Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
104746-6200
1047466200
ISUZU
8971323190
8971323190

Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
104746-6200
1047466200
ISUZU
8971323190
8971323190
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105780-0060
Bosch type code
NP-DN0SD1510
Nozzle holder
105780-2150
Opening pressure
MPa
13
13
13.3
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
133
133
136
Injection pipe
157805-7320
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-450
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-450
Joint assembly
157641-4720
Tube assembly
157641-4020
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1150
1150
1150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
51.8
51.3
52.3
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
4
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
30.8
27.3
34.3
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
35.8
32.3
39.3
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1150
1150
1150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
51.8
50.8
52.8
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
4
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
2050
2050
2050
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
61.9
57.4
66.4
Oil temperature
degC
52
50
54
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2350
2350
2350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
40.6
37.6
43.6
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
8
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
52
50
54
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2700
2700
2700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
2350
2350
2350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
40.6
37.6
43.6
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
8
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
52
50
54
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8.4
6.4
10.4
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8.4
6.4
10.4
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60
60
100
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Full
Full
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60
60
100
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Full
Full
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Magnet OFF at idling position
Magnet OFF at idling position
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Overflow quantity
cm3/min
370
240
500
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Pressure
kPa
412
392
432
Pressure
kgf/cm2
4.2
4
4.4
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle_02
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Pressure
kPa
412
392
432
Pressure
kgf/cm2
4.2
4
4.4
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Timer stroke
mm
2.7
2.5
2.9
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_02
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Timer stroke
mm
0.5
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Timer stroke
mm
2.7
2.5
2.9
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_04
Pump speed
r/min
1600
1600
1600
Timer stroke
mm
3.9
3.5
4.3
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_05
Pump speed
r/min
1950
1950
1950
Timer stroke
mm
5.3
5
5.7
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.1
3
3.2
KF dimension
mm
5.5
5.4
5.6
MS dimension
mm
0.8
0.7
0.9
Pre-stroke
mm
0.45
0.43
0.47
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
18
14
22
Control lever angle beta
deg.
37
32
42
Test data Ex:
0000001801 W-CSD ADJUSTMENT
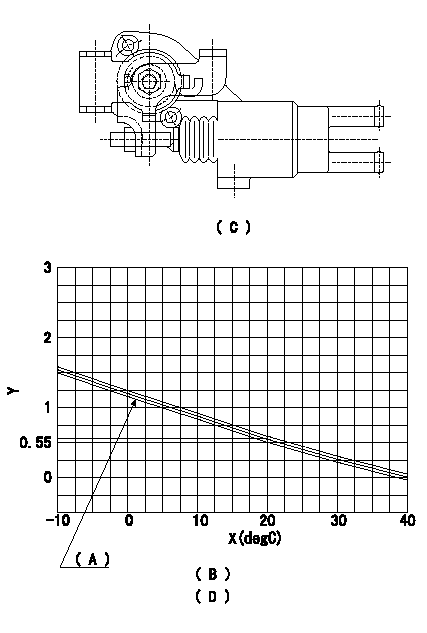
Adjustment of the W-CSD
1. Adjustment of the advance angle of the timer
(1)Determine the timer advance angle from the graph in Fig. 2 (D).
(2)(1) Adjust with the screw so that the timer advance angle determined in the item (1) is obtained.
(C) Fig. 1
(D) Fig. 2
(A): TA+-0.1
(B): Timer stroke TA:
X:Temperature X
Y:Timer stroke TA (mm)
----------
----------
(B)=-10<=t(degC)<=20:TA=-0.0367t+1.284 (D)=20<=t(degC)<=40:TA=-0.0275t+1.1
----------
----------
(B)=-10<=t(degC)<=20:TA=-0.0367t+1.284 (D)=20<=t(degC)<=40:TA=-0.0275t+1.1
0000001901 V-FICD ADJUSTMENT

Adjustment of the V-FICD
1. Adjust the actuator rod to obtain L1mm.
2. Apply negative pressure of P1kPa {P2 mmHg} to the actuator and confirm that it moves through its full stroke.
A:Control lever idling position
----------
L=1+1mm P1=-53.3kPa P2=-400mmHg
----------
T1=3.4~4.9N-m{0.35~0.5kgf-m} T2=1.4~2.0N-m{0.14~0.2kgf-m} L=1+1mm
----------
L=1+1mm P1=-53.3kPa P2=-400mmHg
----------
T1=3.4~4.9N-m{0.35~0.5kgf-m} T2=1.4~2.0N-m{0.14~0.2kgf-m} L=1+1mm
Information:
Replace:
Thrust, Main and Rod Bearings, Valve Rotators, Thermostat and Throttle Position SensorIn most probability, these components will not last until the second overhaul. Therefore, Caterpillar recommends the installation of these components new at each overhaul period.Inspect:
Crankshaft, Camshaft, Camshaft Followers, Vibration Damper, Spacer Block, Oil Pump and Fuel Transfer PumpThe ideal time for inspecting your crankshaft, camshaft and vibration damper is while the engine is disassembled for overhaul. Inspect each component for potential damage as follows:Crankshaft - Inspect for bend, journal damage and bearing material seized to the journal. At the same time, check the taper and profile of the crankshaft journals by interpreting your main and rod bearing wear patterns. In case of an out-of-frame overhaul, use the magnetic particle inspection process to check the crankshaft for cracks.* Camshaft - Inspect the camshaft for journal damage. In case of an out-of-frame overhaul, use the magnetic particle inspection process to check the camshaft for cracks.* Camshaft Followers - For out-of-frame overhaul, inspect the cam bearing for fatigue and wear.* Vibration Damper - Inspect the damper for rubber deterioration and movement of the outer ring relative to the inner hub.* Spacer Block - Inspect the spacer block for excessive wear or warping. For additional information regarding these components, contact your local Caterpillar dealer for assistance.Test:
Electronic Unit Injectors For additional information regarding this component, contact your local Caterpillar dealer for assistance.Clean/Test:
Oil Cooler Core and Aftercooler CoreCaterpillar recommends that the oil cooler core and the air-to-air aftercooler core be cleaned and pressure tested at each overhaul. For additional specifications and/or pressure test information, contact your local Caterpillar dealer.Cleaning Procedure for Air-to-Air Aftercooler
Caterpillar recommends that the air-to-air aftercooler core be removed, cleaned, and tested at overhaul time, if a turbocharger failure has occurred, or if at any time the turbocharger develops an oil leak.To clean the air-to-air aftercooler system:1. Remove the air-to-air aftercooler core. Turn the core upside down to remove debris from the inlet tank.
Do not use caustic cleaners to clean the air-to-air aftercooler core. Caustic cleaners will attack the internal metals of the core and cause leakage.
2. Back flush internally with a solvent to loosen foreign substances and to remove oil.Caterpillar recommends the use of Caterpillar Hydrosolv 4165 or Hydrosolv 100 Liquid Cleaners. For more information see "General Instructions and Application Guide" Form LEHQ6101 or contact your Caterpillar dealer.3. Shake the core vigorously to eliminate any trapped debris.4. Wash the core with hot, soapy water. Rinse thoroughly with clean water.
The maximum air pressure must not be above 30 psi (205 kPa) for cleaning purposes.
5. Dry the core with compressed air. Blow air in reverse direction of normal flow. Use all necessary safety equipment while using compressed air.6. Inspect the system to ensure cleanliness and install the air-to-air aftercooler core.Caterpillar Recommendation
The "repair before failure" concept makes sense. It saves money, lowers operating costs and minimizes downtime.As previously illustrated, it is not cheaper to operate the truck until an engine component fails, since failing components may increase fuel costs and upon failure, could
Thrust, Main and Rod Bearings, Valve Rotators, Thermostat and Throttle Position SensorIn most probability, these components will not last until the second overhaul. Therefore, Caterpillar recommends the installation of these components new at each overhaul period.Inspect:
Crankshaft, Camshaft, Camshaft Followers, Vibration Damper, Spacer Block, Oil Pump and Fuel Transfer PumpThe ideal time for inspecting your crankshaft, camshaft and vibration damper is while the engine is disassembled for overhaul. Inspect each component for potential damage as follows:Crankshaft - Inspect for bend, journal damage and bearing material seized to the journal. At the same time, check the taper and profile of the crankshaft journals by interpreting your main and rod bearing wear patterns. In case of an out-of-frame overhaul, use the magnetic particle inspection process to check the crankshaft for cracks.* Camshaft - Inspect the camshaft for journal damage. In case of an out-of-frame overhaul, use the magnetic particle inspection process to check the camshaft for cracks.* Camshaft Followers - For out-of-frame overhaul, inspect the cam bearing for fatigue and wear.* Vibration Damper - Inspect the damper for rubber deterioration and movement of the outer ring relative to the inner hub.* Spacer Block - Inspect the spacer block for excessive wear or warping. For additional information regarding these components, contact your local Caterpillar dealer for assistance.Test:
Electronic Unit Injectors For additional information regarding this component, contact your local Caterpillar dealer for assistance.Clean/Test:
Oil Cooler Core and Aftercooler CoreCaterpillar recommends that the oil cooler core and the air-to-air aftercooler core be cleaned and pressure tested at each overhaul. For additional specifications and/or pressure test information, contact your local Caterpillar dealer.Cleaning Procedure for Air-to-Air Aftercooler
Caterpillar recommends that the air-to-air aftercooler core be removed, cleaned, and tested at overhaul time, if a turbocharger failure has occurred, or if at any time the turbocharger develops an oil leak.To clean the air-to-air aftercooler system:1. Remove the air-to-air aftercooler core. Turn the core upside down to remove debris from the inlet tank.
Do not use caustic cleaners to clean the air-to-air aftercooler core. Caustic cleaners will attack the internal metals of the core and cause leakage.
2. Back flush internally with a solvent to loosen foreign substances and to remove oil.Caterpillar recommends the use of Caterpillar Hydrosolv 4165 or Hydrosolv 100 Liquid Cleaners. For more information see "General Instructions and Application Guide" Form LEHQ6101 or contact your Caterpillar dealer.3. Shake the core vigorously to eliminate any trapped debris.4. Wash the core with hot, soapy water. Rinse thoroughly with clean water.
The maximum air pressure must not be above 30 psi (205 kPa) for cleaning purposes.
5. Dry the core with compressed air. Blow air in reverse direction of normal flow. Use all necessary safety equipment while using compressed air.6. Inspect the system to ensure cleanliness and install the air-to-air aftercooler core.Caterpillar Recommendation
The "repair before failure" concept makes sense. It saves money, lowers operating costs and minimizes downtime.As previously illustrated, it is not cheaper to operate the truck until an engine component fails, since failing components may increase fuel costs and upon failure, could