Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
104741-3800
1047413800
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
104741-3800
1047413800
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
104741-3800
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105780-0060
Bosch type code
NP-DN0SD1510
Nozzle holder
105780-2150
Opening pressure
MPa
13
13
13.3
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
133
133
136
Injection pipe
157805-7320
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-450
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-450
Joint assembly
157641-4720
Tube assembly
157641-4020
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
57.1
56.6
57.6
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
4.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Remarks
NA
NA
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
46.7
45.4
48
Boost pressure
mmHg
350
340
360
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
73.8
73.3
74.3
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
5.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Remarks
CBS
CBS
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
84.4
83.9
84.9
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
6.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Remarks
Full
Full
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
57.1
56.1
58.1
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Remarks
NA
NA
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
46.7
45.4
48
Boost pressure
mmHg
350
340
360
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
73.8
72.8
74.8
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Remarks
CBS
CBS
Injection timing adjustment_06
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
84.4
83.4
85.4
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
7
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Remarks
Full
Full
Injection timing adjustment_07
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
71.8
67.8
75.8
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2475
2475
2475
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
26.4
23.4
29.4
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
8
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
3000
3000
3000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
2475
2475
2475
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
26.4
21.4
31.4
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
8.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
55
52
58
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18.9
16.9
20.9
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18.9
16.4
21.4
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2.5
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Governor adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
5
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
78.1
58.1
98.1
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Full
Full
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
78.1
58.1
98.1
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Full
Full
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Oil temperature
degC
48
46
50
Remarks
Magnet OFF at idling position
Magnet OFF at idling position
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Overflow quantity
cm3/min
740
610
870
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Pressure
kPa
500
480
520
Pressure
kgf/cm2
5.1
4.9
5.3
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
3.7
3.5
3.9
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_02
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
1.7
1.1
2.3
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
3.7
3.3
4.1
Basic
*
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_04
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
6.9
6.3
7.5
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
_05
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Boost pressure
kPa
73.3
72
74.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
8.6
8.1
9
Oil temperature
degC
50
48
52
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.8
5.7
5.9
MS dimension
mm
0.9
0.8
1
BCS stroke
mm
5.5
5.3
5.7
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
59
55
63
Control lever angle beta
deg.
41
36
46
Test data Ex:
0000001801 POTENTIOMETER ADJUSTMENT
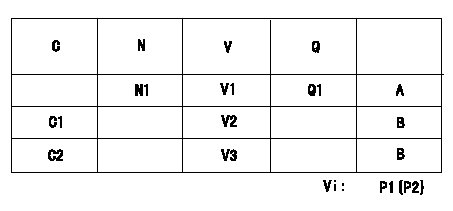
Adjustment of the potentiometer
Adjusting method (service voltage Vi, dummy bolt):
1. Hold the dummy bolt against the control lever when N = N1 r/min, Q = Q1 mm3/st.
Fix using the lock nut.
2. When adjusting the potentiometer, position the control lever against the dummy bolt and adjust the potentiometer so that the output voltage is V1 (V).
3. Remove the dummy bolt after the completion of adjustment.
Confirm that the potentiometer output voltage is within the standards mentioned when the control lever is idling and in full-speed position.
Vi:Applied voltage
C:Position of the control lever
N:Pump speed (r/min)
V:Output voltage (V)
Q:Injection quantity (mm3/st)
A:Adjusting point
B:Checking point
C1:Idling
C2:Full speed
P1:Boost pressure
P2:Boost pressure
----------
N1=750r/min V1=4.16+-0.03V Q1=34.7+-1.0cm3/1,000st
----------
N1=750r/min V1=4.16+-0.03V V2=2.16+-0.52V V3=9.02+-0.72V Q1=34.7+-1.0cm3/1,000st Vi=10V P1=0kPa P2=0mmHg
----------
N1=750r/min V1=4.16+-0.03V Q1=34.7+-1.0cm3/1,000st
----------
N1=750r/min V1=4.16+-0.03V V2=2.16+-0.52V V3=9.02+-0.72V Q1=34.7+-1.0cm3/1,000st Vi=10V P1=0kPa P2=0mmHg
Information:
Starter Motor - Model - CA45
General Description
Designed for flange mounting, the C.A.45 starter motor has a uniform cylindrical shape with no surface protrusion. This is because the solenoid and main switch assemblies are housed within the drive end-shield, around (i.e., co-axially with) the armature shaft.The essential feature of the co-axial starter is that, the pinion alone moves axially to engage the engine flywheel. There is no longitudinal movement of the whole armature assembly, as in the axial types.Smooth engagement of the pinion with the engine flywheel is constantly ensured by using two-stage operation of the solenoid and switch mechanisms. Thus the risk of damage to both pinion and flywheel, through faulty meshing, is practically eliminated.In construction, the starter consists of three main sections, into which it can be easily dismantled.1. The solenoid switch-gear and pinion assembly housed in the drive end-shield.2. The armature, shaft and commutator assembly.3. The yoke, pole-piece and field-coil assembly.Ready access is possible therefore, to those parts most likely to require adjustment, such as the switchgear and commutator assemblies.The starter is designed for working off a 12 volt supply, with 17 amps solenoid current.Testing on the Vehicle
Ensure that the battery is in a charged condition.Switch on the lamps and operate the starter button. If the starter fails to function, but the lights maintain full brilliance, check the switch and battery connections to the starter and all external leads. Sluggish action of the starter can be caused by a poor or faulty connection.Difficulty in smooth engagement between starter and engine flywheel is probably due to dirt on the starter-shaft helices preventing free pinion movement. The shaft should be thoroughly cleaned with kerosene followed by the application of a small quantity of Caltex Thuben 90 or SAE 90 oil.Operating the Starter
When starting the engine the following points should be rigidly observed
1. Press the starter button firmly and release it immediately the engine fires.2. If the engine does not fire at once, let it come to rest before pressing the switch again.3. Do not run the battery down by keeping the starter switch pressed when the engine refuses to start. Ascertain the cause.4. On some engines it is often helpful to depress the clutch when starting.5. Do not operate the starter when the engine is running as serious damage may occur to both starter and flywheel.Maintenance
Lubrication
The large oil reservoir in the drive end shield need only be replenished during overhaul periods, when a supply of Shelltella T27 or BP Energol SHF 100 oil should be added through the oil plug.An oil impregnated sintered bronze bush is fitted at the commutator end, and needs no further attention.Brush Gear and Commutator
Inspect the brushes at intervals of approximately 500 hours. See that they are free in their guides and that the leads are quite free for movement, by easing back the brush springs and pulling gently on the flexible connections. If a brush is inclined to stick, remove it from its holder and clean the sides with a petrol moistened cloth.Be
General Description
Designed for flange mounting, the C.A.45 starter motor has a uniform cylindrical shape with no surface protrusion. This is because the solenoid and main switch assemblies are housed within the drive end-shield, around (i.e., co-axially with) the armature shaft.The essential feature of the co-axial starter is that, the pinion alone moves axially to engage the engine flywheel. There is no longitudinal movement of the whole armature assembly, as in the axial types.Smooth engagement of the pinion with the engine flywheel is constantly ensured by using two-stage operation of the solenoid and switch mechanisms. Thus the risk of damage to both pinion and flywheel, through faulty meshing, is practically eliminated.In construction, the starter consists of three main sections, into which it can be easily dismantled.1. The solenoid switch-gear and pinion assembly housed in the drive end-shield.2. The armature, shaft and commutator assembly.3. The yoke, pole-piece and field-coil assembly.Ready access is possible therefore, to those parts most likely to require adjustment, such as the switchgear and commutator assemblies.The starter is designed for working off a 12 volt supply, with 17 amps solenoid current.Testing on the Vehicle
Ensure that the battery is in a charged condition.Switch on the lamps and operate the starter button. If the starter fails to function, but the lights maintain full brilliance, check the switch and battery connections to the starter and all external leads. Sluggish action of the starter can be caused by a poor or faulty connection.Difficulty in smooth engagement between starter and engine flywheel is probably due to dirt on the starter-shaft helices preventing free pinion movement. The shaft should be thoroughly cleaned with kerosene followed by the application of a small quantity of Caltex Thuben 90 or SAE 90 oil.Operating the Starter
When starting the engine the following points should be rigidly observed
1. Press the starter button firmly and release it immediately the engine fires.2. If the engine does not fire at once, let it come to rest before pressing the switch again.3. Do not run the battery down by keeping the starter switch pressed when the engine refuses to start. Ascertain the cause.4. On some engines it is often helpful to depress the clutch when starting.5. Do not operate the starter when the engine is running as serious damage may occur to both starter and flywheel.Maintenance
Lubrication
The large oil reservoir in the drive end shield need only be replenished during overhaul periods, when a supply of Shelltella T27 or BP Energol SHF 100 oil should be added through the oil plug.An oil impregnated sintered bronze bush is fitted at the commutator end, and needs no further attention.Brush Gear and Commutator
Inspect the brushes at intervals of approximately 500 hours. See that they are free in their guides and that the leads are quite free for movement, by easing back the brush springs and pulling gently on the flexible connections. If a brush is inclined to stick, remove it from its holder and clean the sides with a petrol moistened cloth.Be
Have questions with 104741-3800?
Group cross 104741-3800 ZEXEL
104741-3800
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY