control lever
(D): Actuator
(E): Lock nut (torque T)
----------
L1=1+1mm L2=1.45+-0.1mm P1=-53.3kPa P2=-400mmHg
----------
L1=1+1mm L2=1.45+-0.1mm T=1.2~1.5N-m{0.12~0.15kgf-m}
----------
L1=1+1mm L2=1.45+-0.1mm P1=-53.3kPa P2=-400mmHg
----------
L1=1+1mm L2=1.45+-0.1mm T=1.2~1.5N-m{0.12~0.15kgf-m}
0000001901 W-CSD ADJUSTMENT
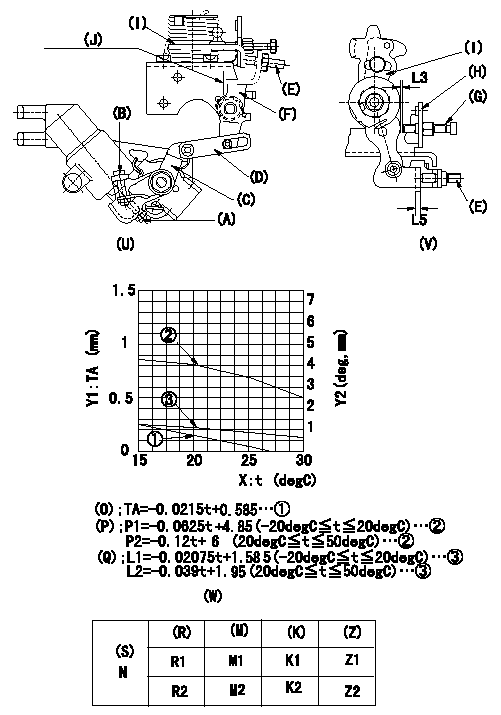
Adjustment of the W-CSD
1. Adjustment of the timer stroke
Adjust using screw (A) so that the timer stroke is the value determined using the graph (W). [(K), (M)]
2. Adjustment of the position of the intermediate lever.
With a shim L5 inserted between the control lever (I) and the FICD set screw (E), insert a shim (L3) between (I) and the idle screw (G).
Align the intermediate lever (F) with the aligning mark (J) and then fix the intermediate lever adjusting screw (E) so that (E) contacts the shim between (E) and (I). [(U), (V)]
3. Adjustment of the FICD
Insert the shim (L4) between the control lever (I) and the idle set screw (G).
Use adjusting screw (B) to fix the CSD lever (C) in the position where it operates the intermediate lever (F) via the rod (D). [(U), (V)]
However, set with a shim L5 inserted. [(U), (V), (W)]
(O) Timer stroke adjustment (mm)
(P): lever angle (deg)
(Q): lever angle (deg)
The (Q) indicates the clearance between the control lever and the idle set screw.
X:Temperature t (deg C)
Y1:Timer stroke TA (mm)
Y2:Control lever position at theta L (deg, mm)
(R): cooling water temperature (deg C)
(S): cooling water temperature: increase direction
N:Pump speed
(M): timer piston stroke (mm)
(K): colored ring
(Z): lever position (mm)
----------
L3=1.2+-0.05mm L4=L3+-0.05mm L5=-mm
----------
L3=1.2+-0.05mm L5=-mm N=500r/min R1=20deg R2=-20deg M1=0.16+-0.2mm M2=1.0+-0.4mm K1=3.6+-1deg K2=6.1+-3deg Z1=1.2+-0.3mm Z2=2+-1mm
----------
L3=1.2+-0.05mm L4=L3+-0.05mm L5=-mm
----------
L3=1.2+-0.05mm L5=-mm N=500r/min R1=20deg R2=-20deg M1=0.16+-0.2mm M2=1.0+-0.4mm K1=3.6+-1deg K2=6.1+-3deg Z1=1.2+-0.3mm Z2=2+-1mm
Information:
Example of Pulse Width Modulation SignalsRated Rack PositionA limit on rack position which provides the specified horsepower and torque curves. this value comes from maps programmed into the personality module at the factory.Rack Position SensorA linear position sensor which follows movement of the rack assembly and sends an electrical signal to the ECM.Rack Solenoid (BTM)A rotary proportional solenoid (also called a BTM) used to move the fuel rack servo spool valve.Reference VoltageA regulated voltage supplied by the ECM to a sensor. The reference voltage is used by the sensor to generate a signal voltage.Retarder Enable SignalThe Retarder Enable signal is provided by the ECM to indicate that conditions are acceptable for an engine retarder to operate. Operation of the retarder is inhibited during undesirable engine operating conditions (such as while the engine is being fueled).SensorA device used to detect and convert a change in pressure, temperature, or mechanical movement into an electrical signal.Service Program ModuleA software program on a factory programmable computer chip, designed to adapt an ECAP or DDT to a specific application.Short CircuitA condition where an electrical circuit is unintentionally connected to an undesirable point. Example: a wire which rubs against a vehicle frame until it wears off its insulation and makes electrical contact with the frame.SignalA voltage or waveform used to transmit information typically from a sensor to the ECM.Speed "burp"A sudden brief change in engine speed.Static Timing SpecificationFixed number of degrees determined by design of the fuel pump camshaft (determines injection timing with no advance). Note that the value displayed is the specification for static timing, not an electrically measured value.SubsystemAs used here, it is a part of the PEEC III System that relates to a particular function, for instance: throttle subsystem, etc.Supply VoltageA constant voltage supplied to a component to provide electrical power for its operation. It may be generated by the ECM, or it may be vehicle battery voltage supplied by the vehicle wiring."T" HarnessA test harness designed to permit normal circuit operation while measuring voltages, typically inserted between the two ends of a connector.Throttle PositionThe ECM's interpretation of the signal from the Throttle Position Sensor.Throttle Position SensorAn electronic sensor which is connected to the accelerator pedal and sends a Pulse Width Modulated signal to the ECM.Timing Position SensorA linear position sensor which follows movement of the timing advance unit and sends an electrical signal to the ECM.Timing Solenoid (BTM)A rotary proportional solenoid (also called a BTM) used to move the timing advance unit spool valve. Total TattletaleTotal number of changes to all Customer Specified Parameters.TransducerA device which converts a mechanical signal to an electrical signal.Transducer ModuleA sealed unit mounted below the rack actuator housing and contains the engine oil pressure sensor, boost pressure sensor, and protective signal conditioning circuitry.Vehicle Speed BufferA device used to condition and amplify the output of the vehicle speed sensor.Vehicle Speed SensorAn electro-magnetic pickup that measures vehicle speed from the rotation of gear teeth in the drive train of the vehicle.