Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 460 610 207
9460610207
ZEXEL
104740-3660
1047403660
Rating:
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 460 610 207
9460610207
ZEXEL
104740-3660
1047403660
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105000-2010
Bosch type code
NP-DN12SD12TT
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Opening pressure
MPa
14.7
14.7
15.19
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
150
150
155
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-840
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
61.9
61.4
62.4
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
4.5
Basic
*
Injection timing adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
44
42.7
45.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
330
320
340
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60.9
60.4
61.4
Basic
*
Injection timing adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
2650
2650
2650
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
25.2
20.2
30.2
Injection timing adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
2100
2100
2100
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
55.3
52.8
57.8
Injection timing adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
61.9
60.9
62.9
Injection timing adjustment_06
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
44
42.7
45.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
330
320
340
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60.9
59.9
61.9
Injection timing adjustment_07
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
48.3
45.8
50.8
Injection quantity adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
2650
2650
2650
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
25.2
22.2
28.2
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
5.5
Basic
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
3050
3050
3050
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
5
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8
6.5
9.5
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2
Basic
*
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
3
Governor adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8
6
10
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
73
63
83
Basic
*
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
0
0
0
Remarks
Magnet OFF
Magnet OFF
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Overflow quantity
cm3/min
420
288
552
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Pressure
kPa
470.5
441
500
Pressure
kgf/cm2
4.8
4.5
5.1
Basic
*
Stop lever angle_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Pressure
kPa
313.5
284
343
Pressure
kgf/cm2
3.2
2.9
3.5
Stop lever angle_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Pressure
kPa
470.5
441
500
Pressure
kgf/cm2
4.8
4.5
5.1
Stop lever angle_04
Pump speed
r/min
2100
2100
2100
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Pressure
kPa
666.5
637
696
Pressure
kgf/cm2
6.8
6.5
7.1
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
3.7
3.5
3.9
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
1.2
0.6
1.8
_03
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
2
1.4
2.6
_04
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
3.7
3.3
4.1
_05
Pump speed
r/min
2100
2100
2100
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Timer stroke
mm
7.2
6.6
7.8
0000001201
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
0000001401
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
50.3
49.8
50.8
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
0.6
0.4
0.8
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
50.3
49.3
51.3
Timer stroke TA
mm
3.1
3.1
3.1
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
0.6
0.2
1
_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Boost pressure
kPa
73.35
72
74.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
550
540
560
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
40.2
38.7
41.7
Timer stroke TA
mm
2.3
2.3
2.3
Timer stroke variation dT
mm
1.4
0.8
2
Timing setting
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.8
5.7
5.9
MS dimension
mm
1
0.9
1.1
BCS stroke
mm
3.7
3.6
3.8
Control lever angle alpha
deg.
59
55
63
Control lever angle beta
deg.
41
36
46
Test data Ex:
0000001801 ACCELERATOR LINK STROKE
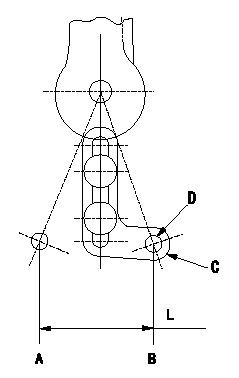
Adjustment of the accelerator link stroke
As shown in the figure, adjust so that the accelerator link's stroke between idle (B) and full speed (A) is L1.
A = full speed
B = idle
C = A/T lever
D = hole with diameter d
----------
L=32.9+-1mm d=Dia.5mm
----------
L=32.9+-1mm
----------
L=32.9+-1mm d=Dia.5mm
----------
L=32.9+-1mm
Information:
Checkto observe for satisfactory conditions, accuracy, safety or performance.Inspectto examine closely, in critical appraisal, while testing or evaluating components or systems.Lubricateto apply a lubricant (oil, grease, etc.) as specified for reducing friction, heat and wear between solid surfaces.Replaceto install something new, remanufactured or rebuilt in place of an existing worn or failing component.Rebuildto repair a worn or failing component with new parts, components and/or remanufactured components.Exchangeto trade a worn or failing component for a remanufactured or rebuilt component.Protective Devicesindicators such as gauges lights, emergency shutoffs, etc., that alerts an operator that a potential problem may exist. Failure to respond to these indicators in a timely manner could result in engine failure.Service Hours (Electrical)records the time (clock hours) the engine is actually running but does not reflect variations in speed, load, etc.Adjustto conform and correspond to specifications.Interval Categories
Engine components can generally be grouped into "speed sensitive" and "load sensitive" categories. Therefore, the maintenance interval for each item listed in the "Maintenance Management Schedule" is primarily based on the item and its relationship to either engine speed or load. Speed sensitive items such as water pumps, air compressors, etc., are not primarily affected by the load on your engine during operation. The load on an engine will not significantly accelerate the repair or replacement cycle for speed sensitive items.Therefore, the maintenance intervals established for speed sensitive items are based on miles (kilometers) or service hours, whichever occurs first. Load sensitive items such as piston rings, cylinder liners, etc., are affected by the load on your engine during operation. Generally speaking, the lower the load, the longer the engine life and conversely, the higher the load, the shorter the engine life. A heavy load on an engine will accelerate the repair or replacement cycle for load sensitive items.Therefore, the maintenance interval for load sensitive items also includes quantity of fuel used, since the amount of fuel consumed is directly related to the load on your engine.Load sensitive items are normally internal engine components. The amount of fuel consumed is directly related to the load on your engine. Since the amount of fuel consumed is a better indicator of performing an overhaul than miles (kilometers) or service hours, Caterpillar recommends performing an overhaul on these items at the specified maintenance interval based on the quantity of fuel consumed.Interval to Overhaul
The specified overhaul interval for this engine rated 350 hp (261 kw) at 1800 rpm and below is "Every 100,000 Gallons (380 000 L) of Fuel or 600,000 Miles (960 000 km) or 10,000 Service Hours." This includes all power ratings BELOW 350 hp (261 kw).The specified overhaul interval for this engine rated 350 hp (261 kw) at 2100 rpm and up is "Every 100,000 Gallons (380 000 L) of Fuel or 500,000 Miles (800 000 km) or 10,000 Service Hours." This includes all power ratings ABOVE 350 hp (261 kw). Two Maintenance Management charts follow. Ensure the correct chart is selected for the engine being maintained. PM Level means Preventive Maintenance Level.
Engine components can generally be grouped into "speed sensitive" and "load sensitive" categories. Therefore, the maintenance interval for each item listed in the "Maintenance Management Schedule" is primarily based on the item and its relationship to either engine speed or load. Speed sensitive items such as water pumps, air compressors, etc., are not primarily affected by the load on your engine during operation. The load on an engine will not significantly accelerate the repair or replacement cycle for speed sensitive items.Therefore, the maintenance intervals established for speed sensitive items are based on miles (kilometers) or service hours, whichever occurs first. Load sensitive items such as piston rings, cylinder liners, etc., are affected by the load on your engine during operation. Generally speaking, the lower the load, the longer the engine life and conversely, the higher the load, the shorter the engine life. A heavy load on an engine will accelerate the repair or replacement cycle for load sensitive items.Therefore, the maintenance interval for load sensitive items also includes quantity of fuel used, since the amount of fuel consumed is directly related to the load on your engine.Load sensitive items are normally internal engine components. The amount of fuel consumed is directly related to the load on your engine. Since the amount of fuel consumed is a better indicator of performing an overhaul than miles (kilometers) or service hours, Caterpillar recommends performing an overhaul on these items at the specified maintenance interval based on the quantity of fuel consumed.Interval to Overhaul
The specified overhaul interval for this engine rated 350 hp (261 kw) at 1800 rpm and below is "Every 100,000 Gallons (380 000 L) of Fuel or 600,000 Miles (960 000 km) or 10,000 Service Hours." This includes all power ratings BELOW 350 hp (261 kw).The specified overhaul interval for this engine rated 350 hp (261 kw) at 2100 rpm and up is "Every 100,000 Gallons (380 000 L) of Fuel or 500,000 Miles (800 000 km) or 10,000 Service Hours." This includes all power ratings ABOVE 350 hp (261 kw). Two Maintenance Management charts follow. Ensure the correct chart is selected for the engine being maintained. PM Level means Preventive Maintenance Level.