Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
104748-1650
1047481650
ISUZU
8944134490
8944134490
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
104748-1650
1047481650
ISUZU
8944134490
8944134490
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105000-2010
Bosch type code
NP-DN12SD12TT
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Opening pressure
MPa
14.7
14.7
15.19
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
150
150
155
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
30.2
29.7
30.7
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2.5
Basic
*
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2965
2965
2965
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
11.1
9.6
12.6
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
2700
2700
2700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
24.6
19.6
29.6
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
2600
2600
2600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
27.2
25.1
29.3
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
2500
2500
2500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
26.8
24.8
28.8
Injection timing adjustment_06
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
28.6
26.6
30.6
Injection timing adjustment_07
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
30.2
29.2
31.2
Injection timing adjustment_08
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
29
27
31
Injection timing adjustment_09
Pump speed
r/min
2965
2965
2965
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
11
11
11
Remarks
Measure with the angle beta (39~41degC) adjusted to within the specifications.
Measure with the angle beta (39~41degC) adjusted to within the specifications.
Injection timing adjustment_10
Pump speed
r/min
2800
2650
2950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
20.9
19.9
21.9
Basic
*
Remarks
Measure with the angle beta (39~41degC) adjusted to within the specifications.
Measure with the angle beta (39~41degC) adjusted to within the specifications.
Injection timing adjustment_11
Pump speed
r/min
2700
2700
2700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
24.6
21.1
28.1
Remarks
Measure with the angle beta (39~41degC) adjusted to within the specifications.
Measure with the angle beta (39~41degC) adjusted to within the specifications.
Injection timing adjustment_12
Pump speed
r/min
2600
2600
2600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
26.8
24.7
28.9
Remarks
Measure with the angle beta (39~41degC) adjusted to within the specifications.
Measure with the angle beta (39~41degC) adjusted to within the specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2965
2965
2965
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
11.1
10.1
12.1
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
3.5
Basic
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2900
2900
2900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
4.5
Remarks
Insert a 4.5+-0.1 mm shim between the C/L and the full speed position and measure injection quantity.
Insert a 4.5+-0.1 mm shim between the C/L and the full speed position and measure injection quantity.
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
6
5
7
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
6
5
7
Governor adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
4
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
50
50
Basic
*
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Remarks
Magnet OFF
Magnet OFF
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Overflow quantity
cm3/min
369
240
498
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Pressure
kPa
362.5
343
382
Pressure
kgf/cm2
3.7
3.5
3.9
Basic
*
Stop lever angle_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Pressure
kPa
186.5
157
216
Pressure
kgf/cm2
1.9
1.6
2.2
Stop lever angle_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Pressure
kPa
362.5
343
382
Pressure
kgf/cm2
3.7
3.5
3.9
Stop lever angle_04
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Pressure
kPa
539.5
510
569
Pressure
kgf/cm2
5.5
5.2
5.8
Stop lever angle_05
Pump speed
r/min
2300
2300
2300
Pressure
kPa
637.5
608
667
Pressure
kgf/cm2
6.5
6.2
6.8
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Timer stroke
mm
3.1
2.9
3.3
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Timer stroke
mm
3.1
2.8
3.4
_03
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Timer stroke
mm
6.1
5.5
6.7
_04
Pump speed
r/min
2300
2300
2300
Timer stroke
mm
7.4
7
7.8
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
0000001401
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18.1
17.9
18.3
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
0.8
0.7
0.9
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18.1
17.4
18.8
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
0.8
0.6
1
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
7
5.5
8.5
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
2.2
1.7
2.7
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.8
5.7
5.9
MS dimension
mm
1.6
1.5
1.7
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
20
16
24
Control lever angle beta
deg.
