Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
104748-0211
1047480211
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
104748-0211
1047480211
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105000-2010
Bosch type code
NP-DN12SD12TT
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Opening pressure
MPa
14.7
14.7
15.19
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
150
150
155
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
38.7
38.2
39.2
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2.5
Basic
*
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2400
2400
2400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13.1
10.1
16.1
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
2125
2125
2125
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
34
32
36
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
38.7
37.7
39.7
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
32.7
30.7
34.7
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2400
2400
2400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13.1
11.1
15.1
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
4
Basic
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2500
2500
2500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
4
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8
6
10
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12
6
18
Governor adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
450
450
450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
4
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
42
42
Basic
*
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Remarks
Magnet OFF
Magnet OFF
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Overflow quantity
cm3/min
430.2
298.2
562.2
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Pressure
kPa
510
481
539
Pressure
kgf/cm2
5.2
4.9
5.5
Basic
*
Stop lever angle_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Pressure
kPa
294.5
265
324
Pressure
kgf/cm2
3
2.7
3.3
Stop lever angle_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Pressure
kPa
510
481
539
Pressure
kgf/cm2
5.2
4.9
5.5
Stop lever angle_04
Pump speed
r/min
2125
2125
2125
Pressure
kPa
745.5
716
775
Pressure
kgf/cm2
7.6
7.3
7.9
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Timer stroke
mm
3.5
3.3
3.7
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Timer stroke
mm
3.5
3.2
3.8
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Timer stroke
mm
4.7
4.1
5.3
_04
Pump speed
r/min
2125
2125
2125
Timer stroke
mm
7.6
7
8.2
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
0000001401
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
28.2
27.2
29.2
Timer stroke TA
mm
2.7
2.5
2.9
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
28
26.5
29.5
Timer stroke TA
mm
2.7
2.4
3
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18
16.5
19.5
Timer stroke TA
mm
1.5
0.8
2.2
0000001501
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Atmospheric pressure difference
kPa
-18.7
-18.7
-18.7
Atmospheric pressure difference
mmHg
-140
-140
-140
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
34.1
33.1
35.1
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Atmospheric pressure difference
kPa
-18.7
-18.7
-18.7
Atmospheric pressure difference
mmHg
-140
-140
-140
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
34.1
32.6
35.6
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.8
5.7
5.9
MS dimension
mm
1.5
1.4
1.6
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
30
26
34
Control lever angle beta
deg.
45
40
50
Test data Ex:
0000001801 M-CSD ADJUSTMENT
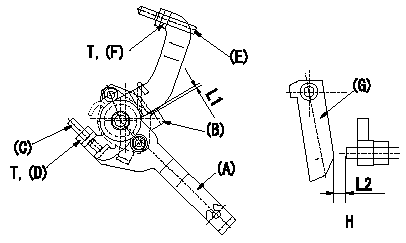
M-CSD adjustment
1. Fixing the M-CSD
(1)At roller holder advance angle a adjust the lever shaft ball pin so that it contacts the roller holder.
(2)At this time, adjust the position of the M-CSD lever (A) using adjusting screw (C) so that the clearance between the M-CSD lever (A) and the stopper (B) becomes L1. Then fix using nut (D).
TT
2. M-FICD adjustment
(1)Move the CSD lever (A) through its full stroke.
(2)Adjust screw (E) so that the control lever (G)'s position is b (the clearance between the control lever and the idling set screw is L2). Then fix using the nut (F).
