Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 460 610 240
9460610240
ZEXEL
104740-9340
1047409340
NISSAN-DIESEL
1670002N14
1670002n14
Rating:
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 460 610 240
9460610240
ZEXEL
104740-9340
1047409340
NISSAN-DIESEL
1670002N14
1670002n14
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
104740-9340
9 460 610 240
1670002N14 NISSAN-DIESEL
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
AD23 K
AD23 K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105000-2010
Bosch type code
NP-DN12SD12TT
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Opening pressure
MPa
14.7
14.7
15.19
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
150
150
155
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
44.6
44.1
45.1
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
3
Basic
*
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
43.5
41.5
45.5
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
44.6
43.6
45.6
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
2150
2150
2150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
38
35.9
40.1
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
2350
2350
2350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
30.3
27.8
32.8
Injection timing adjustment_06
Pump speed
r/min
2550
2550
2550
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8.85
5.3
12.4
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2350
2350
2350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
30.3
28.3
32.3
Basic
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2700
2700
2700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
5
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
6.5
4.5
8.5
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
6.5
4.5
8.5
Governor adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
450
450
450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
2
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
62.5
45
80
Basic
*
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Remarks
Magnet OFF
Magnet OFF
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Overflow quantity with S/T ON
cm3/min
390
258
522
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1700
1700
1700
Pressure with S/T OFF
kPa
510
481
539
Pressure with S/T OFF
kgf/cm2
5.2
4.9
5.5
Basic
*
Stop lever angle_02
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Pressure with S/T OFF
kPa
372.5
343
402
Pressure with S/T OFF
kgf/cm2
3.8
3.5
4.1
Stop lever angle_03
Pump speed
r/min
1700
1700
1700
Pressure with S/T OFF
kPa
510
481
539
Pressure with S/T OFF
kgf/cm2
5.2
4.9
5.5
Stop lever angle_04
Pump speed
r/min
2150
2150
2150
Pressure with S/T OFF
kPa
598.5
569
628
Pressure with S/T OFF
kgf/cm2
6.1
5.8
6.4
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1700
1700
1700
Timer stroke with S/T OFF
mm
4.6
4.4
4.8
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Timer stroke with S/T OFF
mm
2.5
2
3
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1700
1700
1700
Timer stroke with S/T ON
mm
6.45
5.5
7.4
Timer stroke with S/T OFF
mm
4.6
4.3
4.9
_04
Pump speed
r/min
2550
2550
2550
Timer stroke with S/T OFF
mm
6.9
6.4
7.4
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.8
5.7
5.9
MS dimension
mm
1
0.9
1.1
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
54
50
58
Control lever angle beta
deg.
42
37
47
Test data Ex:
0000001801 CONTROL LEVER ANGLE
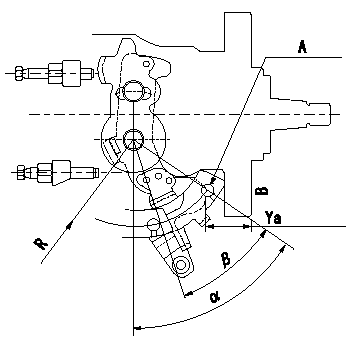
Control lever angle measurement
1. Measure dimension Ya between the end of the lever and the flange face.
2. Measure the lever angle from the pin hole R (plate).
A = lever angle measuring position
B = flange face
----------
Ya=23.7~28.3mm R=49mm
----------
Ya=23.7~28.3mm R=49mm
----------
Ya=23.7~28.3mm R=49mm
----------
Ya=23.7~28.3mm R=49mm
Information:
Introduction
***#i00660713/i00660713*** contains the abbreviations, symbols, wiring sizes, wiring color and number codes for the ETR/ETS electric protection system which are placed on drawings and wiring, and referenced in the text of this Service Manual.The electrical system for the engine contains five subsystems. Each subsystem has different symbols and wire number codes. Abbreviations, symbols, numbering and lettering codes, and wiring requirements are described for the following subsystems.
Starting
Charging
Control
Monitoring
ProtectionThe engine electrical system is designed to improve operational reliability, reduce maintenance problems, improve the flexibility for making changes or additions to the system, and comply with international standards. In order to accomplish these goals, the engine electrical system contains the following components.
A steel junction box for the control, monitoring, and protection subsystems with standardized mounting locations on each engine series.
A steel power distribution box for the high amperage starting and charging subsystems with standardized mounting locations on each engine series.
A wiring harness in a protective nylon conduit that connects the junction box, power distribution box, and the electrical components located on the engine.
Common heat stamped wire number codes on each wire in the wiring harness for all engine models.
Common logic for all subsystems on all engine models."Description of Electrical System Symbols And Codes" explains how to use and understand the graphical representation of the ETR/ETS electric protection system by component and wiring abbreviations, symbols, and codes.Description of Electrical System Symbols And Codes
The Point-To-Point graphical system is used in all the wiring diagrams and schematics which help describe the systems operation and troubleshooting of the ETR/ETS electric protection system.Each wire in the wiring harness is heat stamped the length of the wire with the wire number code as shown in the ETR/ETS Wiring Using Wire Number Codes diagram on Illustration 7. The first number pair of the wiring code identifies the terminal on an engine component to which one end of the wire should be attached. The second number pair of the wiring code identifies the terminal on the component to which the other end of the wire should be attached. The number assigned to each terminal of each component will be the same for all engine models.The two numbers in the wiring code differentiate between left and right hand mounting. Illustration 2 contains the Number Codes and an example of usage.The symbols for the engine components will be the same for all 3200-3500 Series Engines.The use of abbreviations, symbols, and codes is provided by the following example. In order to locate and identify the wire which connects the starting motor magnetic switch and the starting motor, first determine the correct drawing abbreviation. The Abbreviation List on Illustration 1 shows ("SMMS") as the abbreviation symbol for the starting motor magnetic switch. ("SM") is shown as the abbreviation symbol for the starting motor. The symbols for both the starting motor magnetic switch and the starting motor are listed under the Starting System on 3.Locate the ("SMMS") and ("SM") symbols on the Starting System list on Illustration 3. Because an engine option exists for two
***#i00660713/i00660713*** contains the abbreviations, symbols, wiring sizes, wiring color and number codes for the ETR/ETS electric protection system which are placed on drawings and wiring, and referenced in the text of this Service Manual.The electrical system for the engine contains five subsystems. Each subsystem has different symbols and wire number codes. Abbreviations, symbols, numbering and lettering codes, and wiring requirements are described for the following subsystems.
Starting
Charging
Control
Monitoring
ProtectionThe engine electrical system is designed to improve operational reliability, reduce maintenance problems, improve the flexibility for making changes or additions to the system, and comply with international standards. In order to accomplish these goals, the engine electrical system contains the following components.
A steel junction box for the control, monitoring, and protection subsystems with standardized mounting locations on each engine series.
A steel power distribution box for the high amperage starting and charging subsystems with standardized mounting locations on each engine series.
A wiring harness in a protective nylon conduit that connects the junction box, power distribution box, and the electrical components located on the engine.
Common heat stamped wire number codes on each wire in the wiring harness for all engine models.
Common logic for all subsystems on all engine models."Description of Electrical System Symbols And Codes" explains how to use and understand the graphical representation of the ETR/ETS electric protection system by component and wiring abbreviations, symbols, and codes.Description of Electrical System Symbols And Codes
The Point-To-Point graphical system is used in all the wiring diagrams and schematics which help describe the systems operation and troubleshooting of the ETR/ETS electric protection system.Each wire in the wiring harness is heat stamped the length of the wire with the wire number code as shown in the ETR/ETS Wiring Using Wire Number Codes diagram on Illustration 7. The first number pair of the wiring code identifies the terminal on an engine component to which one end of the wire should be attached. The second number pair of the wiring code identifies the terminal on the component to which the other end of the wire should be attached. The number assigned to each terminal of each component will be the same for all engine models.The two numbers in the wiring code differentiate between left and right hand mounting. Illustration 2 contains the Number Codes and an example of usage.The symbols for the engine components will be the same for all 3200-3500 Series Engines.The use of abbreviations, symbols, and codes is provided by the following example. In order to locate and identify the wire which connects the starting motor magnetic switch and the starting motor, first determine the correct drawing abbreviation. The Abbreviation List on Illustration 1 shows ("SMMS") as the abbreviation symbol for the starting motor magnetic switch. ("SM") is shown as the abbreviation symbol for the starting motor. The symbols for both the starting motor magnetic switch and the starting motor are listed under the Starting System on 3.Locate the ("SMMS") and ("SM") symbols on the Starting System list on Illustration 3. Because an engine option exists for two
Have questions with 104740-9340?
Group cross 104740-9340 ZEXEL
Nissan-Diesel
Nissan-Diesel
104740-9340
9 460 610 240
1670002N14
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
AD23
AD23