40
37
43
Test data Ex:
0000001801 W-CSD ADJUSTMENT
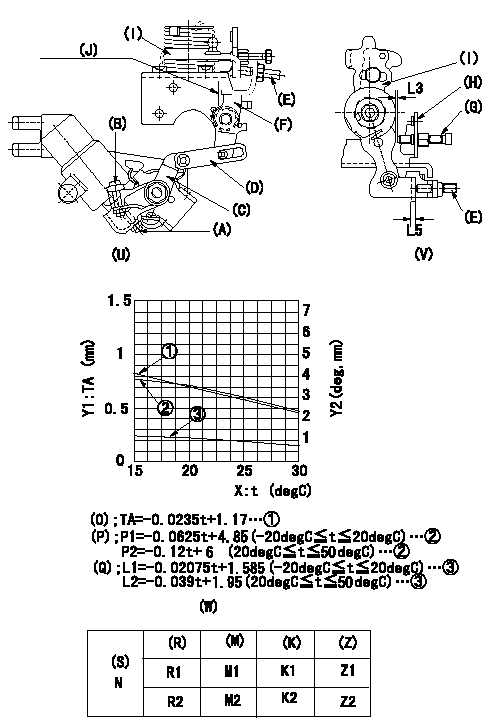
Adjustment of the W-CSD
1. Adjustment of the timer stroke
Adjust using screw (A) so that the timer stroke is the value determined using the graph (W). [(K), (M)]
2. Adjustment of the position of the intermediate lever.
With a shim L5 inserted between the control lever (I) and the FICD set screw (E), insert a shim (L3) between (I) and the idle screw (G).
Align the intermediate lever (F) with the aligning mark (J) and then fix the intermediate lever adjusting screw (E) so that (E) contacts the shim between (E) and (I). [(U), (V)]
3. Adjustment of the FICD
Insert the shim (L4) between the control lever (I) and the idle set screw (G).
Use adjusting screw (B) to fix the CSD lever (C) in the position where it operates the intermediate lever (F) via the rod (D). [(U), (V)]
However, set with a shim L5 inserted. [(U), (V), (W)]
(O) Timer stroke adjustment (mm)
(P): lever angle (deg)
(Q): lever angle (deg)
The (Q) indicates the clearance between the control lever and the idle set screw.
X:Temperature t (deg C)
Y1:Timer stroke TA (mm)
Y2:Control lever position at theta L (deg, mm)
(R): cooling water temperature (deg C)
(S): cooling water temperature: increase direction
N:Pump speed
(M): timer piston stroke (mm)
(K): colored ring
(Z): lever position (mm)
----------
L3=1.2+-0.05mm L4=L3+-0.05mm
----------
L3=1.2+-0.05mm L4=L+-0.05mm L5=-mm R1=- R2=- M1=- M2=- K1=- K2=- Z1=- Z2=-
----------
L3=1.2+-0.05mm L4=L3+-0.05mm
----------
L3=1.2+-0.05mm L4=L+-0.05mm L5=-mm R1=- R2=- M1=- M2=- K1=- K2=- Z1=- Z2=-
Information:
ACTIVE Diagnostic Codes
Diagnostic codes are used by the PEEC III system to warn the vehicle operator of a problem and indicate to the service technician the nature of the problem. Some codes are used only to record an event, and do not indicate problems.An ACTIVE Diagnostic code represents a problem that should be investigated and corrected AS SOON AS POSSIBLE. Repairing the cause of an ACTIVE code will cause the code to be cleared from the ACTIVE Diagnostic Code screen.When an ACTIVE code is generated, the PEEC III lamp will turn ON and remain ON, blinking every five seconds. If the condition generating the fault occurs only for a brief moment, the lamp will go OFF after five seconds and the fault will be LOGGED. After a problem has been investigated and corrected, the related diagnostic code should be cleared from memory.ACTIVE codes may be viewed using either of the electronic service tools (ECAP or DDT), and may also be viewed using the diagnostic lamp and cruise control switches. The diagnostic lamp should not be confused with the warning lamp which is used with PEEC III engine protection.Using The ECAP Or DDT To Display ACTIVE Codes
A. With key OFF, install an ECAP or DDT into the PEEC III system.B. Turn key ON (engine does not need to be started to view codes).C. Refer to the Operating Manual and Special Instructions for the service tool (listed under PEEC III Service Tools) to read the code(s). On the ECAP, the display menu will direct you to the proper screen to display diagnostic messages similar to the example below.Using The Cruise Control Switches To Display ACTIVE Codes:
A. Turn key ON (engine does not need to be started to view codes).B. The PEEC III Diagnostic Lamp will turn ON for five seconds, blink OFF for 1/10 second, turn ON again for five seconds, then OFF for five seconds. At the end of that time, the lamp will begin to flash the first number of the two-digit code (count the flashes). After two seconds OFF, then it will flash the second digit. If two or more codes are present, they will follow the first after a few seconds and be displayed in the same manner.C. Active Diagnostic codes may be displayed at any time by using cruise control switches. With key ON or engine running, turn the cruise control ON/OFF switch to OFF, and move the SET/RESUME switch to RESUME position. Once the codes begin to flash the switch may be released. The PEEC III Diagnostic Lamp will flash out all the codes that are currently active, or intermittent codes that have occurred since the key was turned on. LOGGED Diagnostic Codes
When an ECM generates a diagnostic code, it usually logs the code in permanent memory within the ECM. The time the code occurred (in hours on the internal diagnostic clock) is logged along with the code. The logged codes can then be later retrieved or erased using an ECAP or DDT service
Diagnostic codes are used by the PEEC III system to warn the vehicle operator of a problem and indicate to the service technician the nature of the problem. Some codes are used only to record an event, and do not indicate problems.An ACTIVE Diagnostic code represents a problem that should be investigated and corrected AS SOON AS POSSIBLE. Repairing the cause of an ACTIVE code will cause the code to be cleared from the ACTIVE Diagnostic Code screen.When an ACTIVE code is generated, the PEEC III lamp will turn ON and remain ON, blinking every five seconds. If the condition generating the fault occurs only for a brief moment, the lamp will go OFF after five seconds and the fault will be LOGGED. After a problem has been investigated and corrected, the related diagnostic code should be cleared from memory.ACTIVE codes may be viewed using either of the electronic service tools (ECAP or DDT), and may also be viewed using the diagnostic lamp and cruise control switches. The diagnostic lamp should not be confused with the warning lamp which is used with PEEC III engine protection.Using The ECAP Or DDT To Display ACTIVE Codes
A. With key OFF, install an ECAP or DDT into the PEEC III system.B. Turn key ON (engine does not need to be started to view codes).C. Refer to the Operating Manual and Special Instructions for the service tool (listed under PEEC III Service Tools) to read the code(s). On the ECAP, the display menu will direct you to the proper screen to display diagnostic messages similar to the example below.Using The Cruise Control Switches To Display ACTIVE Codes:
A. Turn key ON (engine does not need to be started to view codes).B. The PEEC III Diagnostic Lamp will turn ON for five seconds, blink OFF for 1/10 second, turn ON again for five seconds, then OFF for five seconds. At the end of that time, the lamp will begin to flash the first number of the two-digit code (count the flashes). After two seconds OFF, then it will flash the second digit. If two or more codes are present, they will follow the first after a few seconds and be displayed in the same manner.C. Active Diagnostic codes may be displayed at any time by using cruise control switches. With key ON or engine running, turn the cruise control ON/OFF switch to OFF, and move the SET/RESUME switch to RESUME position. Once the codes begin to flash the switch may be released. The PEEC III Diagnostic Lamp will flash out all the codes that are currently active, or intermittent codes that have occurred since the key was turned on. LOGGED Diagnostic Codes
When an ECM generates a diagnostic code, it usually logs the code in permanent memory within the ECM. The time the code occurred (in hours on the internal diagnostic clock) is logged along with the code. The logged codes can then be later retrieved or erased using an ECAP or DDT service