TT
Pump speed NE
H = from idle to position b
----------
L1=0.5+2mm L2=4.8+-1mm a=0deg b=7deg T=6~9Nm(0.6~0.9kgfm)
----------
L1=0.5+2mm L2=4.8+-1mm T=6~9Nm(0.6~0.9kgfm) b=7deg
----------
L1=0.5+2mm L2=4.8+-1mm a=0deg b=7deg T=6~9Nm(0.6~0.9kgfm)
----------
L1=0.5+2mm L2=4.8+-1mm T=6~9Nm(0.6~0.9kgfm) b=7deg
0000001901 ANEROID COMPENSATOR
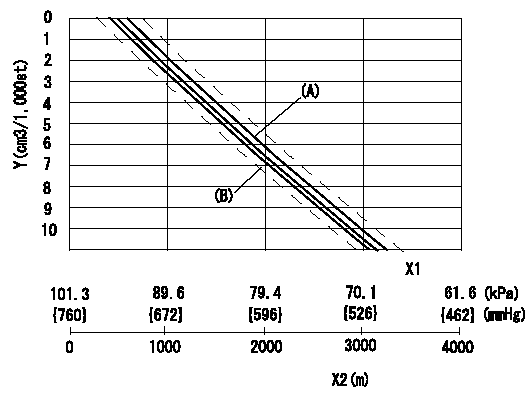
ACS adjustment
Full load injection quantity at high altitudes and ACS adjusting method
1. Full load injection quantity adjustment
(1)Remove the ACS cover and remove the bellows and adjusting shim.
(2)Perform all adjustments as per the adjustment standard except for ACS adjustment.
2. ACS adjustment
(1)Assemble the ACS cover, bellows and adjusting shim.
(2)At pump speed N1, adjust using a shim to obtain the decrease for the altitude shown in the table.
Adjustment of the V-FICD
(1)Operate the V-actuator through its full stroke.
(2)Adjust the V-actuator screw so that the control lever position is a (clearance from the screw is L).
X1 = atmospheric pressure
X2 = altitude
Y = decrease quantity
(A) = adjustment value
(B) = test value
----------
N1=1500r/min a=5deg L=3.4+-1mm
----------
----------
N1=1500r/min a=5deg L=3.4+-1mm
----------
Information:
Stopping the engine immediately after it has been working under load can result in overheating and accelerated wear of the engine components. Allow the engine to cool down before stopping. Avoiding hot engine shutdowns will maximize turbocharger shaft and bearing life.
Emergency Stopping
Emergency shutoff controls are for EMERGENCY use ONLY. DO NOT use Emergency shutoff devices or controls for normal stopping procedure.
Make sure that any external system components that have been operating to support engine operation are secured after any stop.Emergency Stop Buttons
Emergency Stop Button, shown mounted on a junction box.Emergency stops may be made by pushing the Emergency Stop Button located on the junction box (if equipped). Both the Button and the air inlet shutoff (if equipped) require resetting before the engine will start.
Control Panel Emergency Stop Button.If equipped with the EMCPII Control Panel, press the Emergency Stop Button for an emergency stop. The ECS must be reset before resuming operation. Move the ECS to the OFF/RESET position. The ECS can also be used to shut the engine off in an emergency. Move the ECS to the OFF/RESET position. The engine will immediately shut off.Manual Stopping
A manual shutoff shaft is provided to override the governor control. The shaft will move the fuel control linkage to the FUEL OFF position. Refer to the Model Views for the engine location of the shaft. The engine may be stopped by using the shaft and the Woodward Actuator (if equipped) or the Mechanical Governor (if equipped).
Typical Woodward Actuator Control Lever.If equipped with a Woodward Actuator, move the control lever to the FUEL OFF position.
Typical Mechanical Governor ControlIf equipped with a Mechanical Governor Control, move the control to the FUEL OFF position.Hold the lever at the FUEL OFF position until the engine stops.Air Shutoff (If Equipped)
Some engines are equipped with an air shutoff, located between the aftercooler and the turbocharger. If equipped with an air shutoff lever, move the lever to the OFF position.Manual Stop Procedure
There may be several ways to shut off your engine. Make sure the shutoff procedures are understood. Use the following general guidelines for stopping the engine.EPG Engines
If the ECS is in the AUTO position and the remote contact opens, the engine will run for a pre-programmed cool down period. This will only occur when the cool down mode is used. If the cool down mode is not used, the engine will shut off immediately.
If the ECS is in the AUTO position, the remote contact opens, and the cool down time expires, the CTR will be unlatched and the starting motors may be re-engaged.1. Open the main electrical circuit breaker to remove the load.2. The engine should be run for a cool down period before being shut off. This can be accomplished with the COOLDOWN STOP switch, or the operator can control the cool down and shut off.
To use the COOLDOWN/STOP switch, turn the ECS to the COOLDOWN/STOP position. The engine will operate for a pre-programmed time period. The timer will active the fuel shutoff after the cool down.Alternatively,