Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
104746-1140
1047461140
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
104746-1140
1047461140
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
104746-1140
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105780-0060
Bosch type code
NP-DN0SD1510
Nozzle holder
105780-2150
Opening pressure
MPa
13
13
13.3
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
133
133
136
Injection pipe
157805-7320
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-450
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-450
Joint assembly
157641-4720
Tube assembly
157641-4020
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Boost pressure
kPa
30
28.7
31.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
225
215
235
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
63.8
63.3
64.3
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
4.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Remarks
CBS
CBS
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69.7
69.2
70.2
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
3.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Remarks
Full
Full
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Boost pressure
kPa
30
28.7
31.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
225
215
235
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
63.8
62.8
64.8
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
4.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
55.9
55.9
55.9
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69.7
68.7
70.7
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
3.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_06
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
54.3
54.3
54.3
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection timing adjustment_07
Pump speed
r/min
1800
1800
1800
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
67.9
67.9
67.9
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2300
2300
2300
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
34.6
31.6
37.6
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
5.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
52
50
54
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2550
2550
2550
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
5
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
2300
2300
2300
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
34.6
31.6
37.6
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
5.5
Oil temperature
degC
52
50
54
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15.8
13.8
17.8
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15.8
13.8
17.8
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
105
105
145
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
IDLE
IDLE
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
105
105
145
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Magnet OFF
Magnet OFF
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Overflow quantity
cm3/min
650
520
780
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Pressure
kPa
490
470
510
Pressure
kgf/cm2
5
4.8
5.2
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Pressure
kPa
490
470
510
Pressure
kgf/cm2
5
4.8
5.2
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
3.3
3.1
3.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_02
Pump speed
r/min
675
675
675
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
0.5
0.1
1.3
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
3.3
3.1
3.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_04
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
4.5
4.1
4.9
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_05
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
6.6
6.3
7
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
0000001401
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
47.9
46.9
48.9
Timer stroke TA
mm
2.4
2.2
2.6
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
0.9
0.9
0.9
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
47.9
46.4
49.4
Timer stroke TA
mm
2.4
2
2.8
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
31.3
29.8
32.8
Timer stroke TA
mm
1.4
0.8
2
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.8
5.7
5.9
MS dimension
mm
0.7
0.6
0.8
BCS stroke
mm
3
2.8
3.2
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
24
20
28
Control lever angle beta
deg.
45
40
50
Test data Ex:
0000001801 W-CSD ADJUSTMENT
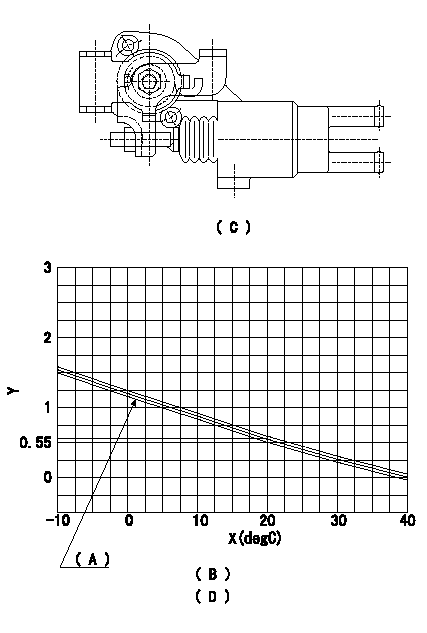
Adjustment of the W-CSD
1. Adjustment of the advance angle of the timer
(1)Determine the timer advance angle from the graph in Fig. 2 (D).
(2)(1) Adjust with the screw so that the timer advance angle determined in the item (1) is obtained.
(C) Fig. 1
(D) Fig. 2
(A): TA+-0.1
(B): Timer stroke TA:
X:Temperature X
Y:Timer stroke TA (mm)
----------
----------
(B)=-10<=t(degC)<=20:TA=-0.0367t+1.284 (D)=20<=t(degC)<=40:TA=-0.0275t+1.1
----------
----------
(B)=-10<=t(degC)<=20:TA=-0.0367t+1.284 (D)=20<=t(degC)<=40:TA=-0.0275t+1.1
Information:
Loose Belt(s)
Loose fan or water pump belts will cause a reduction in air or water flow. Tighten the belts according to V-Belt Tension Chart that is shown in Specification section of this Service Manual.Bad Hose(s)
Bad hoses with leaks can normally be seen. Hoses that have no visual leaks can "collapse" (pull together) during operation and cause a restriction in the flow of coolant. Hoses become soft and/or get cracks after a period of time. Hoses must be changed after 50,000 miles or a year of use. The inside can become loose, and the loose particles of the hose can cause a restriction in the flow of coolant.Shunt Line Restriction
A restriction of the shunt line from the radiator top tank to the engine front cover, or a shunt line not installed correctly, will cause a reduction in water pump efficiency. The result will be low coolant flow and overheating.Shutters Not Opening Correctly
Check the opening temperature of the shutters. The shutters must be completely closed at a temperature below the fully open temperature of the water temperature regulators. Also, verify that fan control switches or viscous fans are operating correctly.Bad Water Temperature Regulators
A regulator that does not open, or only opens part of the way, can cause above normal heating. To test the thermostats, see the Testing and Adjusting section of this Service Manual.Bad Water Pump
A water pump with a loose impeller does not pump enough coolant for correct engine cooling. A loose impeller can be found by removing the water pump, and by pushing the shaft back and pulling it forward. If the impeller has no damage, check the impeller clearance. The clearance between the impeller and the housing is 0.56 to 1.50 mm (.022 to .059 in).Air in Cooling System
Air can get into the cooling system in different ways. The most common causes are not filling the cooling system correctly, and combustion gas leaking into the system. Combustion gas can get into the system through inside cracks or bad cylinder head gaskets. Air in the cooling system causes a reduction in coolant flow and bubbles in the coolant. Air bubbles hold coolant away from engine parts, preventing heat flow.Air in the cooling system can be found by the Bottle Test. The equipment needed to make this test is a one pint bottle, a bucket of water, and a hose which will fit the end of the overflow pipe of the radiator.Before testing, make sure the cooling system is filled correctly. Use a wire to hold the relief valve in the radiator cap open. Install the radiator cap and tighten it. Put the hose over the end of the overflow pipe.Start the engine and operate it at high idle rpm for a minimum of five minutes after the engine is at normal operating temperature. Use a cover on the radiator core to keep the engine at operating temperature. After five or more minutes at operating temperature, place the loose end of the hose in the bottle filled with water.
Loose fan or water pump belts will cause a reduction in air or water flow. Tighten the belts according to V-Belt Tension Chart that is shown in Specification section of this Service Manual.Bad Hose(s)
Bad hoses with leaks can normally be seen. Hoses that have no visual leaks can "collapse" (pull together) during operation and cause a restriction in the flow of coolant. Hoses become soft and/or get cracks after a period of time. Hoses must be changed after 50,000 miles or a year of use. The inside can become loose, and the loose particles of the hose can cause a restriction in the flow of coolant.Shunt Line Restriction
A restriction of the shunt line from the radiator top tank to the engine front cover, or a shunt line not installed correctly, will cause a reduction in water pump efficiency. The result will be low coolant flow and overheating.Shutters Not Opening Correctly
Check the opening temperature of the shutters. The shutters must be completely closed at a temperature below the fully open temperature of the water temperature regulators. Also, verify that fan control switches or viscous fans are operating correctly.Bad Water Temperature Regulators
A regulator that does not open, or only opens part of the way, can cause above normal heating. To test the thermostats, see the Testing and Adjusting section of this Service Manual.Bad Water Pump
A water pump with a loose impeller does not pump enough coolant for correct engine cooling. A loose impeller can be found by removing the water pump, and by pushing the shaft back and pulling it forward. If the impeller has no damage, check the impeller clearance. The clearance between the impeller and the housing is 0.56 to 1.50 mm (.022 to .059 in).Air in Cooling System
Air can get into the cooling system in different ways. The most common causes are not filling the cooling system correctly, and combustion gas leaking into the system. Combustion gas can get into the system through inside cracks or bad cylinder head gaskets. Air in the cooling system causes a reduction in coolant flow and bubbles in the coolant. Air bubbles hold coolant away from engine parts, preventing heat flow.Air in the cooling system can be found by the Bottle Test. The equipment needed to make this test is a one pint bottle, a bucket of water, and a hose which will fit the end of the overflow pipe of the radiator.Before testing, make sure the cooling system is filled correctly. Use a wire to hold the relief valve in the radiator cap open. Install the radiator cap and tighten it. Put the hose over the end of the overflow pipe.Start the engine and operate it at high idle rpm for a minimum of five minutes after the engine is at normal operating temperature. Use a cover on the radiator core to keep the engine at operating temperature. After five or more minutes at operating temperature, place the loose end of the hose in the bottle filled with water.
Have questions with 104746-1140?
Group cross 104746-1140 ZEXEL
Isuzu
Isuzu
Isuzu
104746-1140
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY