Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
104740-3730
1047403730
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
104740-3730
1047403730
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105000-2010
Bosch type code
NP-DN12SD12TT
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Opening pressure
MPa
14.7
14.7
15.19
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
150
150
155
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
45.8
45.3
46.3
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
3
Basic
*
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2550
2550
2550
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18.1
13.1
23.1
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
2100
2100
2100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
39.2
37.2
41.2
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
45.8
44.8
46.8
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
44.3
42.3
46.3
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2550
2550
2550
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
18.1
15.1
21.1
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
4
Basic
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
2900
2900
2900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
5
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10
8.5
11.5
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10
8.5
11.5
Governor adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
5
Governor adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
3
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
73
63
83
Basic
*
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Remarks
Magnet OFF
Magnet OFF
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Overflow quantity with S/T ON
cm3/min
522
222
822
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Pressure with S/T ON
kPa
470.5
441
500
Pressure with S/T ON
kgf/cm2
4.8
4.5
5.1
Basic
*
Stop lever angle_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Pressure with S/T ON
kPa
313.5
284
343
Pressure with S/T ON
kgf/cm2
3.2
2.9
3.5
Stop lever angle_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Pressure with S/T ON
kPa
470.5
441
500
Pressure with S/T ON
kgf/cm2
4.8
4.5
5.1
Stop lever angle_04
Pump speed
r/min
2100
2100
2100
Pressure with S/T ON
kPa
666.5
637
696
Pressure with S/T ON
kgf/cm2
6.8
6.5
7.1
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1750
1750
1750
Timer stroke with S/T OFF
mm
3.7
3.5
3.9
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Timer stroke with S/T ON
mm
1.2
0.4
2
_03
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Timer stroke with S/T ON
mm
2
1.2
2.8
_04
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Timer stroke with S/T ON
mm
3.7
2.9
4.5
Timer stroke with S/T OFF
mm
1.6
1
2.2
_05
Pump speed
r/min
1750
1750
1750
Timer stroke with S/T ON
mm
5.8
5
6.6
Timer stroke with S/T OFF
mm
3.7
3.3
4.1
_06
Pump speed
r/min
2100
2100
2100
Timer stroke with S/T ON
mm
7.2
6.4
8
Timer stroke with S/T OFF
mm
5.1
4.5
5.7
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.8
5.7
5.9
MS dimension
mm
1.2
1.1
1.3
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
23
19
27
Control lever angle beta
deg.
48
43
53
Test data Ex:
0000001801 POTENTIOMETER ADJUSTMENT
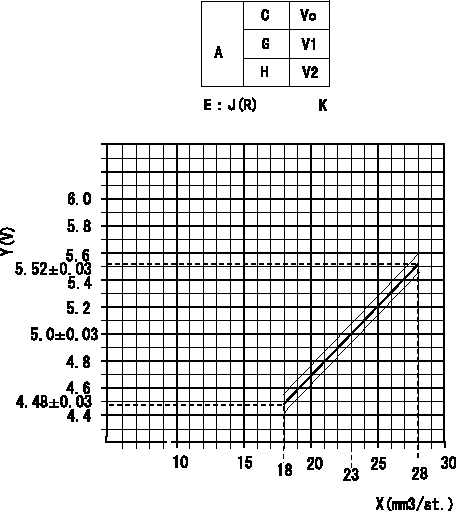
Adjustment of the potentiometer
In the following condition, change the installation position of the potentiometer to adjust the output voltage to within the specified values.
Measure the injection quantity at control lever position a (shim thickness = approximately L mm) at N = N1 r/min, determine the voltage using the formula, and adjust the potentiometer.
A:Performance standards
C:Position of the control lever
N:Pump speed
Vo:Output voltage
E:Conversion formula
G:Idling
H:Full speed
K:Applied voltage
X:Injection quantity (cm3/1,000st)
Y:Voltage (V)
R:Target injection quantity: R1
----------
N1=1,000r/min a=24deg L=15.0mm
----------
V1=1++V V2=(9.3)V K=10V J:V=0.104X+2.608 R1=23+-6cm3/1,000st
----------
N1=1,000r/min a=24deg L=15.0mm
----------
V1=1++V V2=(9.3)V K=10V J:V=0.104X+2.608 R1=23+-6cm3/1,000st
Information:
Operating Cost Information
The term "Life Cycle Cost" can be defined as the sum of the individual costs experienced by an engine from the day of purchase until the day of retirement. In other words, the total Owning and Operating Costs.Owning Costs are fixed costs such as initial purchase price, interest on borrowed money, depreciation and taxes.Operating Costs are a combination of fixed and variable costs such as fuel, oil, operator expenses, road taxes, tires, chassis maintenance and repair, permits, licenses, engine maintenance and repair and downtime.The difference between revenues generated and Life Cycle Costs (total Owning and Operating Costs) is profit.Caterpillar and your Caterpillar dealer cannot guarantee that you will make a profit. However, Caterpillar and your Caterpillar dealer can provide you with a variety of services that can help you reduce the costs that impact your profits.An Engine Operating Cost Analysis is a service provided by your dealer that was developed by Caterpillar to help you reduce the Life Cycle Cost of your engine.More specifically, an Engine Operating Cost Analysis is a computerized program that examines existent and expectant oil, fuel, maintenance, minor repair, overhaul and downtime costs for the period of time you expect to own the engine. It also calculates the operating cost per mile (km), hour or day.This useful tool provides your dealer with the specific information needed to develop a customized Maintenance Management program for your operation which will minimize your engine's operating costs.Before a cost analysis can be performed, your dealer needs to gather as much information as possible about your operation. He will need to know the length of time you plan to keep your engine/vehicle, your average cost of fuel and oil as well as a variety of other ownership and cost related facts and figures.Once this information is obtained, your dealer will enter the data into an established computerized program to produce an Engine Operating Cost Analysis printout reflecting your current and projected operating costs per mile (km), hour or day.The typical printout of the Engine Operating Cost Analysis program has up to four engine scenarios which can be run at one time. The printouts is divided into three major areas: * General Information* Engine Operating Information* Operating Cost SummaryGeneral Information
The General Information section contains basic user data such as name, business, location, ownership, usage per year etc., information.Engine Operating Information
The Engine Operating Information section is divided into eight subsections that address fuel consumption, oil consumption, preventive maintenance, component repairs such as water pumps, turbochargers, air compressors, etc., before failure repairs, after failure repairs, user's revenue rate per hour and lastly, miscellaneous costs such as operator wages, insurance premiums, etc.Current and expected cost information reflected in the Engine Operating Information section is based on the data provided by you. These are the costs that affect your engine's operating cost.Operating Cost Summary
The Operating Cost Summary section is exactly what it implies, a summary. Here the total dollar expense and percentage of the total operating expense is calculated for each of
The term "Life Cycle Cost" can be defined as the sum of the individual costs experienced by an engine from the day of purchase until the day of retirement. In other words, the total Owning and Operating Costs.Owning Costs are fixed costs such as initial purchase price, interest on borrowed money, depreciation and taxes.Operating Costs are a combination of fixed and variable costs such as fuel, oil, operator expenses, road taxes, tires, chassis maintenance and repair, permits, licenses, engine maintenance and repair and downtime.The difference between revenues generated and Life Cycle Costs (total Owning and Operating Costs) is profit.Caterpillar and your Caterpillar dealer cannot guarantee that you will make a profit. However, Caterpillar and your Caterpillar dealer can provide you with a variety of services that can help you reduce the costs that impact your profits.An Engine Operating Cost Analysis is a service provided by your dealer that was developed by Caterpillar to help you reduce the Life Cycle Cost of your engine.More specifically, an Engine Operating Cost Analysis is a computerized program that examines existent and expectant oil, fuel, maintenance, minor repair, overhaul and downtime costs for the period of time you expect to own the engine. It also calculates the operating cost per mile (km), hour or day.This useful tool provides your dealer with the specific information needed to develop a customized Maintenance Management program for your operation which will minimize your engine's operating costs.Before a cost analysis can be performed, your dealer needs to gather as much information as possible about your operation. He will need to know the length of time you plan to keep your engine/vehicle, your average cost of fuel and oil as well as a variety of other ownership and cost related facts and figures.Once this information is obtained, your dealer will enter the data into an established computerized program to produce an Engine Operating Cost Analysis printout reflecting your current and projected operating costs per mile (km), hour or day.The typical printout of the Engine Operating Cost Analysis program has up to four engine scenarios which can be run at one time. The printouts is divided into three major areas: * General Information* Engine Operating Information* Operating Cost SummaryGeneral Information
The General Information section contains basic user data such as name, business, location, ownership, usage per year etc., information.Engine Operating Information
The Engine Operating Information section is divided into eight subsections that address fuel consumption, oil consumption, preventive maintenance, component repairs such as water pumps, turbochargers, air compressors, etc., before failure repairs, after failure repairs, user's revenue rate per hour and lastly, miscellaneous costs such as operator wages, insurance premiums, etc.Current and expected cost information reflected in the Engine Operating Information section is based on the data provided by you. These are the costs that affect your engine's operating cost.Operating Cost Summary
The Operating Cost Summary section is exactly what it implies, a summary. Here the total dollar expense and percentage of the total operating expense is calculated for each of